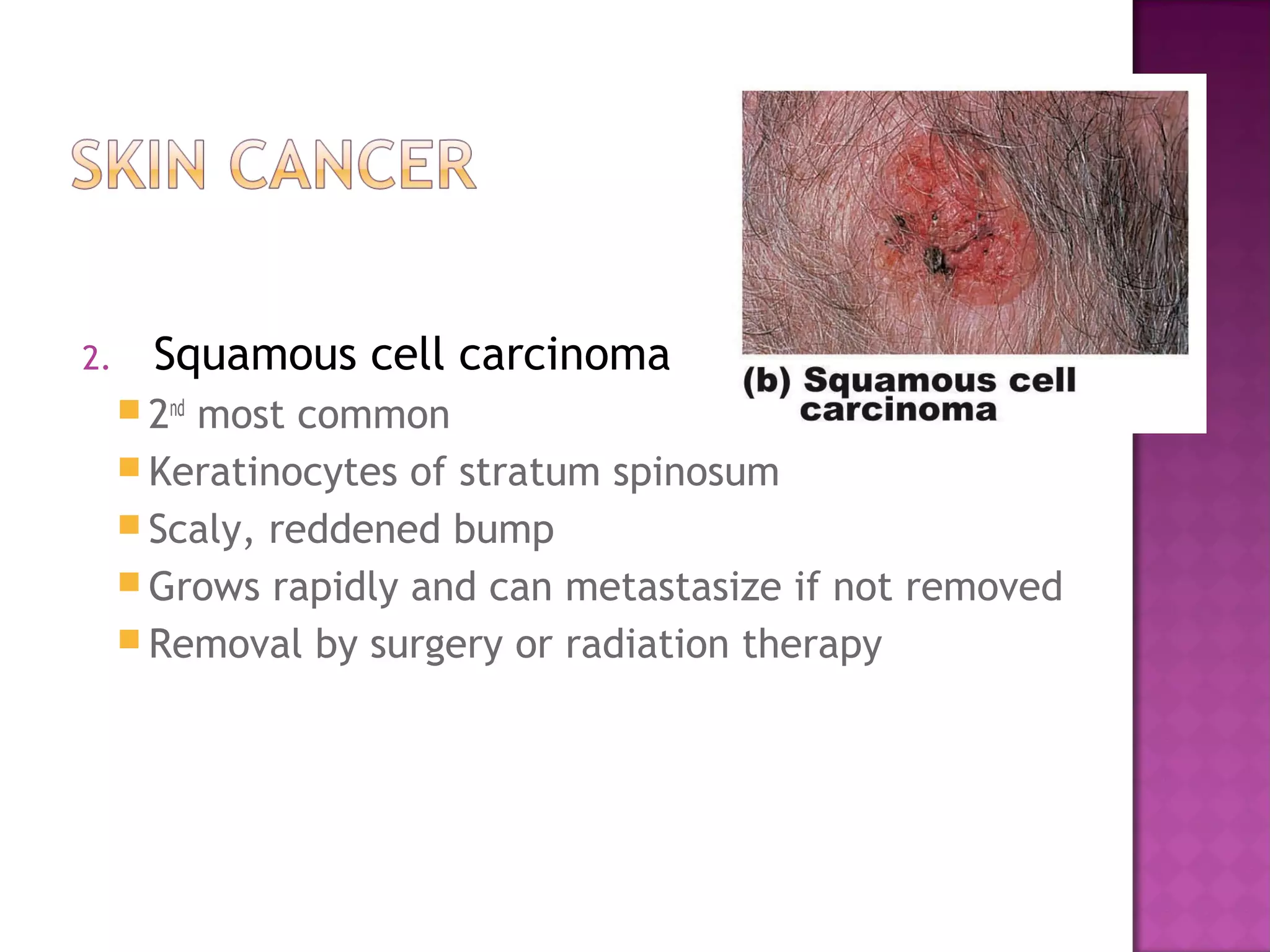
