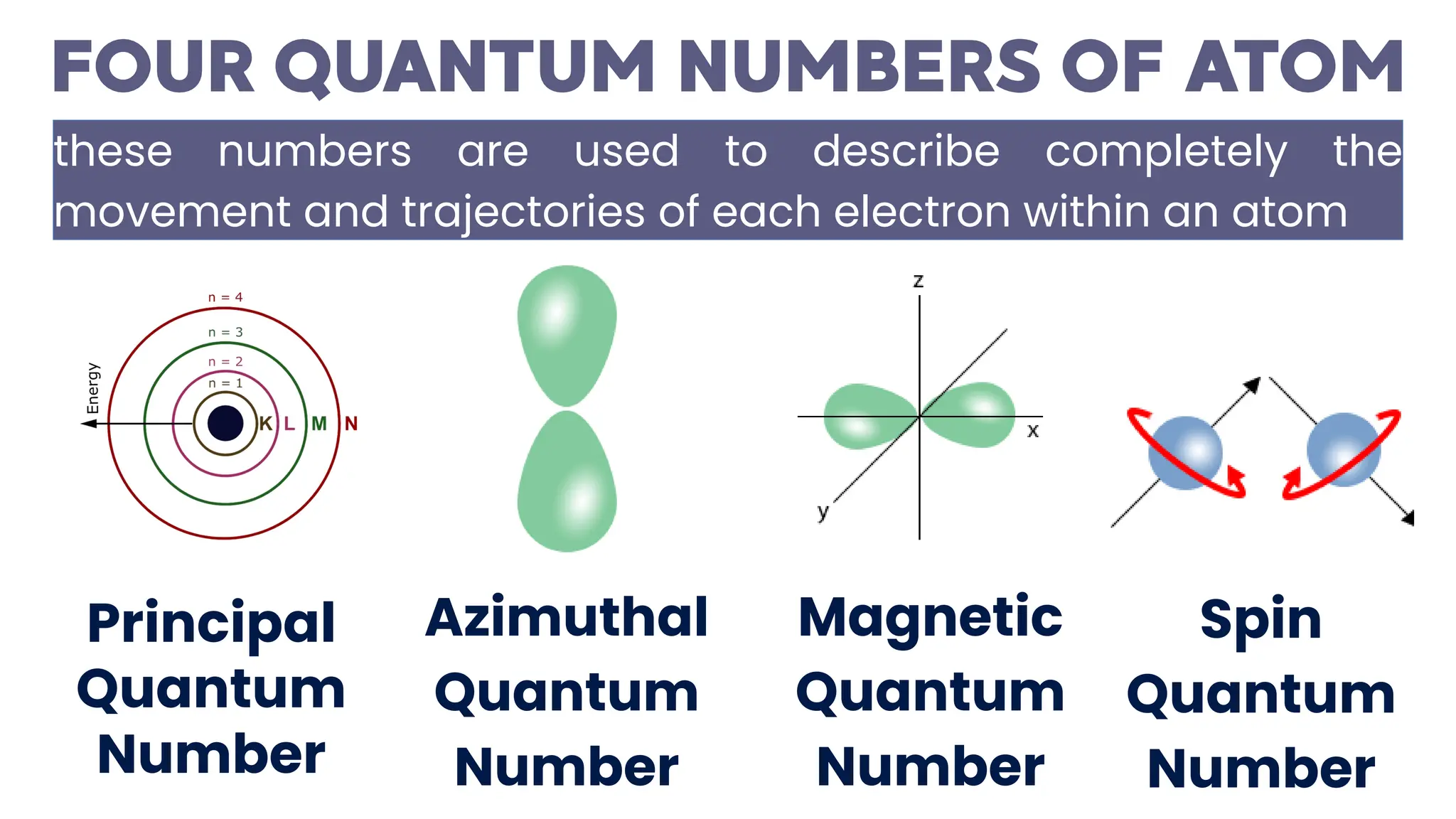
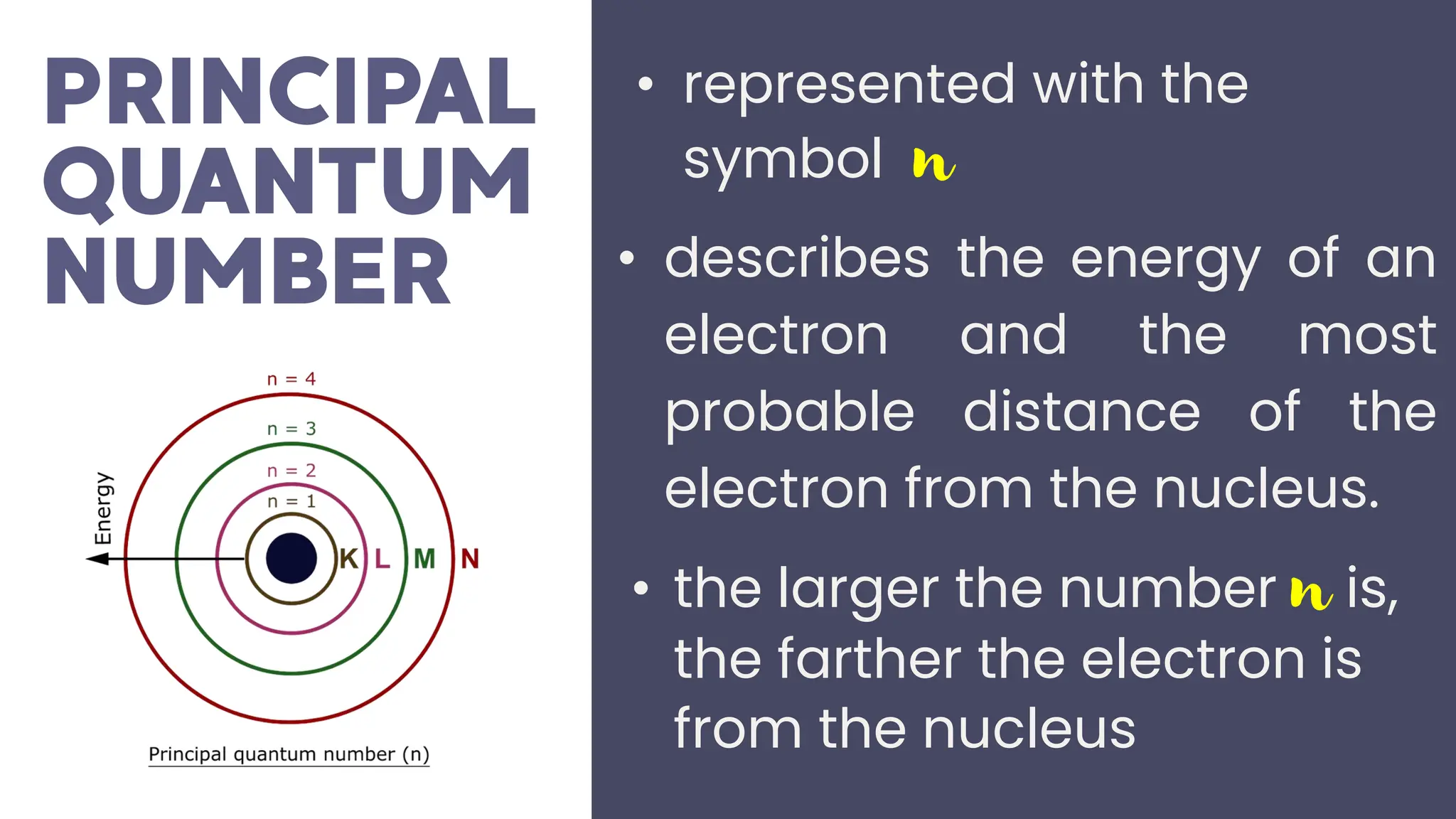
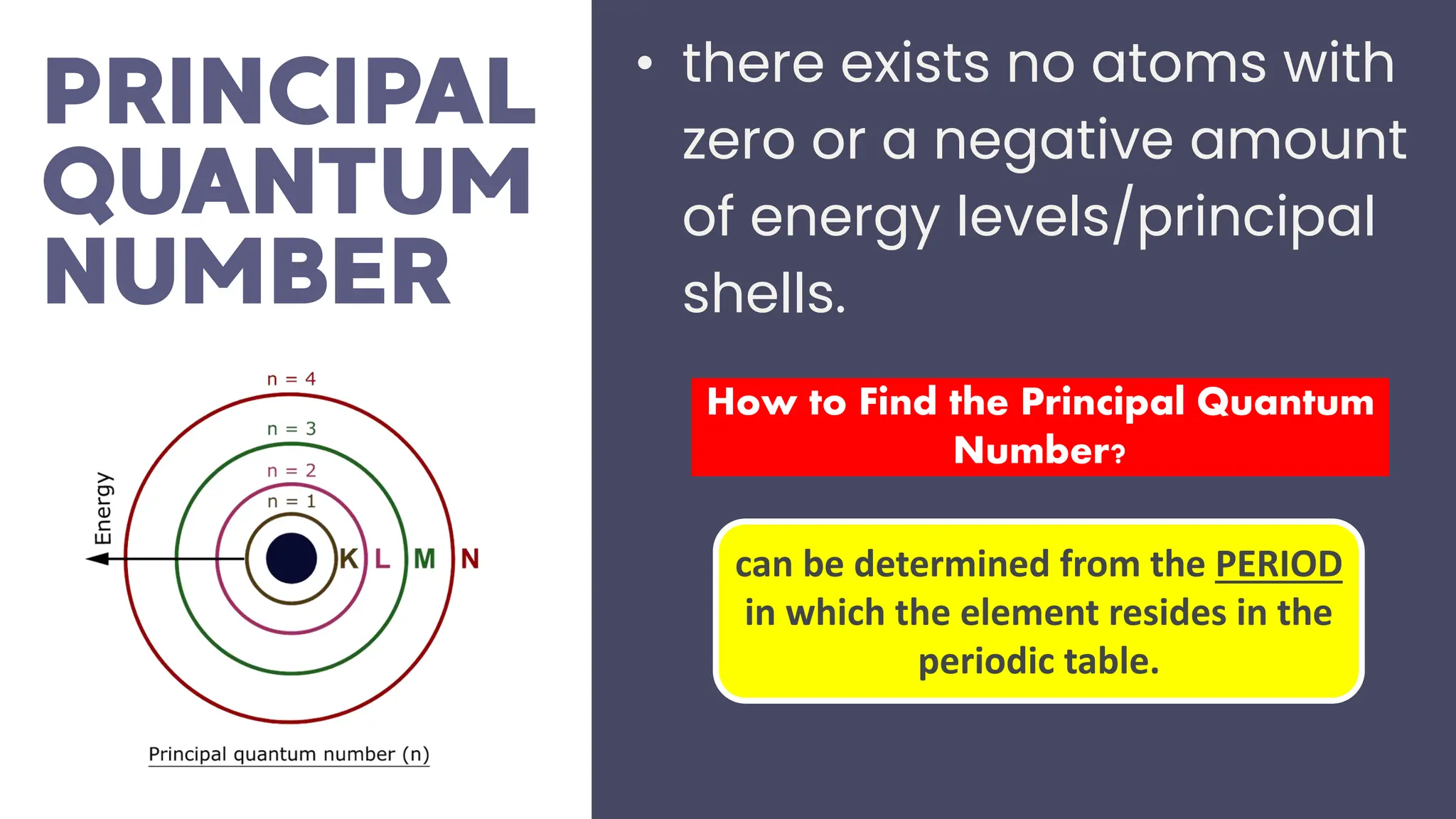
