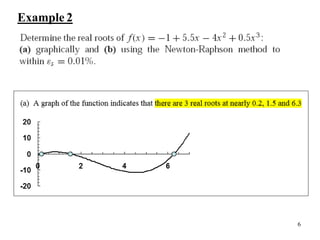
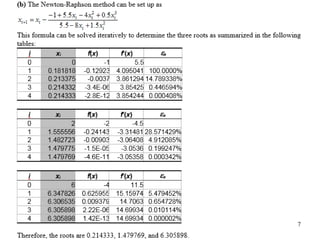
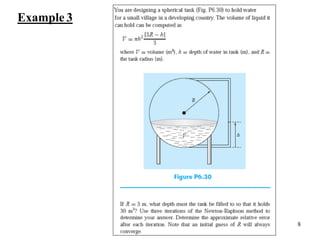
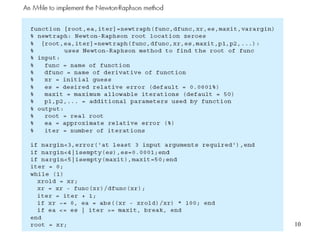
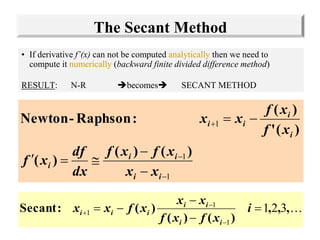
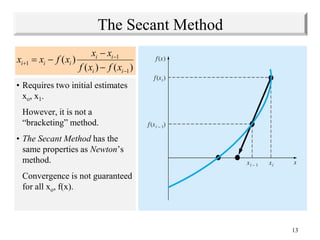
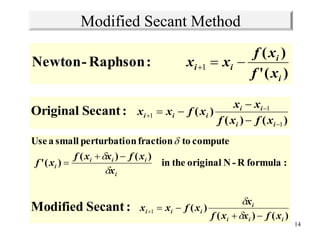
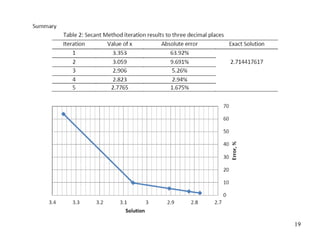
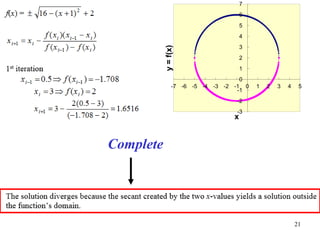
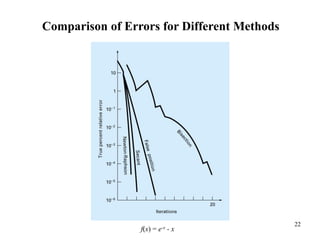
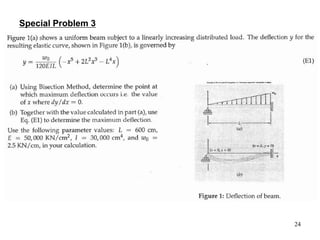
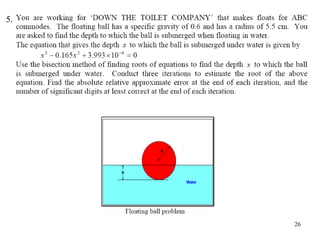
The document discusses various numerical methods for finding the roots of functions, including the Newton-Raphson method, secant method, and bisection method.
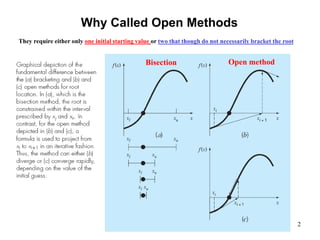
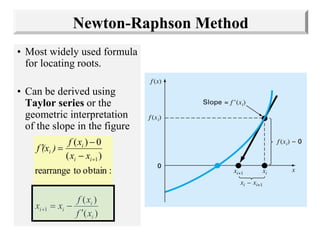
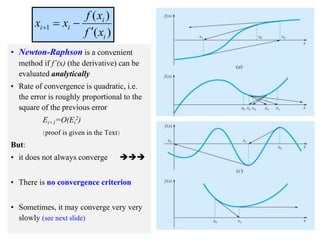
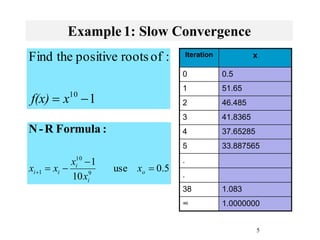
The Newton-Raphson method uses the tangent line approximation at each iteration to quickly converge on roots. It has quadratic convergence but may not always converge. The secant method is similar but computes the derivative numerically when an analytical derivative is not available. Bisection is a bracketing method that uses two initial values to successively narrow the range containing the root.
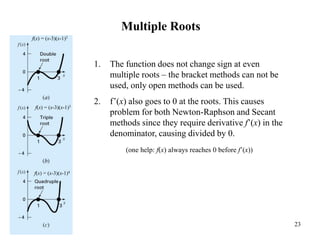
Multiple roots can pose problems as the function value reaches zero before the derivative at the root, preventing convergence of Newton-Raphson and secant methods which rely on the derivative. Special functions