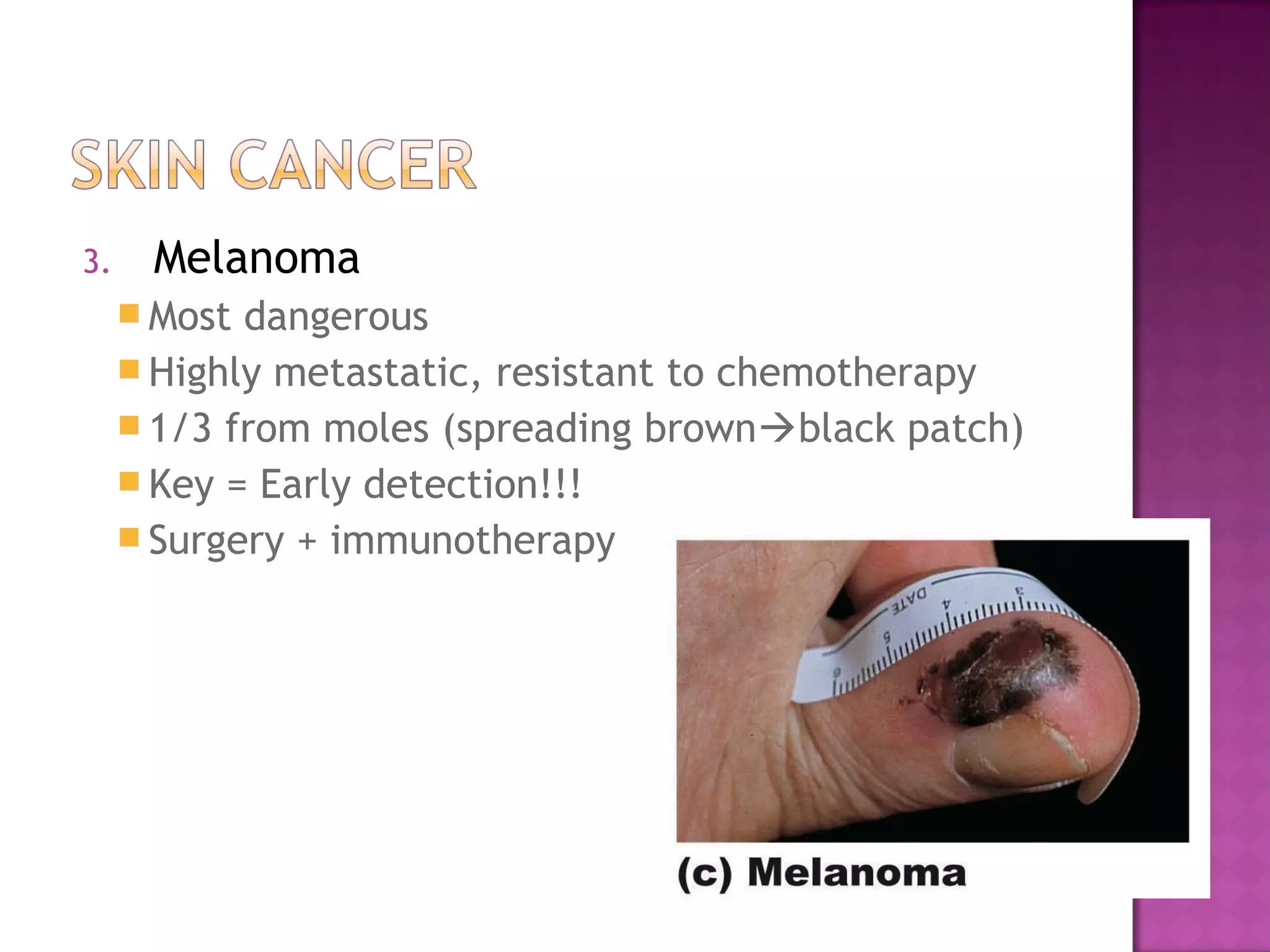
