The document presents a study on the Newton-Raphson method, detailing its history, derivation, and applications in numerical analysis. It explains the method's advantages, such as faster convergence and applicability to various equations, while also acknowledging its disadvantages like higher computational demands. The presentation concludes that the Newton-Raphson method is effective for finding roots of equations with reduced time complexity.






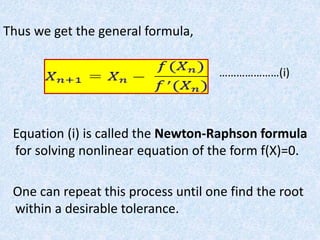




![Neglecting higher power of ϵn and noting also f(α)=0 we have
[neglecting higher order term]
Thus we see that the rate of convergence of N-R method is 2.
ϵn+1 proportional to ϵn
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group-4presentationonnr-method-240514040007-aae0349a/85/GROUP-4-PRESENTATION-ON-NR-METHOD-pptx-13-320.jpg)
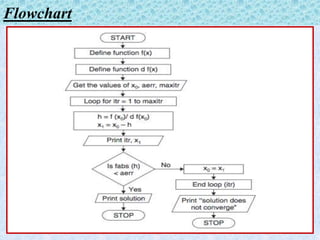
![Algorithm
• Define the function.
• Choose an initial guess X0 such that, [a,b] be any interval in
which f(a)<0 & f(b)>0 , then
• Then
• If f(X1) = 0, then X1 is our exact root.
• For more accuracy by repetition of this process we can find X2
,X3 , X4………. from X1 until we are getting the accurate value of
the root.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group-4presentationonnr-method-240514040007-aae0349a/85/GROUP-4-PRESENTATION-ON-NR-METHOD-pptx-14-320.jpg)