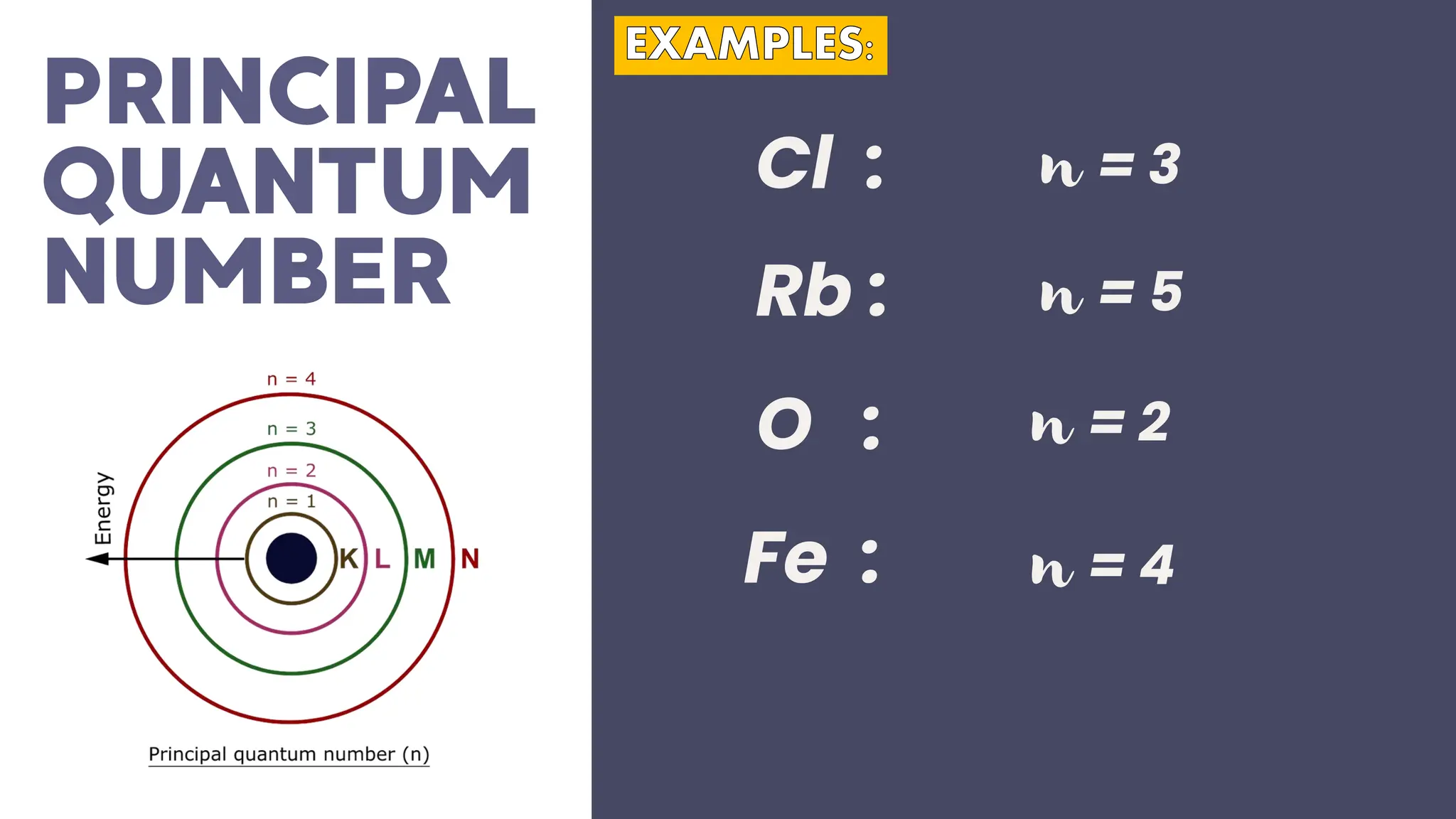
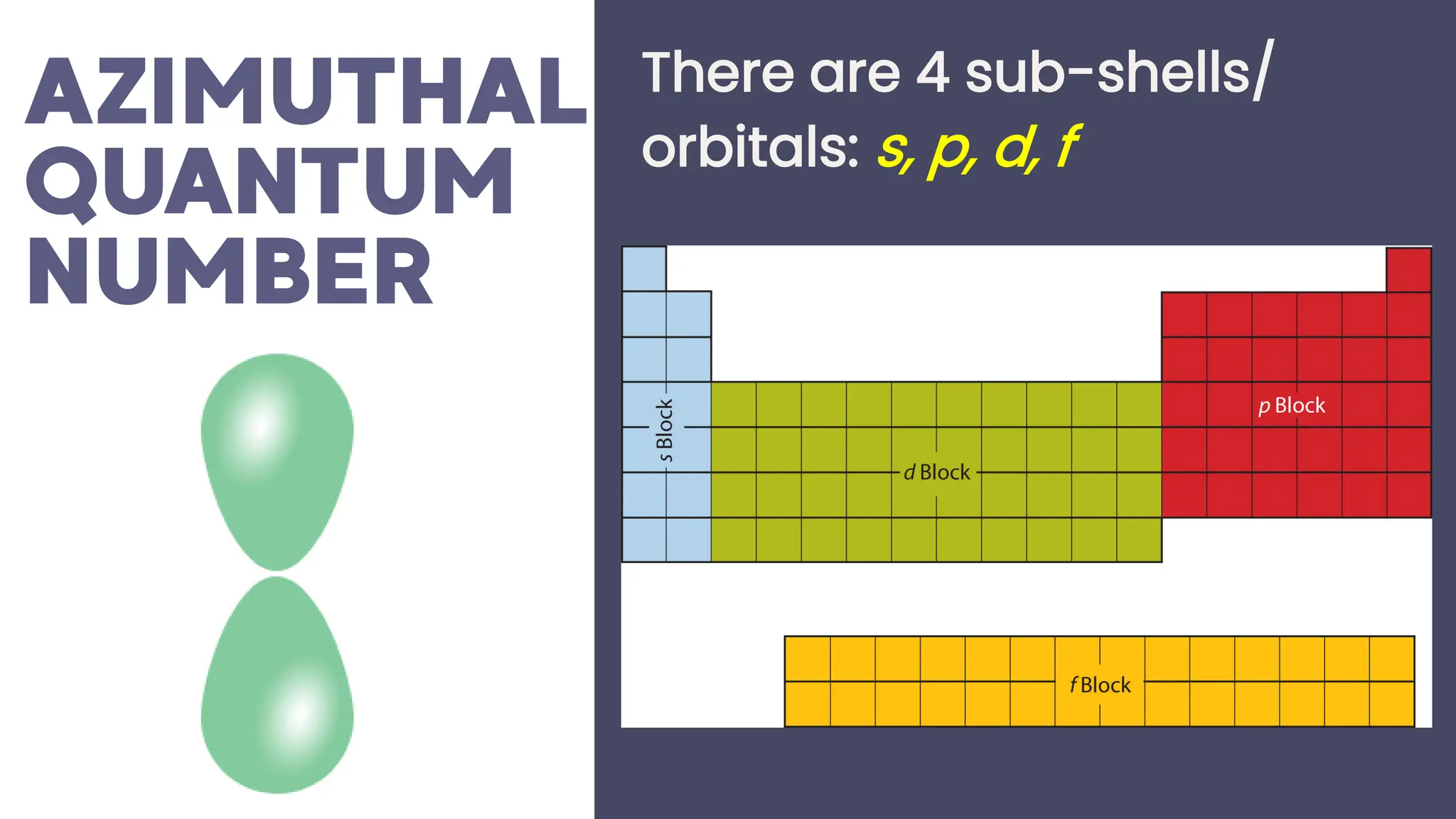
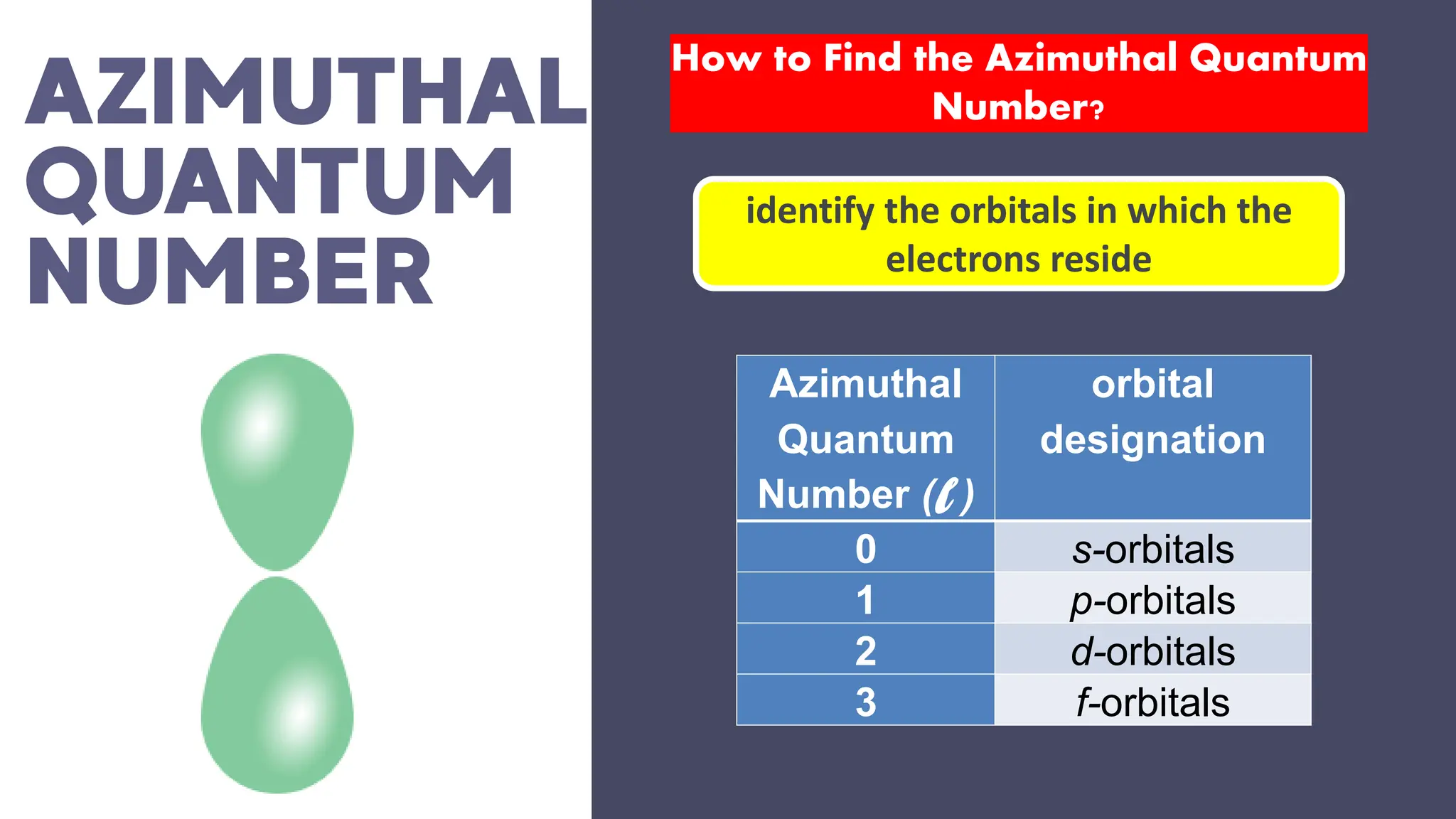