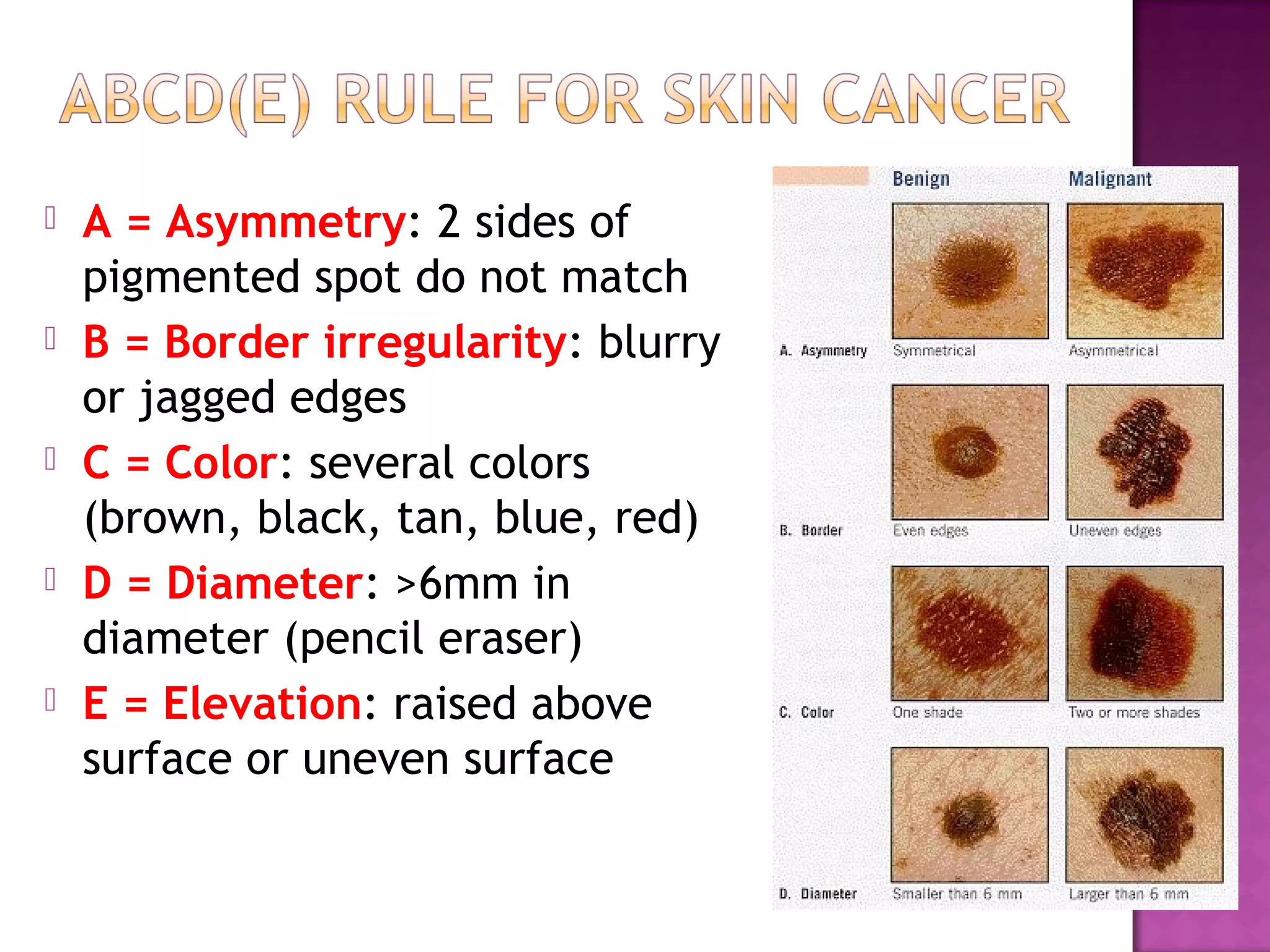
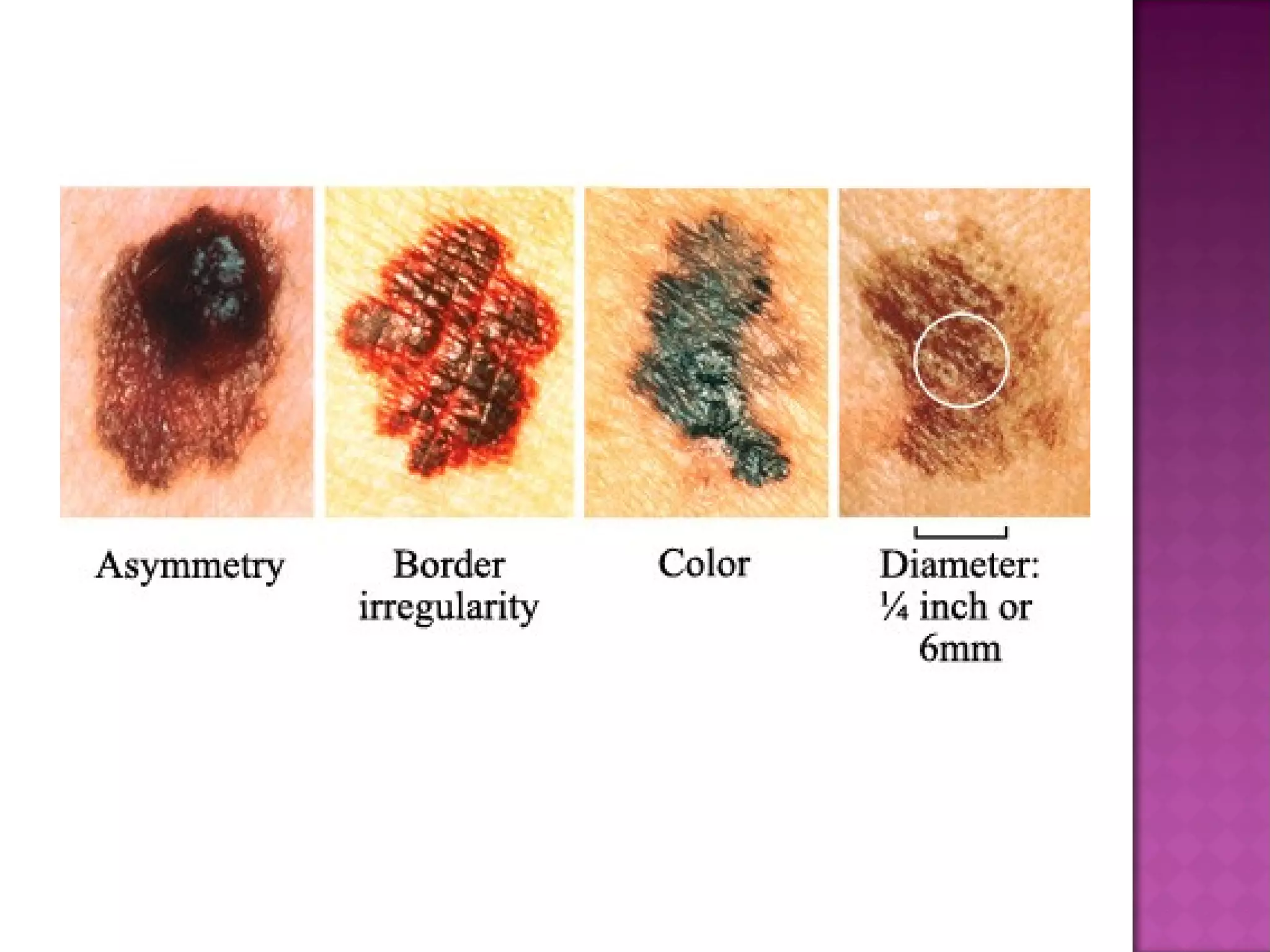
