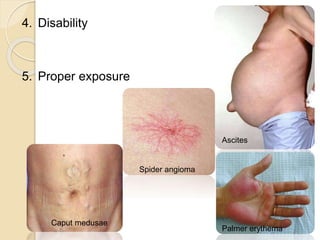
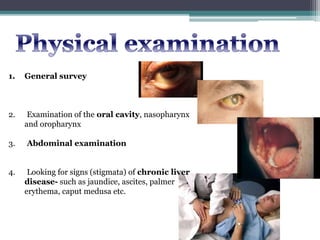
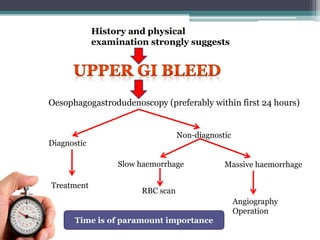
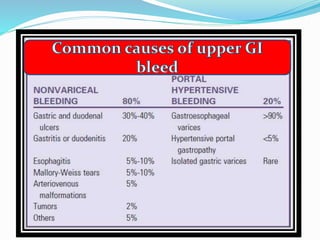
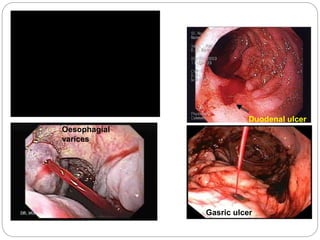
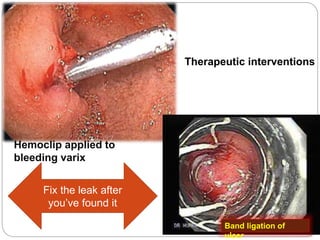
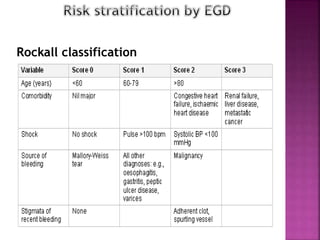
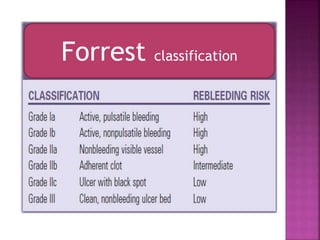
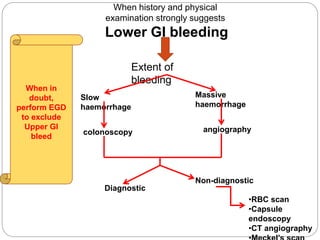
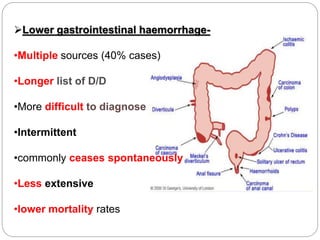
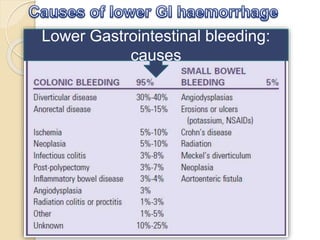
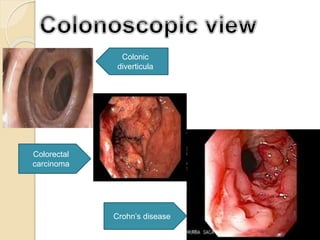
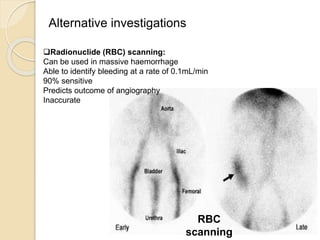
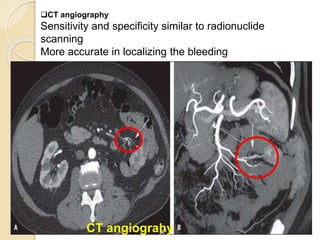
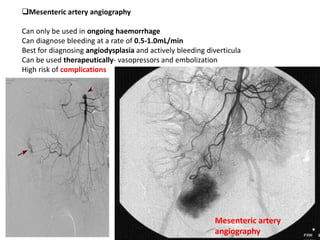
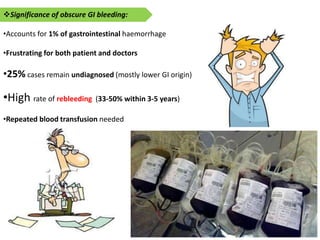
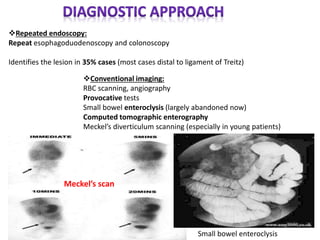
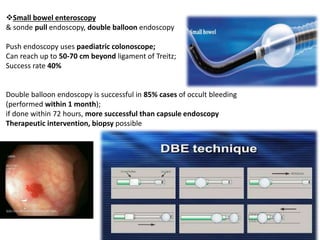
1. Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding accounts for 1% of GI hemorrhage and remains undiagnosed in 25% of cases, mostly of lower GI origin.
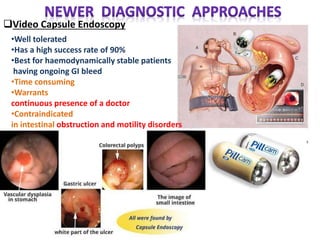
2. Video capsule endoscopy has a high success rate of 90% for evaluating obscure GI bleeding and identifying sources such as small intestinal ulcers or colonic polyps.
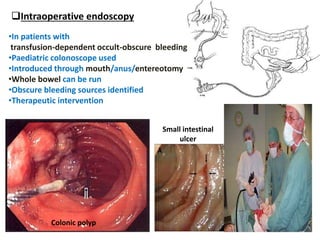
3. For patients with transfusion-dependent obscure-occult bleeding, intraoperative endoscopy using a pediatric colonoscope introduced through the mouth, anus, or entereotomy can examine the whole bowel to locate bleeding sources.