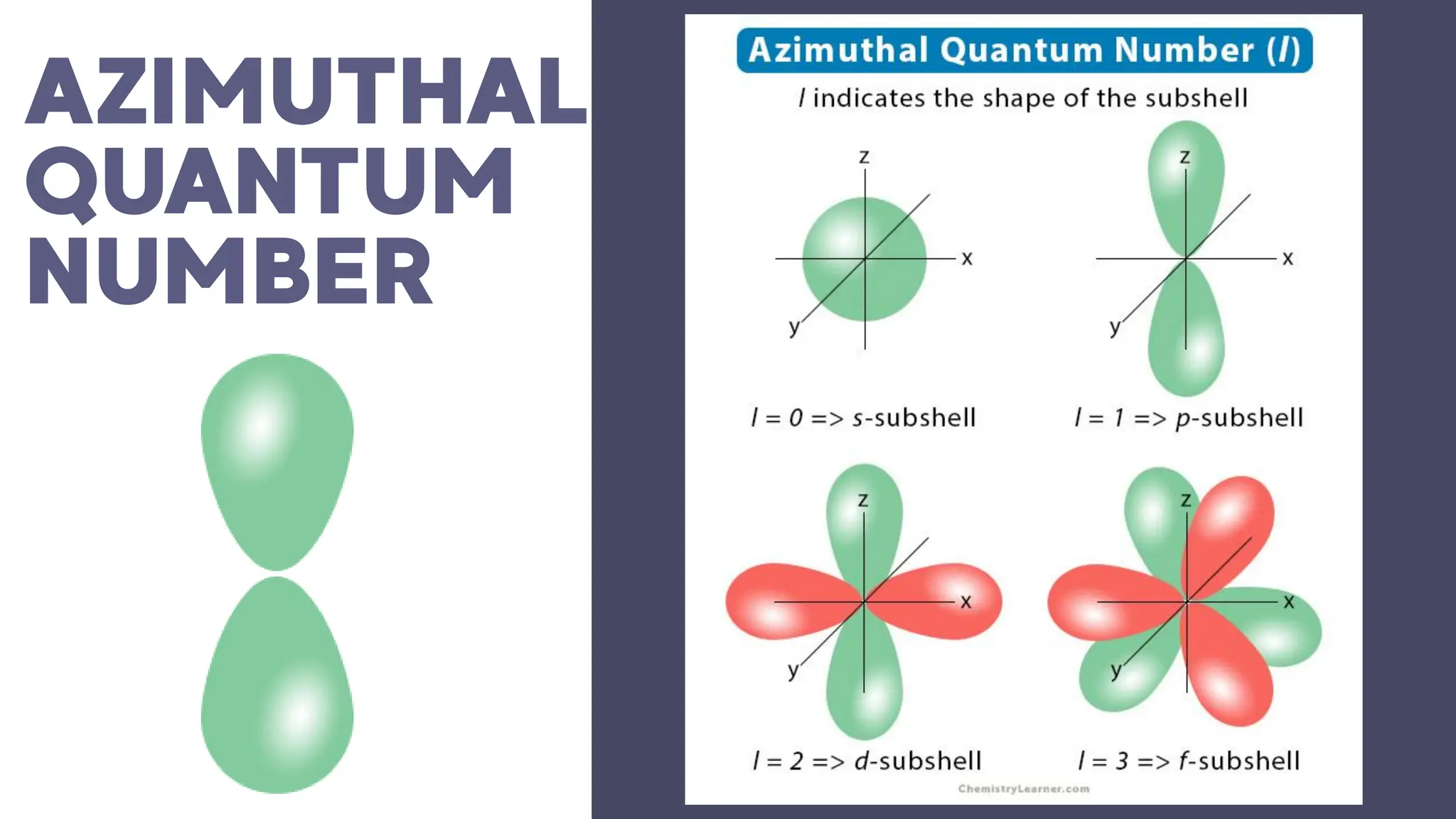
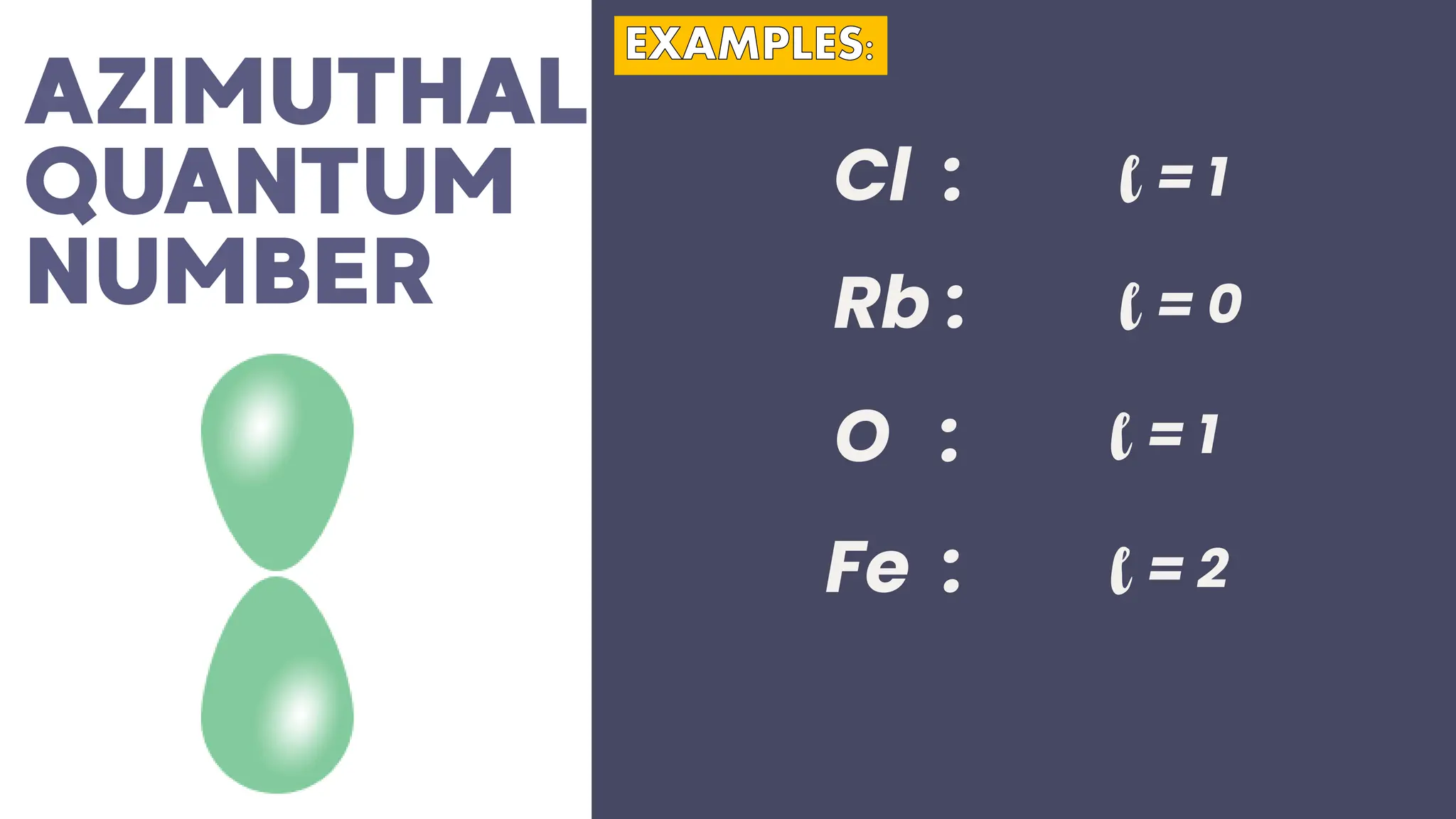
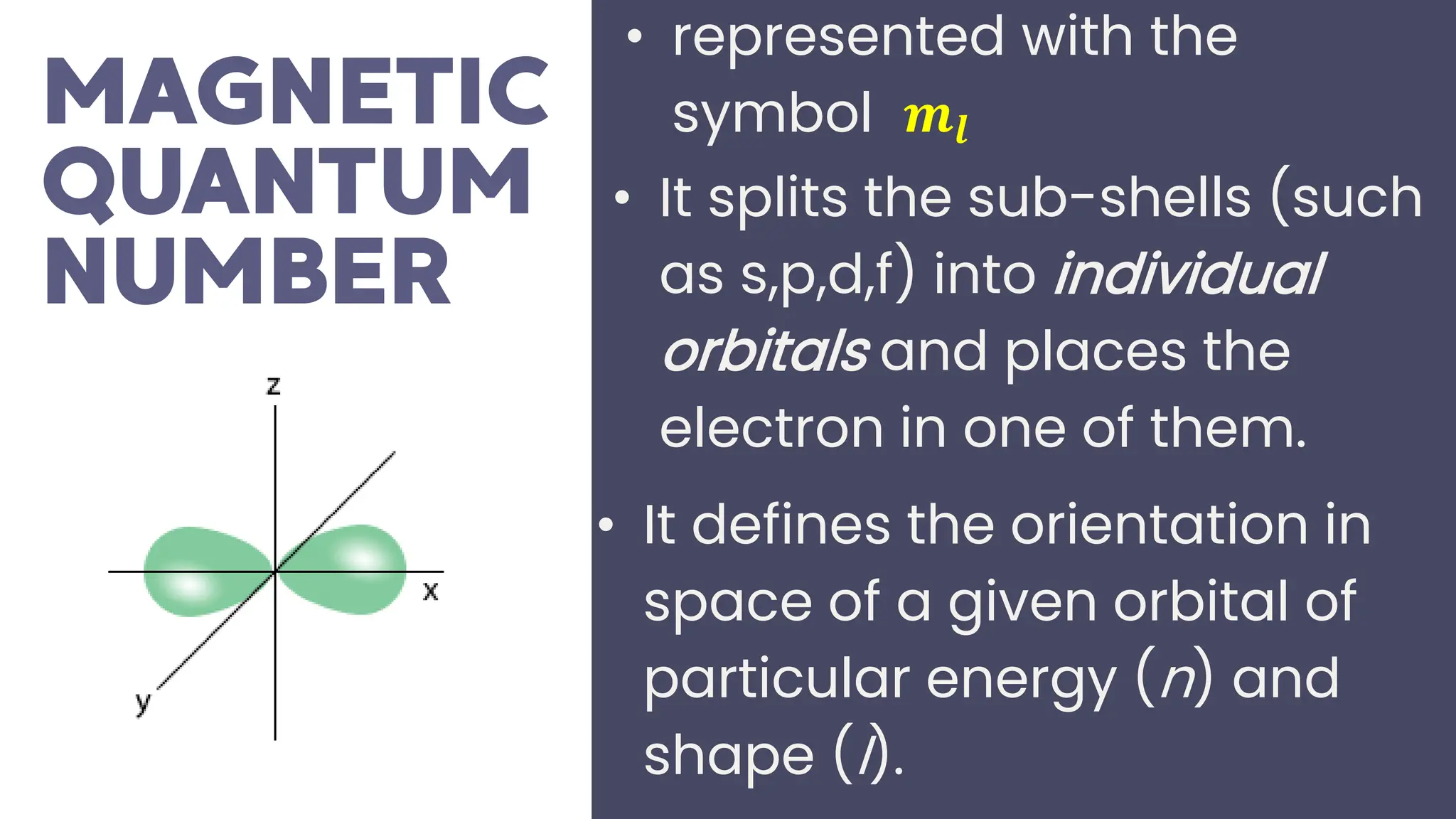