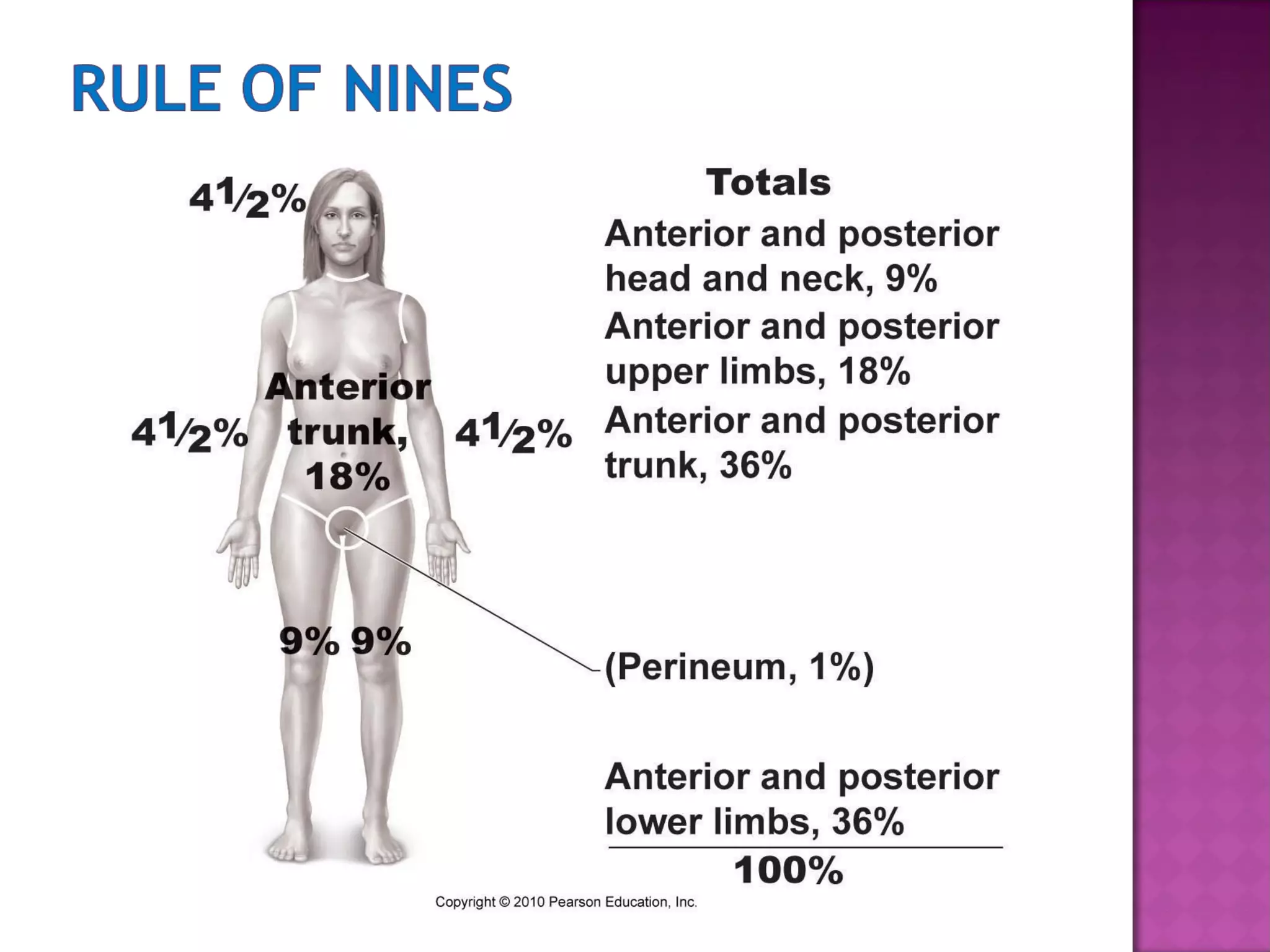
