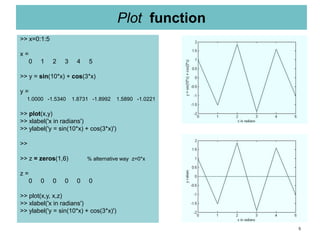
MATLAB is software originally developed as a matrix library that has since added numerical, symbolic, and visualization tools. It allows users to write scripts called m-files to perform calculations and analyze data. Built-in functions include trigonometric, exponential, rounding, and display formatting functions. Plots can be generated by providing x and y data to the plot command. Polynomial roots and solutions to systems of equations can be found. Control structures like for loops are used to iterate calculations.

()( 11 iiiii tttv
m
c
gtvtv ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appliednumericalmethodslec2-150507042248-lva1-app6892/85/Applied-numerical-methods-lec2-2-320.jpg)
()( 11 iiiii tttv
m
c
gtvtv ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appliednumericalmethodslec2-150507042248-lva1-app6892/85/Applied-numerical-methods-lec2-3-320.jpg)

![6
Roots of polynomials
>> r = [1, -2, 4]
r =
1 -2 4
>> poly(r)
ans =
1 -3 -6 8
>> p = poly(r)
p =
1 -3 -6 8
>> solve = roots(p)
solve =
4.0000
-2.0000
1.0000
System of equations
>> x=[-1, 5]
x =
-1 5
>> A = [2, 3; -1, 4]
A =
2 3
-1 4
>> b = A*x'
b =
13
21
>> solveX = inv(A)*b
solveX =
-1.0000
5.0000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appliednumericalmethodslec2-150507042248-lva1-app6892/85/Applied-numerical-methods-lec2-6-320.jpg)
![**here Fundamental control structures in MATLAB
Managing Variables
clear – removes all variables from memory clear x y – removes only x and y from memory
who – displays a list of variables in the memory whos – displays a list of variables in the
memory along with their size and class
FOR-Loop sum = 0;
DOFOR i = start, step, final for i = 2:1:25
(Loop Body) sum = sum + A[i];
ENDDO end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appliednumericalmethodslec2-150507042248-lva1-app6892/85/Applied-numerical-methods-lec2-7-320.jpg)