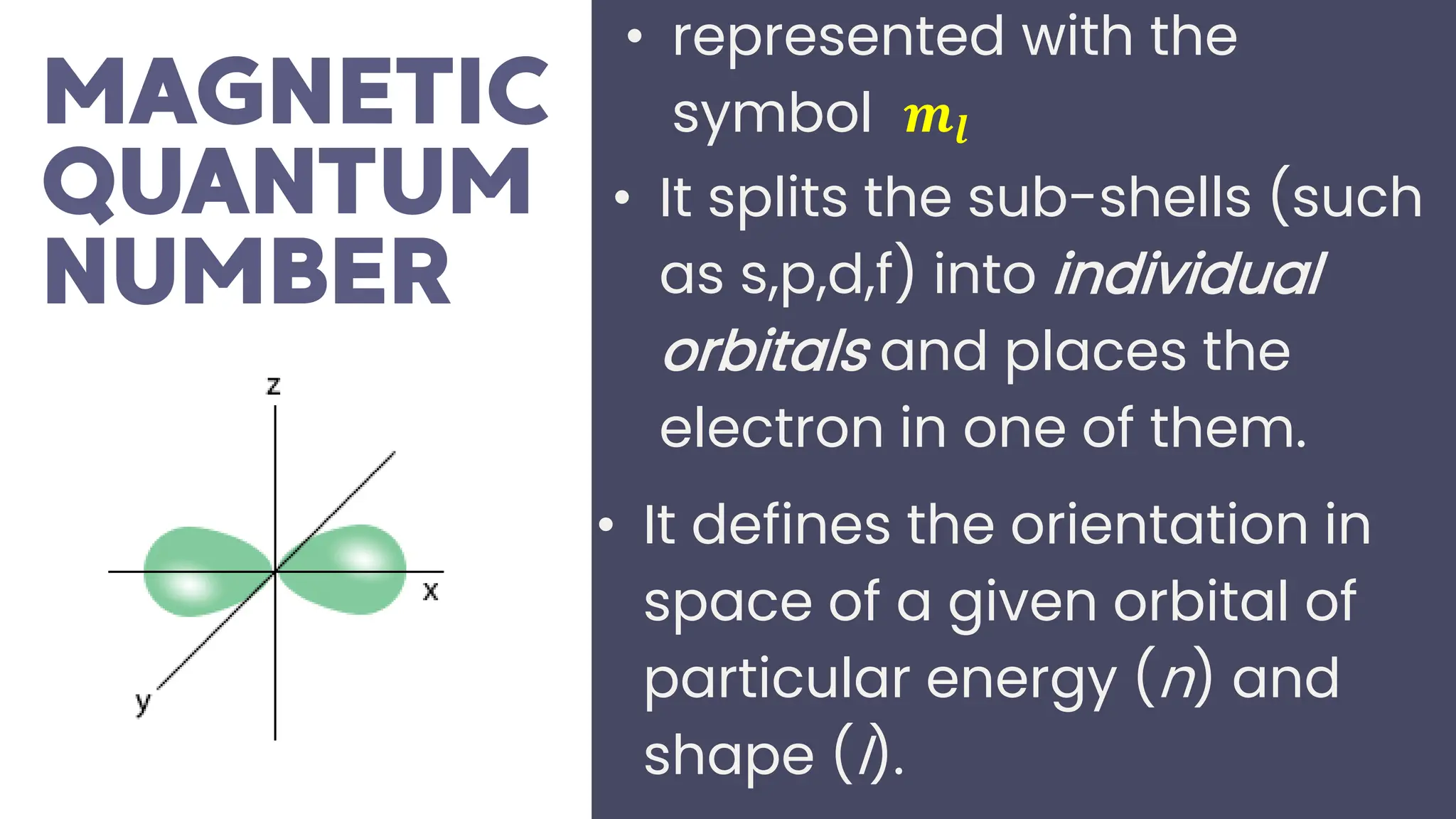
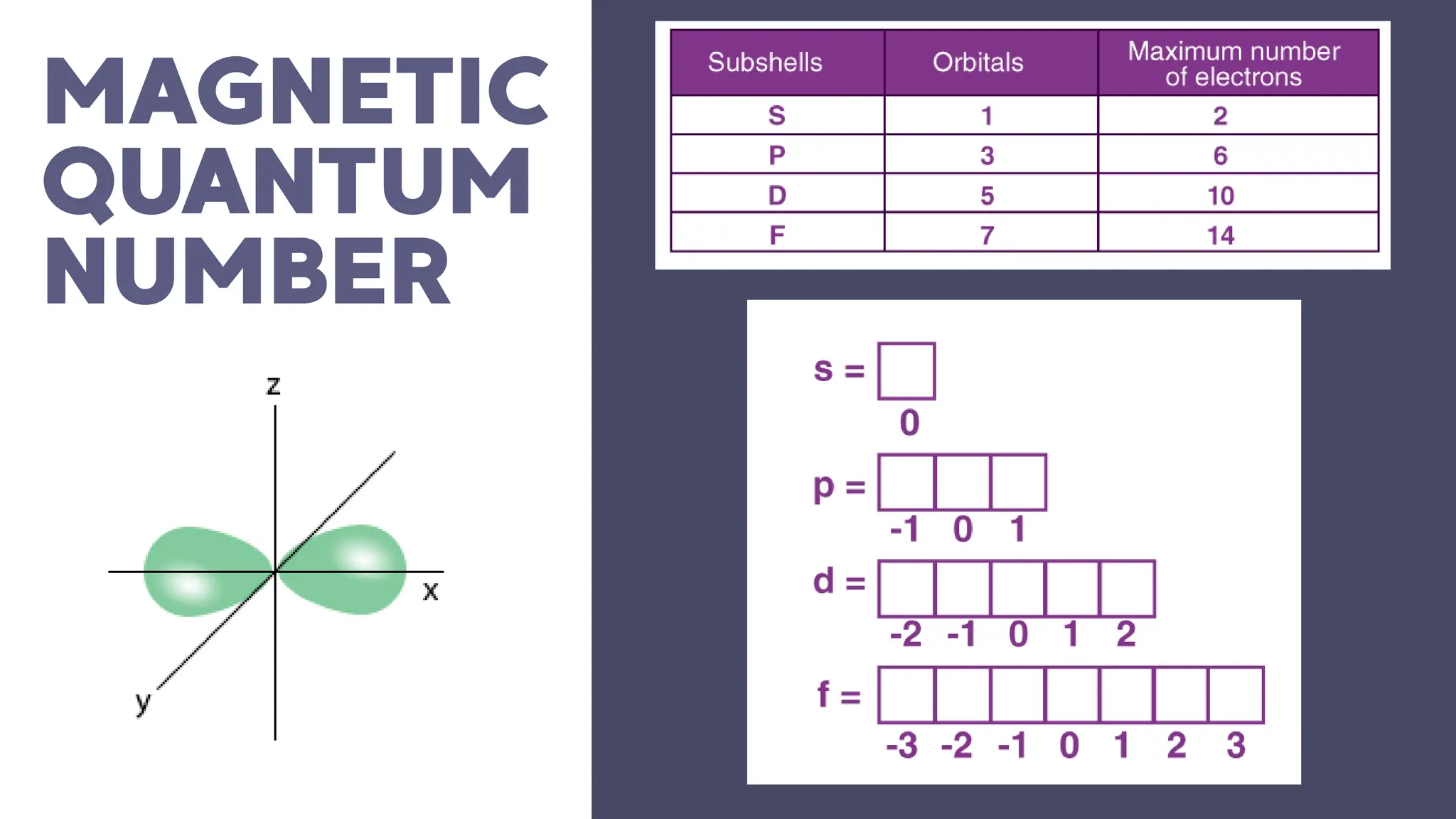
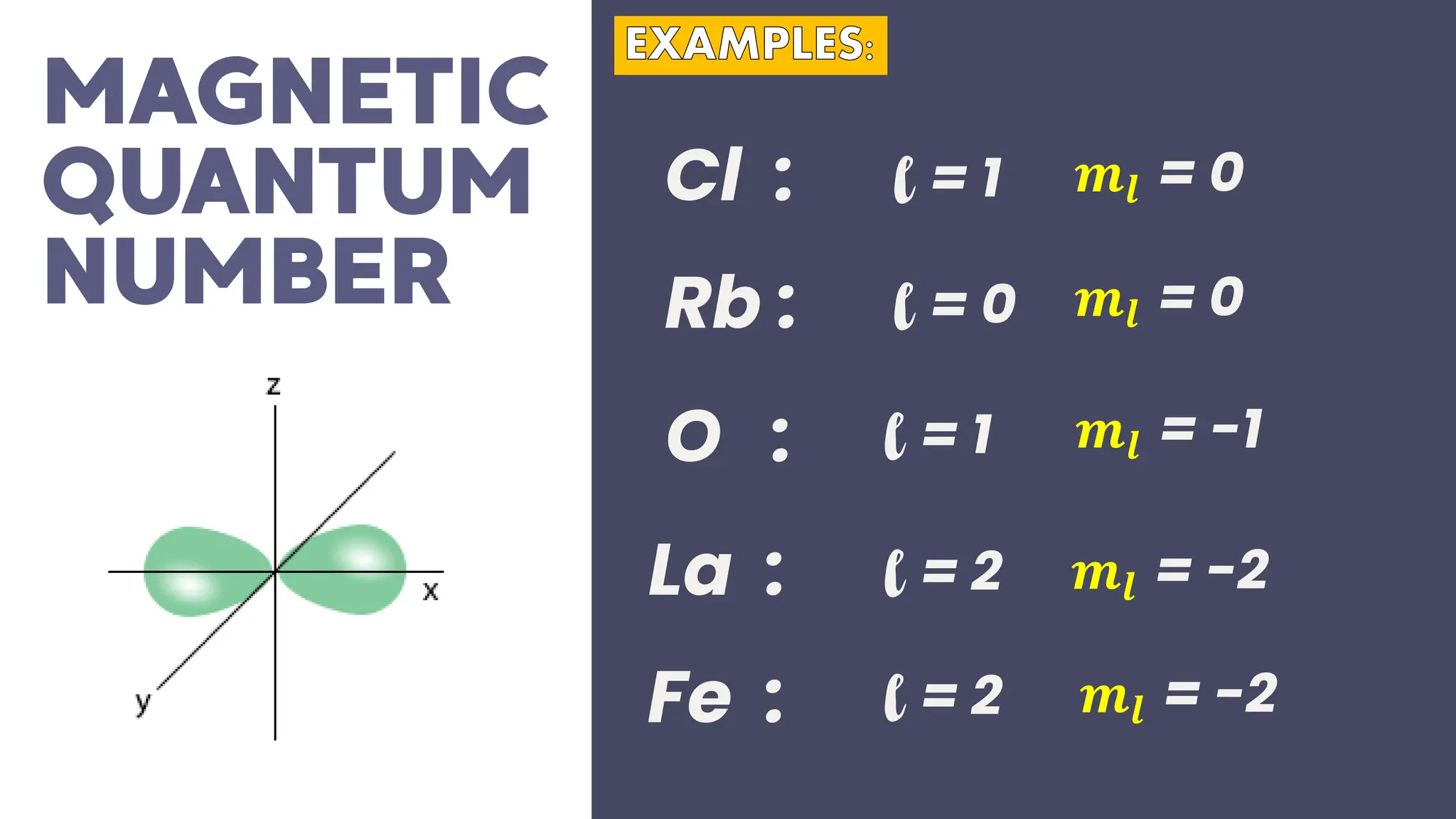
