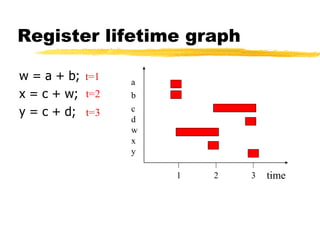
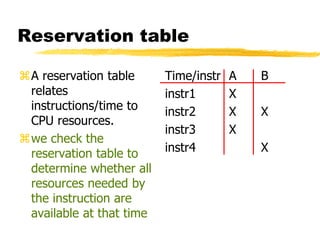
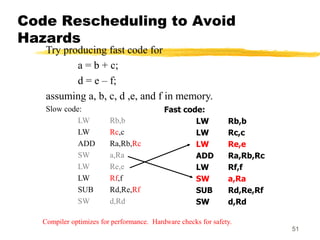
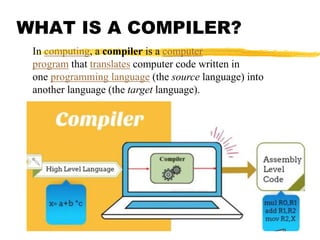
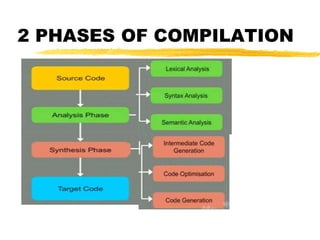
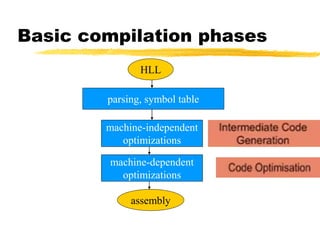
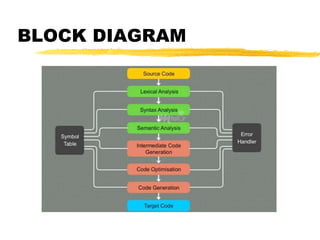
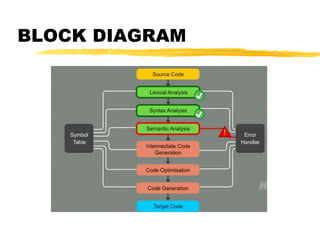
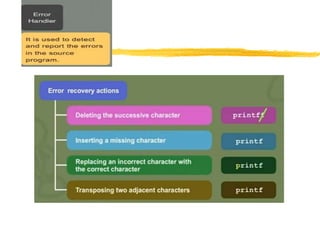
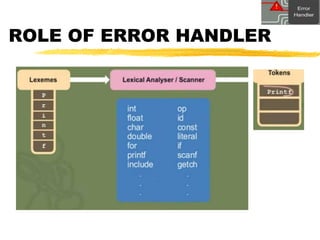
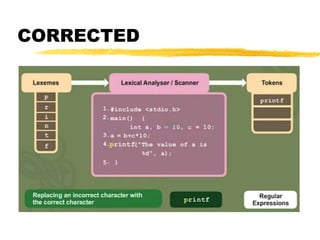
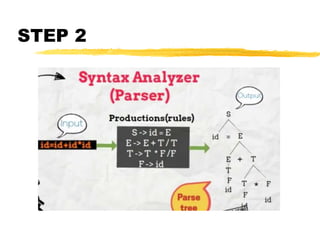
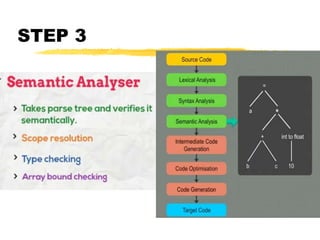
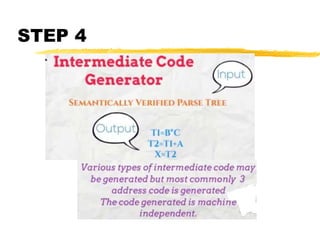
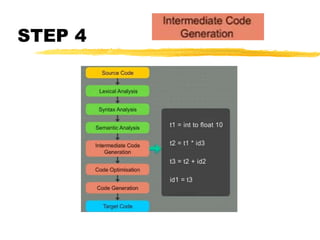
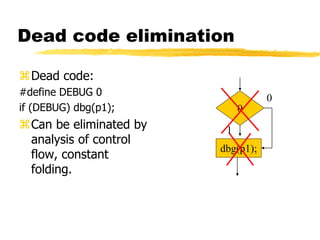
A compiler is a program that translates code written in one programming language into another language. Compilation has two phases - translation and optimization. The basic compilation phases are parsing, symbol table construction, machine-independent optimizations, machine-dependent optimizations, and assembly code generation. Compiler optimizations improve performance by techniques like dead code elimination, loop transformations, register allocation, instruction scheduling, and software pipelining.









