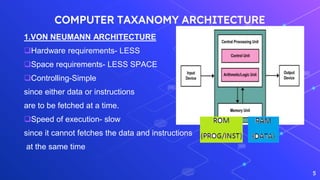
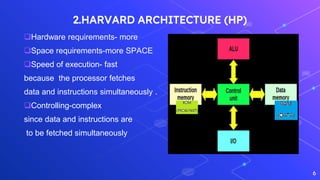
This document provides an introduction to embedded and real-time systems, focusing on the ARM processor, its architecture and peripherals. It discusses ARM architecture versions and instruction sets. It also covers the differences between Von Neumann and Harvard computer architectures. Real-time applications and the ARM dataflow operation are introduced. Specific topics covered include ARM-based products, ARM nomenclature, ARM features like its 32-bit architecture, load/store model and 3-stage pipeline. It also discusses ARM registers, modes of operation and the program status register.














![Load/store model
8086(CISC)
ADD CL,BL
ADD CL,[2000]
⬡ ARM (RISC)
⬡ REGISTER BASED
⬡ LOAD THE DATA INTO THE REGISTR
⬡ PERFORM OPERATION
⬡ EXECUTE RESULT STORE IN REGISTER
⬡ RIGID, HP
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2arm-200718155726/85/Unit2-arm-17-320.jpg)