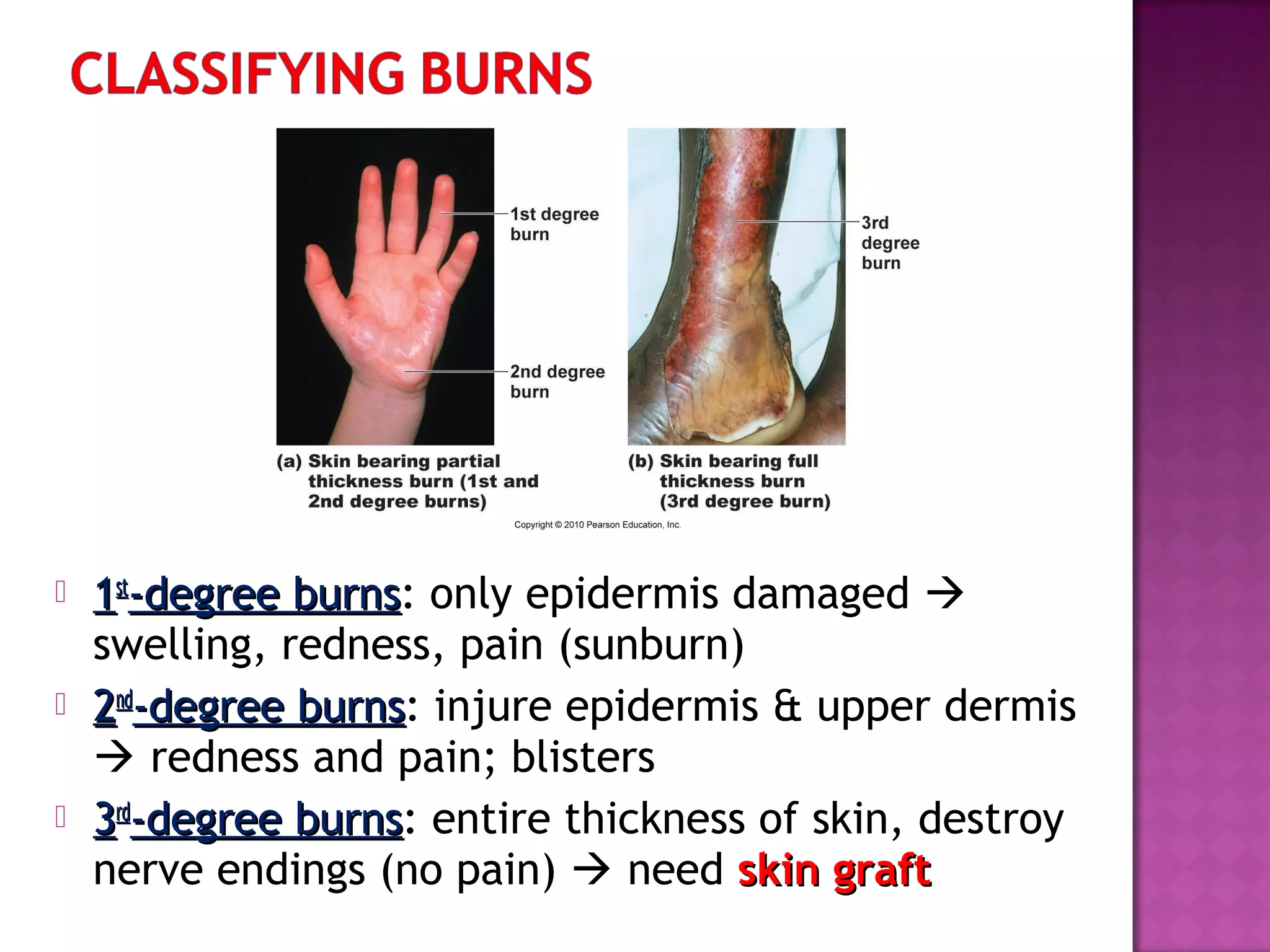
