This document provides an overview of ARM processor fundamentals, including:
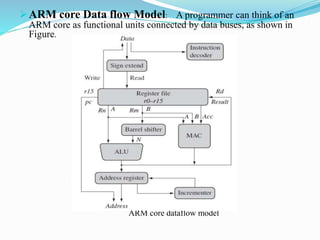
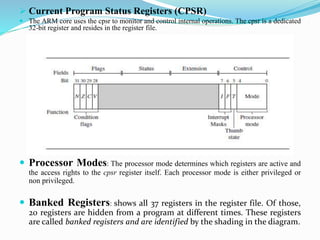
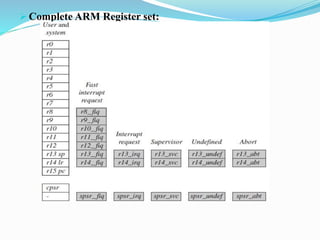
- The ARM core uses a data flow model with functional units connected by data buses. It contains general purpose registers and the current program status register (CPSR).
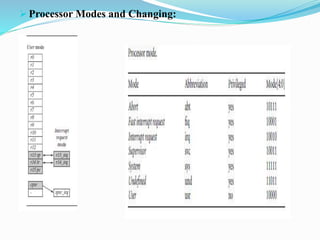
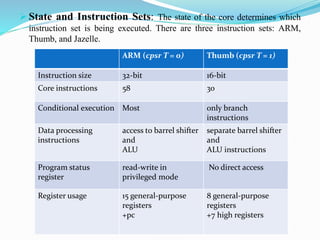
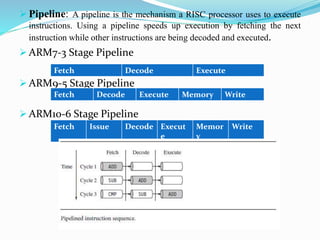
- The processor supports different instruction sets (ARM, Thumb, Jazelle) and modes (user/privileged). It implements pipelining for faster instruction execution.
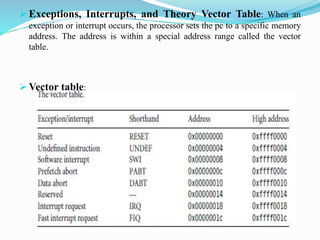
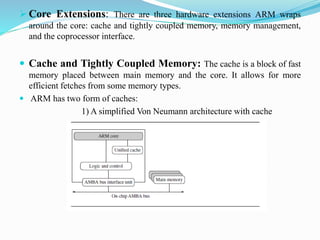
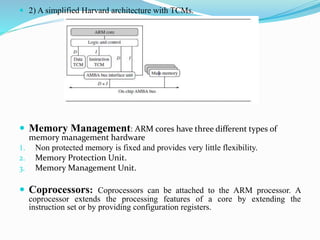
- Exceptions and interrupts trigger the processor to jump to addresses in the vector table. Core extensions include caches, memory management, and a coprocessor interface.
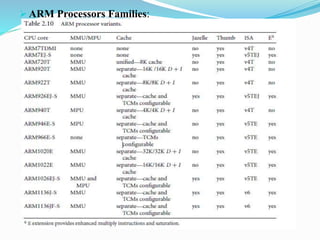
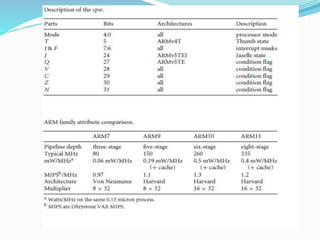
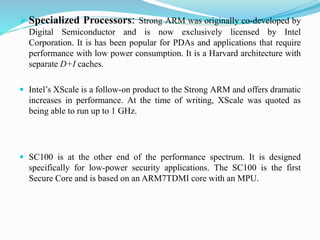
- ARM processors are organized into families and specialized processors exist for different applications like low power usage.