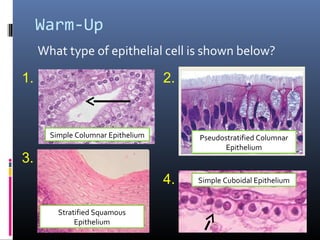
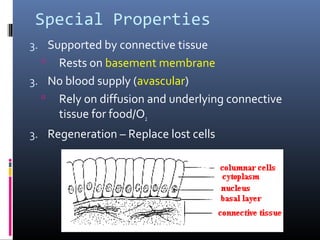
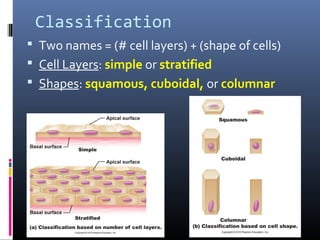
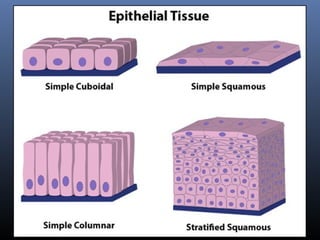
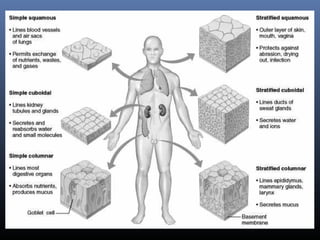
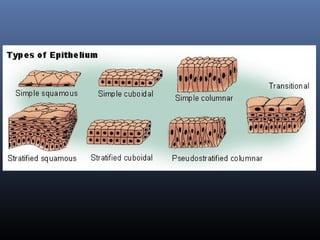
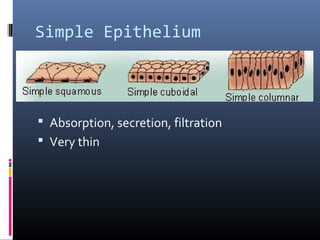
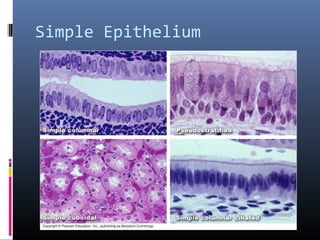
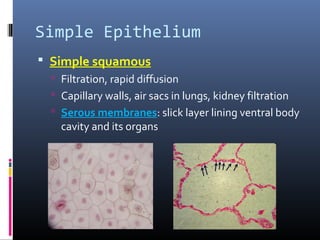
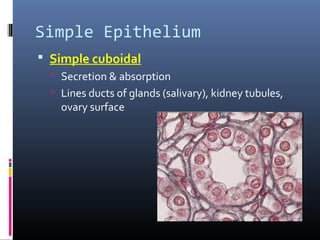
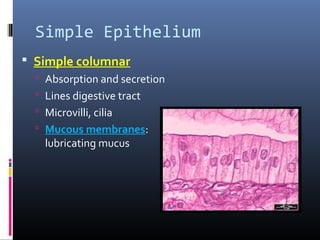
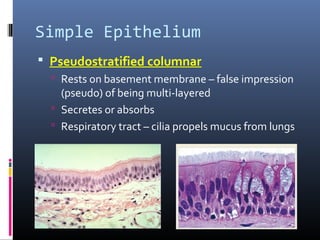
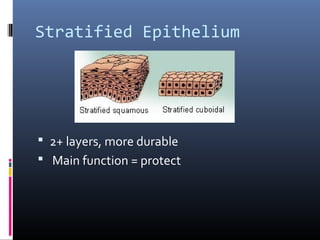
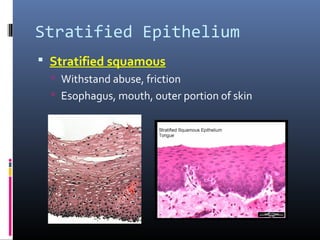
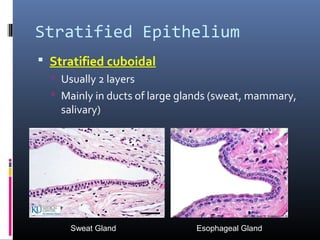
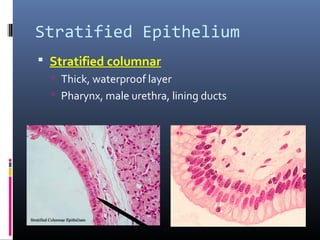
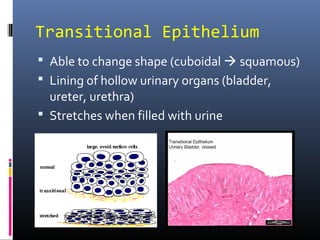
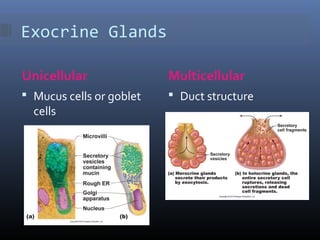
The document provides an overview of tissues, specifically focusing on epithelial tissue, its structure, function, and classification. It discusses the four main types of tissues—epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous—and highlights the special properties of epithelial cells, including their polarity and regeneration capabilities. Additionally, it details various types of epithelial tissue, their functions, and glandular epithelium types.