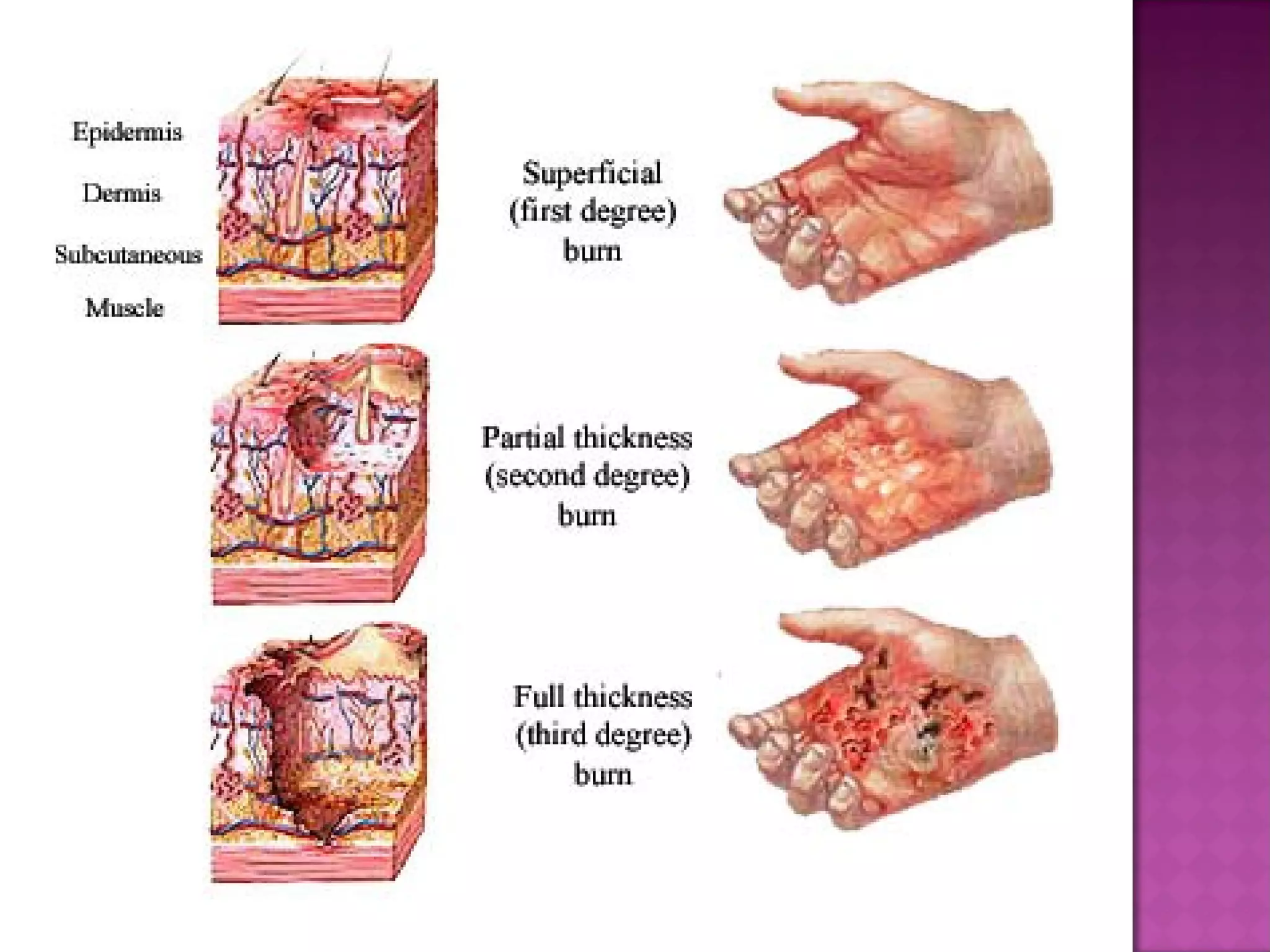
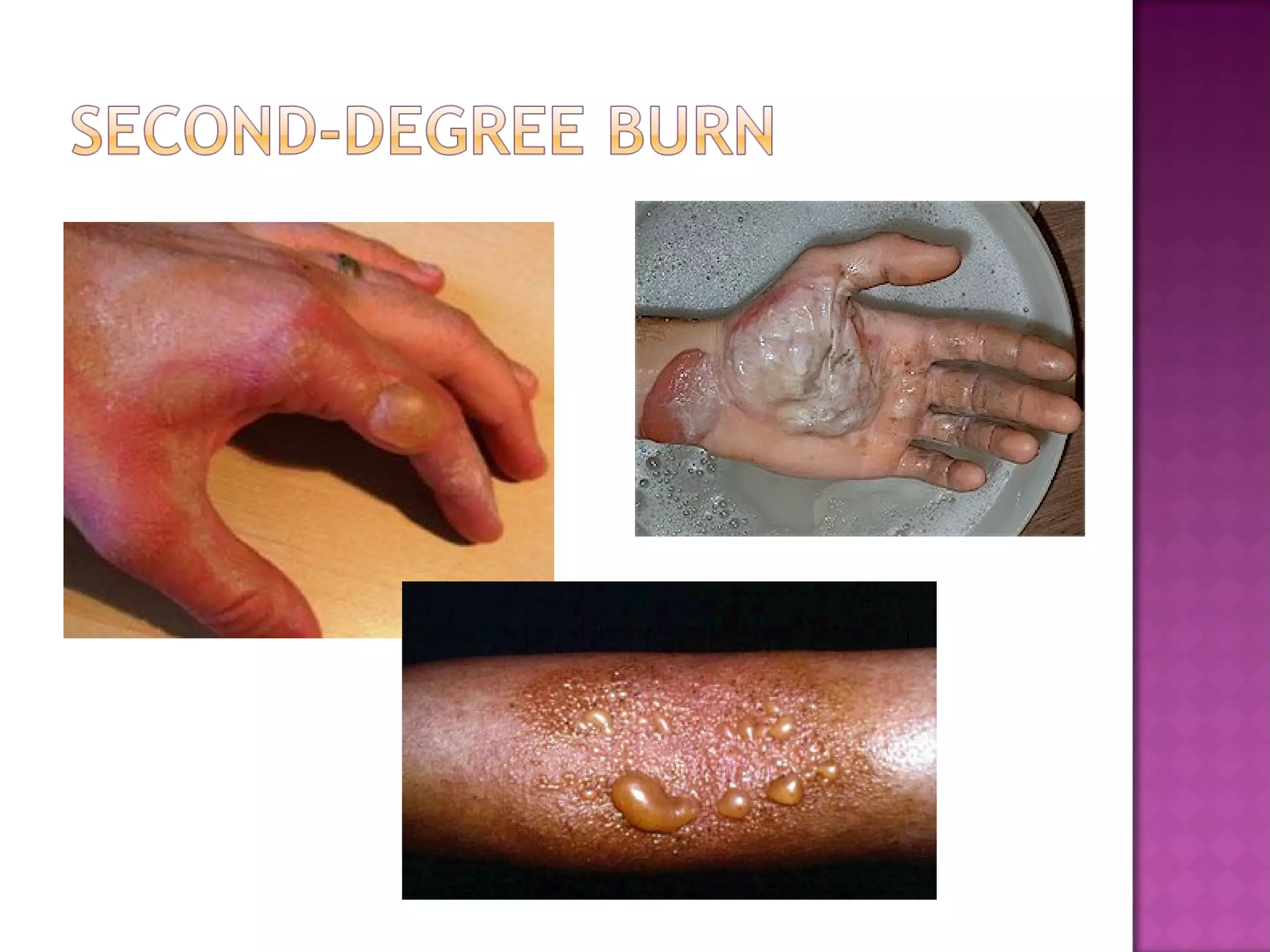