![2
3
4
1
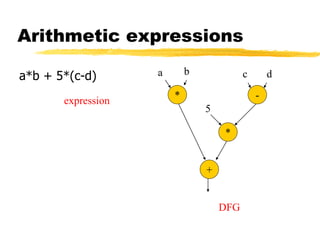
Arithmetic expressions,
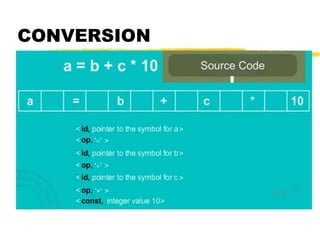
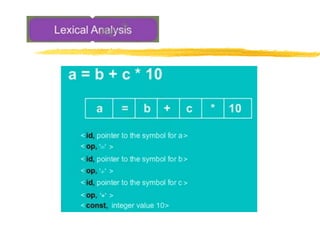
cont’d. a*b + 5*(c-d)
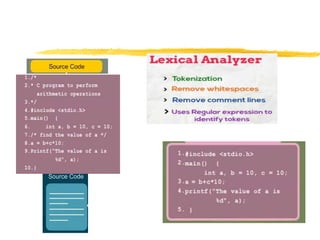
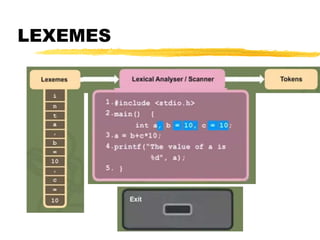
ADR r7,a
LDR r1,[r7]
ADR r7,b
LDR r2,[r7]
MUL r3,r1,r2
DFG
* -
*
+
a b c d
5
ADR r7,c
LDR r4,[r7]
ADR r7,d
LDR r5,[r7]
SUB r6,r4,r5
MOV r8, #5
MUL r9,r8,r6
ADD r10 r3,r9
code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compileroptimization-200903160816/85/Compiler-optimization-31-320.jpg)
![3
21
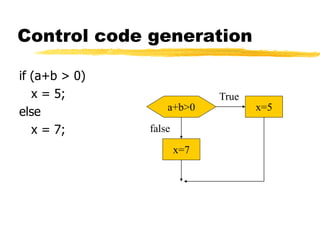
Control code generation,
cont’d.
ADR r5,a
LDR r1,[r5]
ADR r5,b
LDR r2,b
ADD r3,r1,r2
BLE label3
a+b>0 x=5
x=7
LDR r3,#5
ADR r5,x
STR r3,[r5]
B statement
label 3 LDR r3,#7
ADR r5,x
STR r3,[r5]
statement
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compileroptimization-200903160816/85/Compiler-optimization-33-320.jpg)


![One-dimensional arrays
C array name points to 0th element:
a[0]
a[1]
a[2]
a
= *(a + 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compileroptimization-200903160816/85/Compiler-optimization-38-320.jpg)
![Two-dimensional arrays
Column-major layout:
a[0,0]
a[0,1]
a[1,0]
a[1,1] = a[i*M+j]
...
M
...
N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compileroptimization-200903160816/85/Compiler-optimization-39-320.jpg)


![Loop fusion and
distribution
Fusion combines two loops into 1:
for (i=0; i<N; i++)
a[i] = b[i] * 5;
for (j=0; j<N; j++)
w[j] = c[j] * d[j];
for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
a[i] = b[i] * 5;
w[i] = c[i] * d[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compileroptimization-200903160816/85/Compiler-optimization-44-320.jpg)