The document discusses key concepts for stoichiometric calculations including:
- Stoichiometric amount, excess reagent, limiting reagent, theoretical yield, actual yield, and percentage yield.
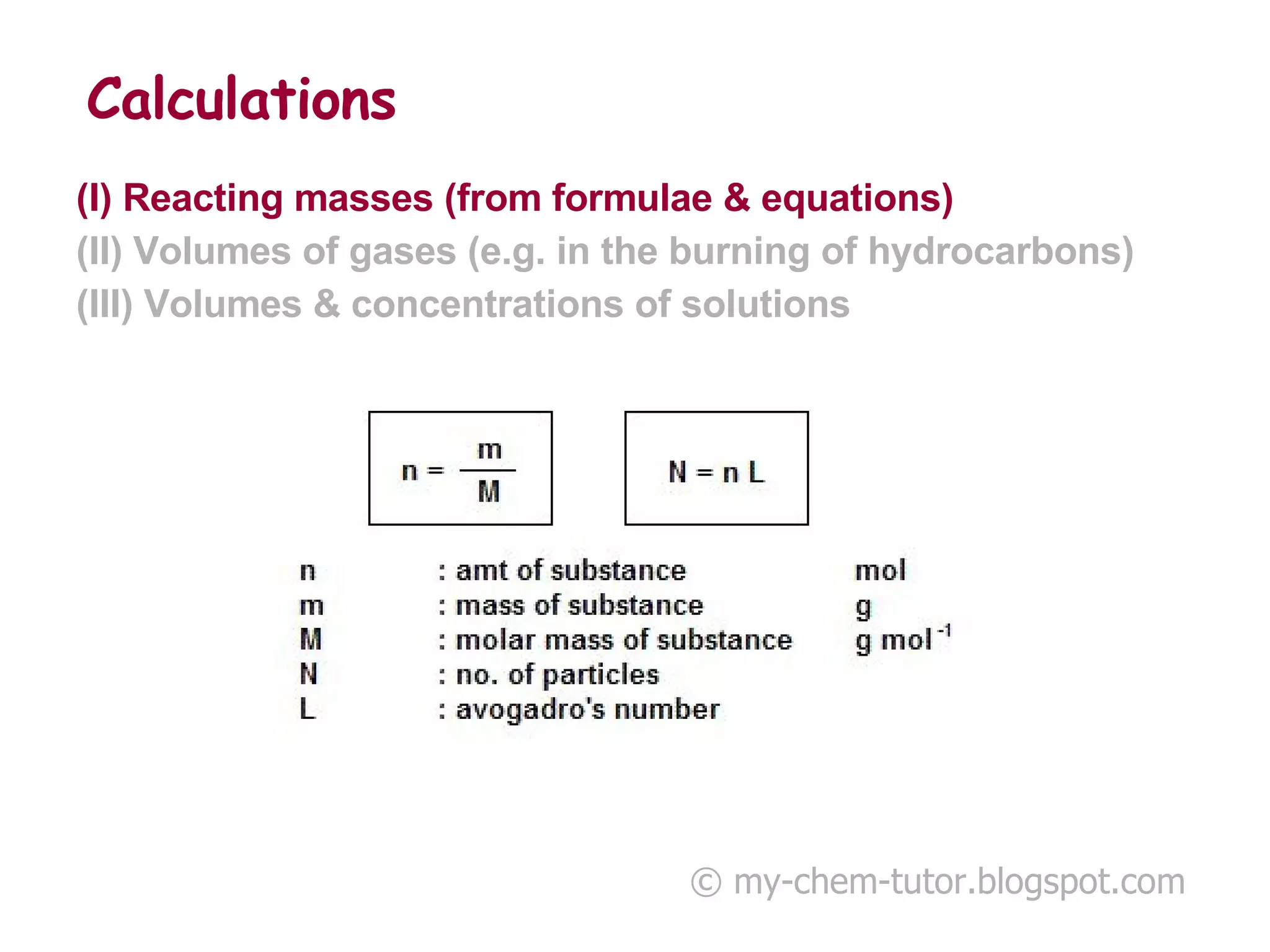
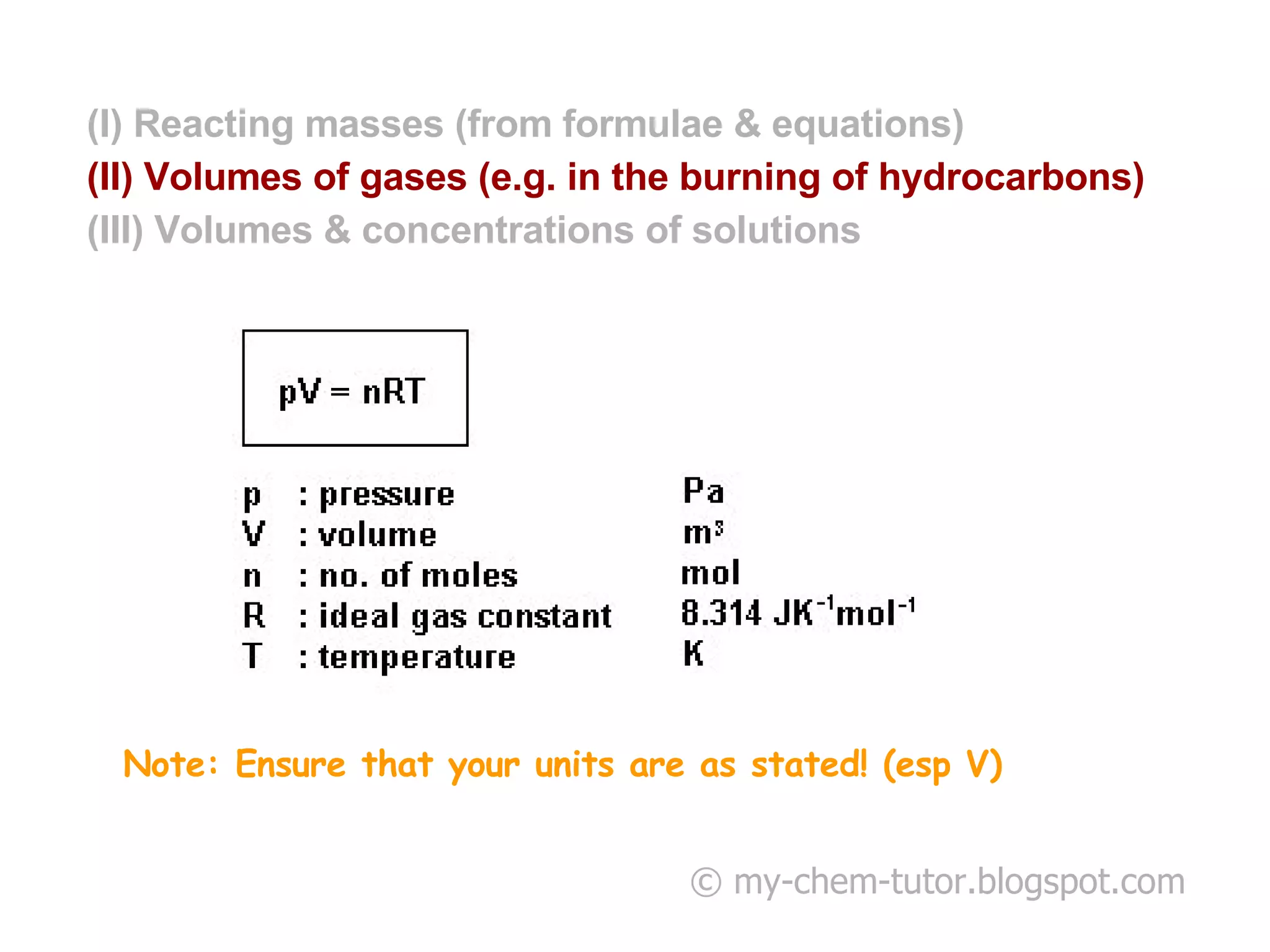
- Reacting masses, volumes of gases, and volumes and concentrations of solutions can be calculated from chemical formulae and equations.
- Avogadro's Law relates equal volumes of gases to equal moles at the same temperature and pressure.
- Common combustion reactions of hydrocarbons are presented.
![Stoichometric (Quantitative) Amount - amount used in the exact proportion as shown in equation. Excess Reagent - reagent that is not completely used up in a chemical reaction Limiting Reagent - reagent that is completely used up in a chemical reaction Theoretical Yield - quantity of product that is calculated to form when all the limiting reagent is reacted Actual Yield - quantity of product that is actually obtained during experiment Percentage Yield - [actual yield / theoretical yield] x 100% © my-chem-tutor.blogspot.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atoms-molecules-stoichometry-iii-1206457061499293-2/75/Atoms-Molecules-Stoichometry-III-2-2048.jpg)
![Avogadro's Law equal volumes of all gases at the same T & P contain equal number of moles (irrespective of type of gas). Molar Volume • At stp [273K, 101325Pa], the molar volume of any gas is 22.4 dm 3 • At rtp [298K, 101325Pa], the molar volume of any gas is 24.0 dm 3 General equation for combustion of alkanes: © my-chem-tutor.blogspot.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atoms-molecules-stoichometry-iii-1206457061499293-2/75/Atoms-Molecules-Stoichometry-III-4-2048.jpg)

![OVERVIEW © my-chem-tutor.blogspot.com From the equations & concepts shown, it is possible to set many different types of questions; [Level 1] Attempt as many questions as possible from different sources. [Level 2] You will notice certain patterns in solving the different types of questions. [Level 3] Understand when & why certain equations/ concepts are used in solving the questions ( upon which you will be able to solve any type of questions ). TIPS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atoms-molecules-stoichometry-iii-1206457061499293-2/75/Atoms-Molecules-Stoichometry-III-6-2048.jpg)