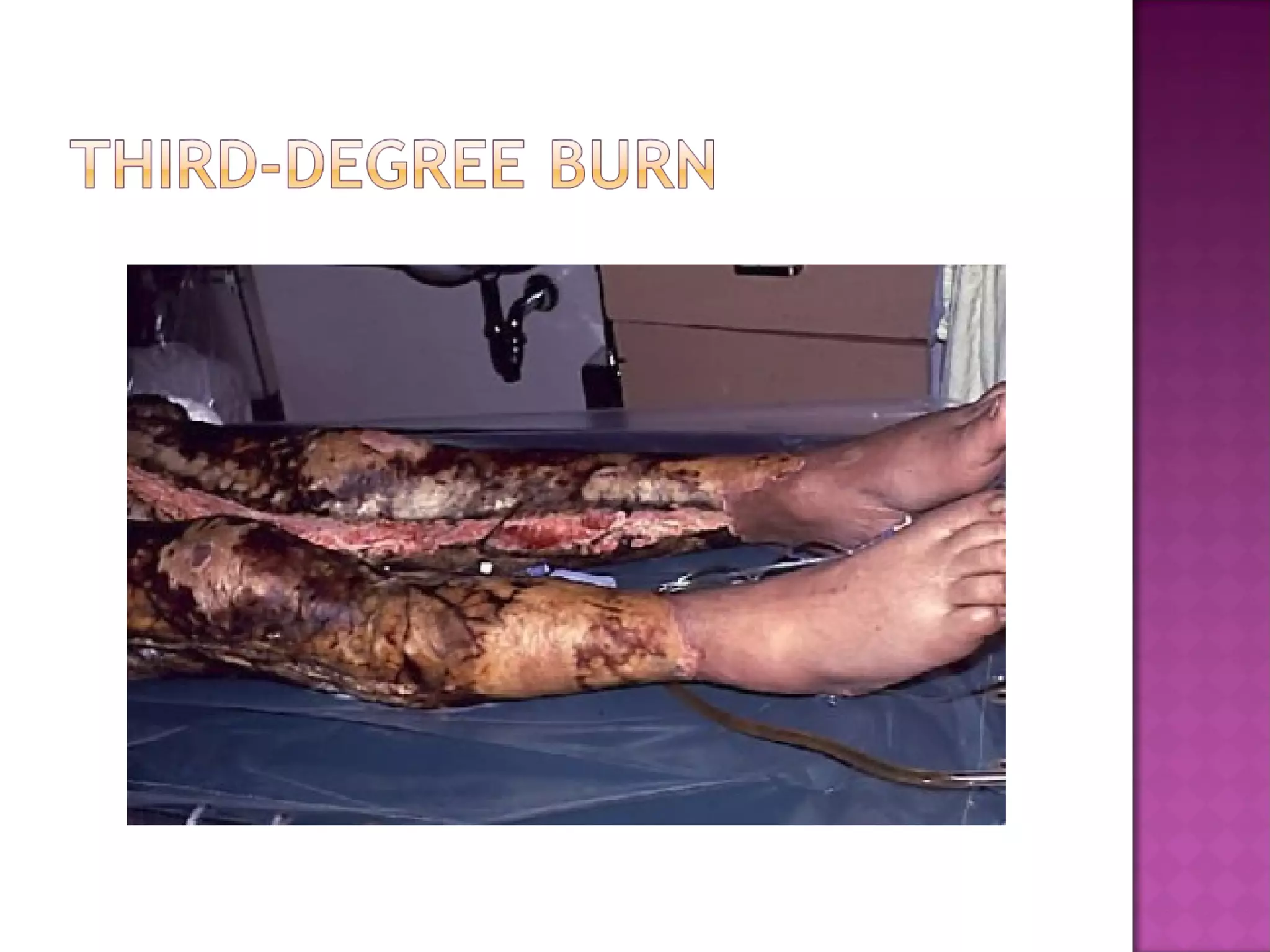
