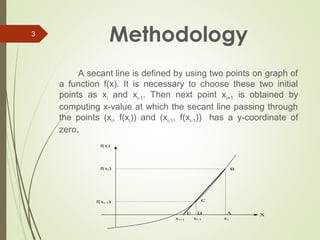
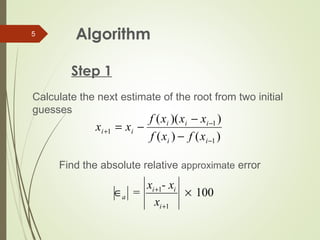
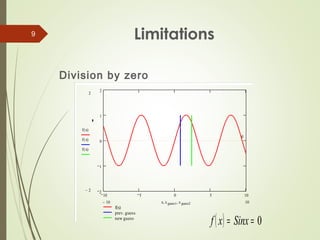
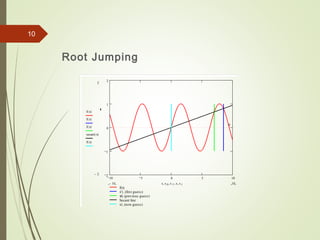
The document discusses the secant method for finding the roots of non-linear equations. It introduces the secant method which uses successive secant lines through points on the graph of a function to better approximate roots. The methodology section explains that a secant line is defined by two initial points and the next point is where the secant line crosses the x-axis. The algorithm involves calculating the next estimate from the two initial guesses and checking if the error is below a tolerance level. Applications include using the secant method for earthquake engineering analysis and limitations include potential division by zero errors or root jumping.