1) The document discusses the evaluation and management of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. It describes differentiating upper from lower GI bleeding, recognizing common causes, and acute management steps.
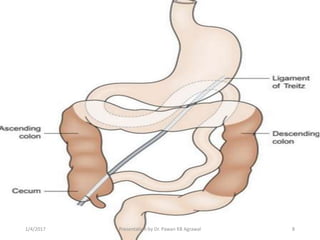
2) A clinical case example involves a patient with hematemesis and melena, where NG tube aspiration can help distinguish upper from lower GI bleeding.
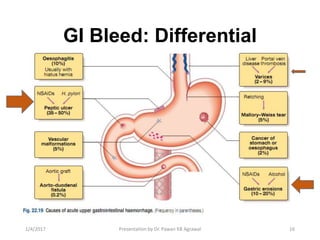
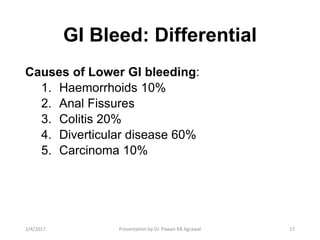
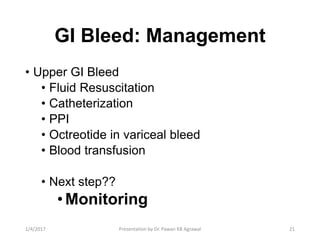
3) Common causes of upper GI bleeding include peptic ulcer disease, while diverticular disease is a common cause of lower GI bleeding. Fluid resuscitation, proton pump inhibitors, and blood transfusion are key to managing acute upper GI bleeding.