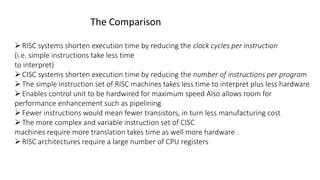
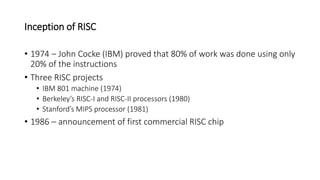
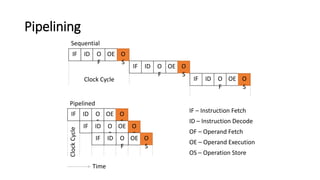
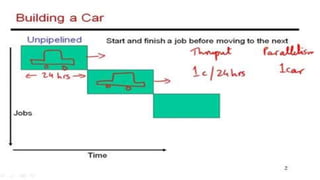
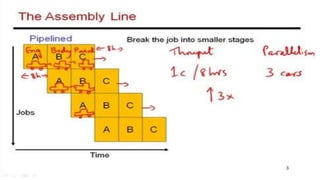
RISC and CISC are two different microprocessor architectures. RISC uses a reduced instruction set with simpler instructions that can operate at higher speeds, while CISC encodes more complex instructions directly. While CISC can complete fewer instructions per program by reducing the number needed, RISC shortens execution time by reducing the clock cycles per instruction through simpler interpretations. RISC also enables faster control units, pipelining for enhanced performance, and fewer transistors for lower manufacturing costs. Initially RISC gained popularity due to improvements in compiler and memory technologies. Today, most processors use a hybrid RISC/CISC approach to gain benefits of both architectures.