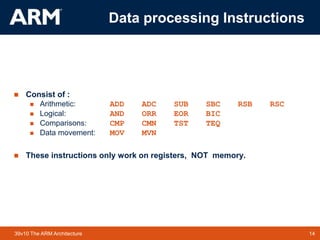
The ARM architecture is a RISC instruction set developed by ARM Holdings. It originated in 1980 and was first used in the BBC Micro home computer. ARM licenses its chip designs and architecture to manufacturers who customize and produce ARM-based chips. ARM chips are widely used in smartphones, tablets, smart TVs and other embedded devices due to their low power consumption. The ARM instruction set comes in 32-bit and 16-bit versions and supports various operating systems including Android, iOS, Windows and Linux distributions.