Embed presentation
Downloaded 127 times










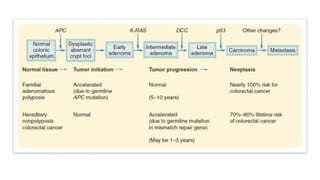


This document discusses potential causes of masses in the right iliac fossa, including appendicular abscess, appendicular mass, ileocecal tuberculosis, and carcinoma of the caecum. It provides characteristics of some common right iliac fossa masses like appendicular masses being tender, soft to firm, and having ill-defined borders, while ileocecal tuberculosis masses are firm to hard and highly placed. The document also reviews colon carcinoma risks such as aging, hereditary factors, and diet high in animal fat or low in fiber, as well as the pathogenesis involving mutations in microsatellite sequences regulating cell growth.











