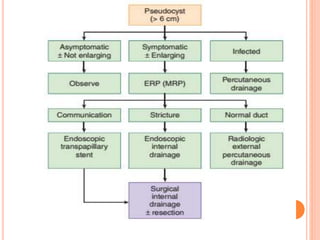
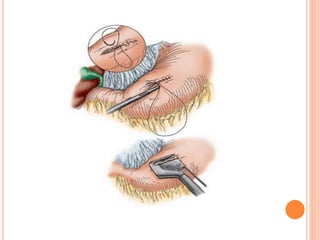
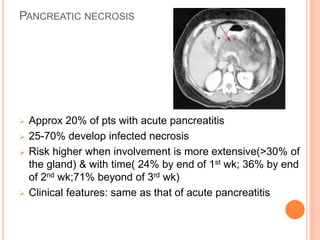
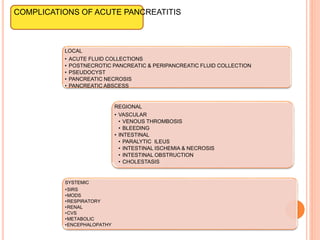
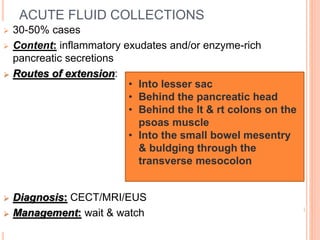
This document discusses complications of acute pancreatitis, with a focus on pseudocyst and pancreatic necrosis. It summarizes that pseudocysts are fluid collections contained by a well-defined capsule that can develop after acute or chronic pancreatitis. Complications include infection, rupture, enlargement, and erosion into blood vessels. Diagnosis involves imaging and labs. Treatment depends on symptoms and includes drainage or resection. Pancreatic necrosis involves death of pancreatic tissue and can become infected. Interventions like drainage may be needed if necrosis is infected or causing other issues. Both conditions are serious complications of acute pancreatitis.



![POSTNECROTIC PANCREATIC &PERIPANCREATIC
FLUID COLLECTION
Contain both solid & fluid components
Arise from liquefaction of solid necrosis and/or
pancreatic duct disruption
Mature lesion has a wall without an epithelial lining
around the collection- “walled off necrosis” (WON)
Diagnosis:
Management: same as that for pancreatic necrosis
CECT, MRI, EUS
CECT- Extraluminal gas
Image guided FNA for Gram’s
stain
& culture [Definitive diagnosis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-170321153555/85/COMPLICATIONS-OF-ACUTE-PANCREATITIS-6-320.jpg)