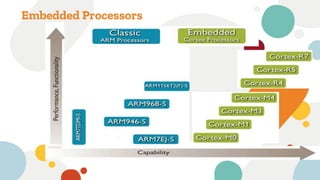
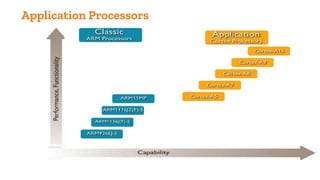
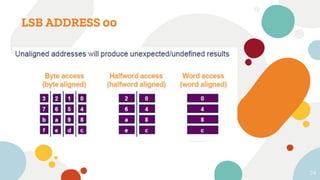
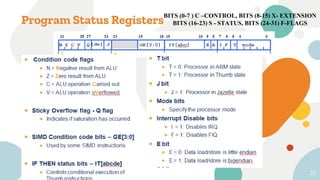
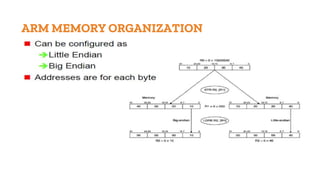
This document discusses embedded and real-time systems based on ARM architecture. It covers the three modes of operation in ARM: ARM instruction set, Thumb instruction set, and Jazelle-DBX/RCT for accelerating Java and supporting interpreted languages. It also summarizes the different ARM architecture versions from ARMv7 to ARMv8, describing their instruction sets and features. Finally, it provides overviews of ARM registers, memory organization, and other key concepts.