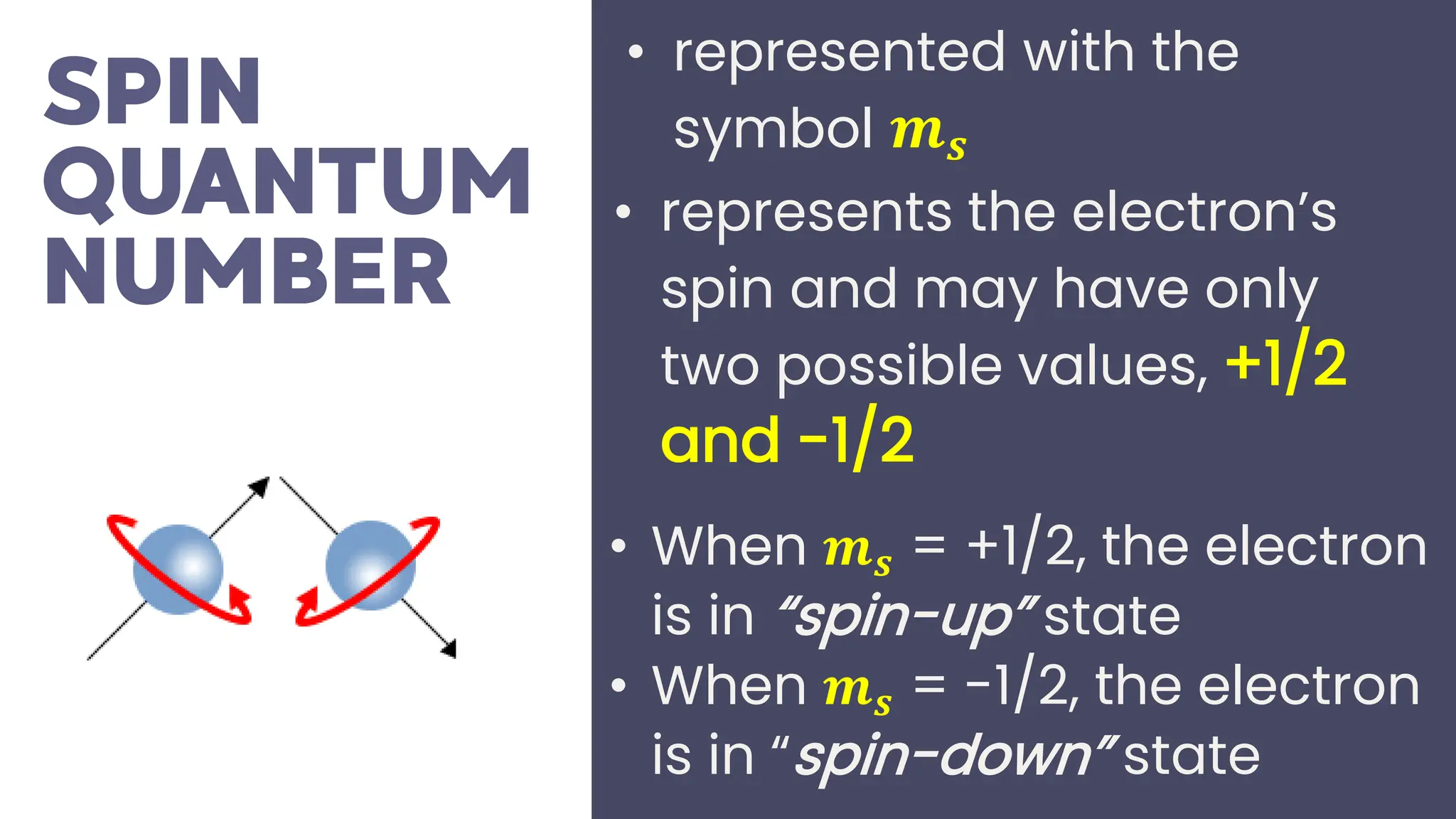
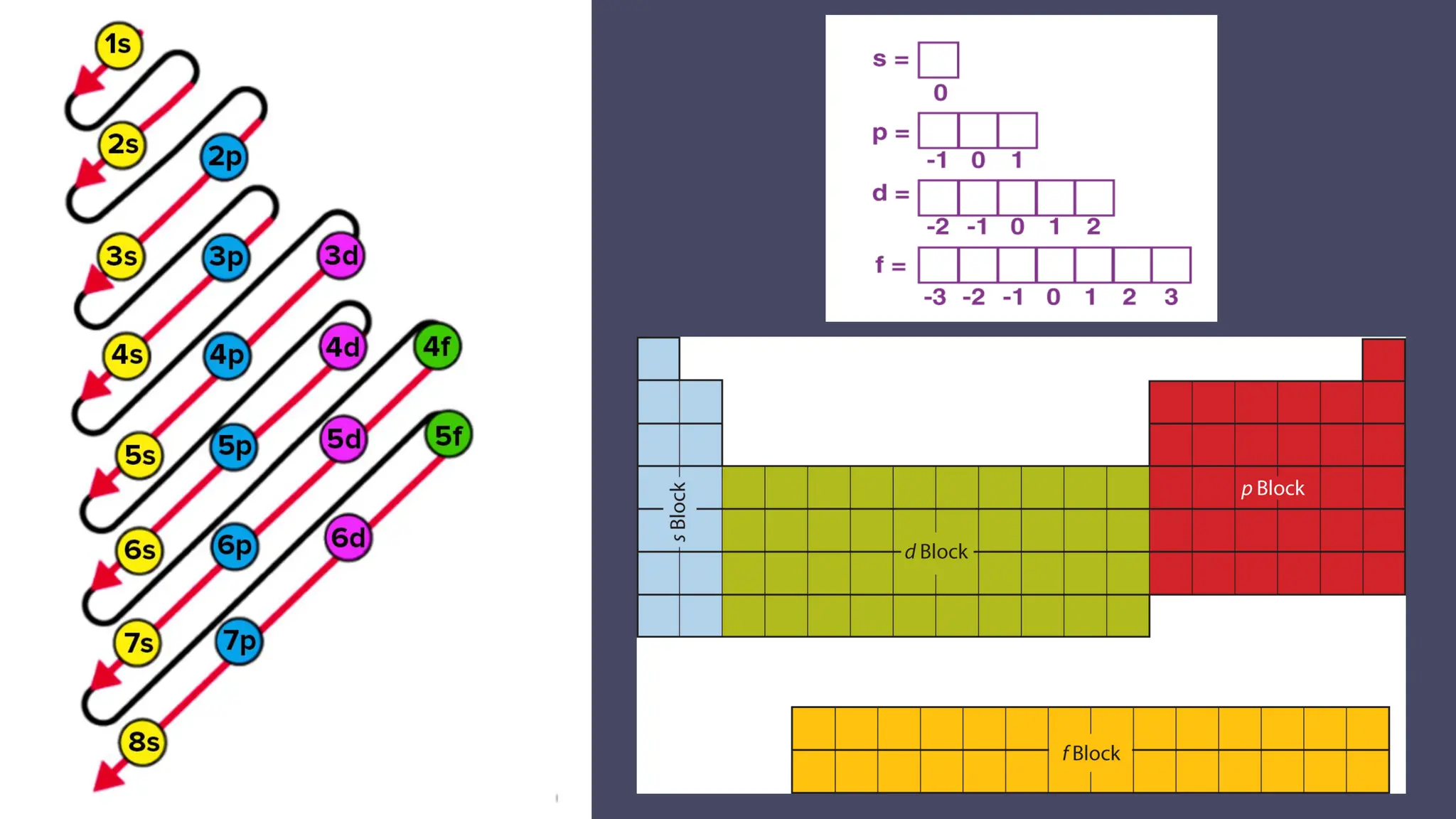
This document describes atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons within them, focusing on four quantum numbers: principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin. These numbers define an electron's energy, shape, orientation, and spin state, crucial for understanding electron behavior in an atom. Examples illustrate how to determine these quantum numbers from elements in the periodic table.