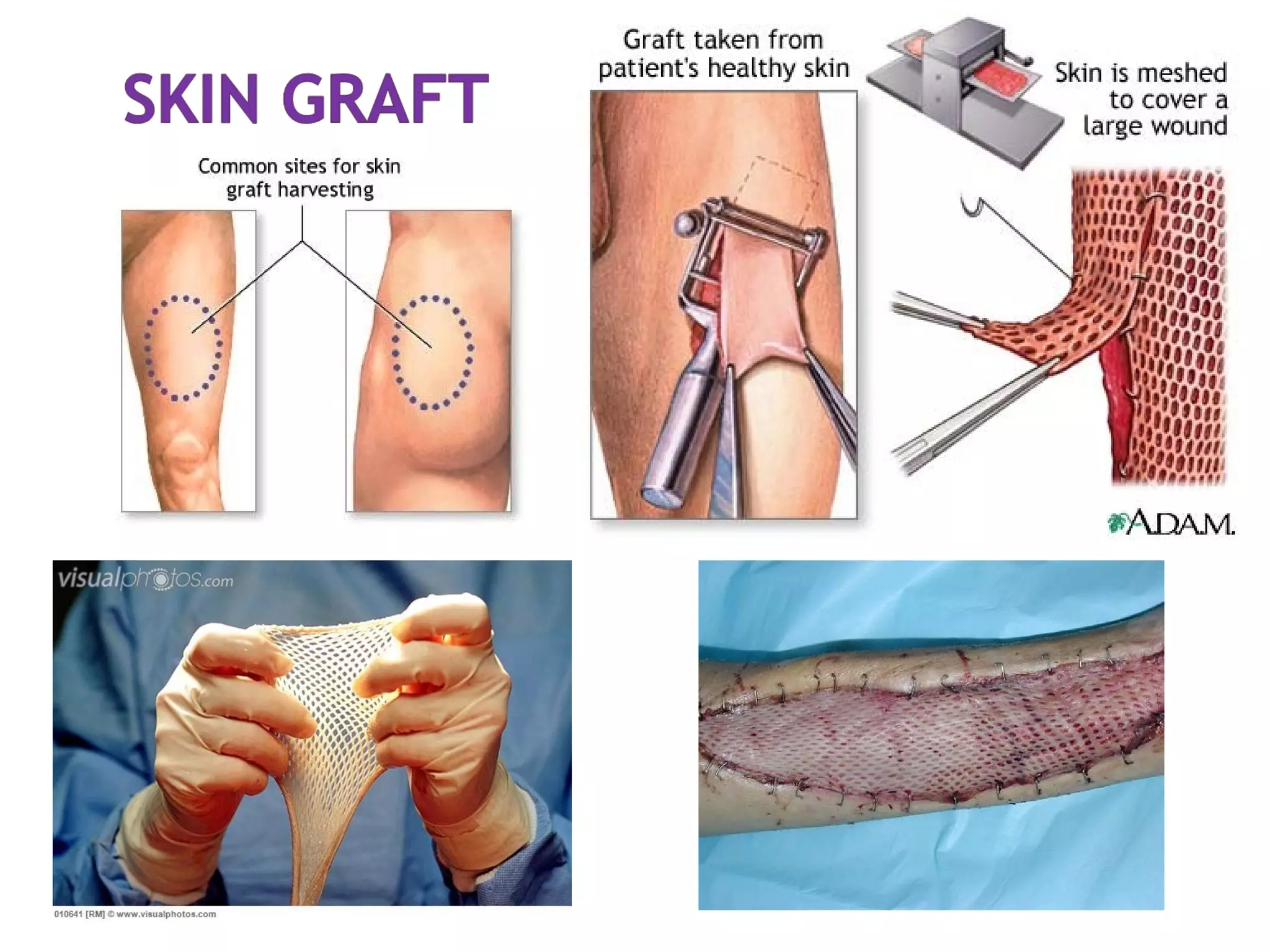
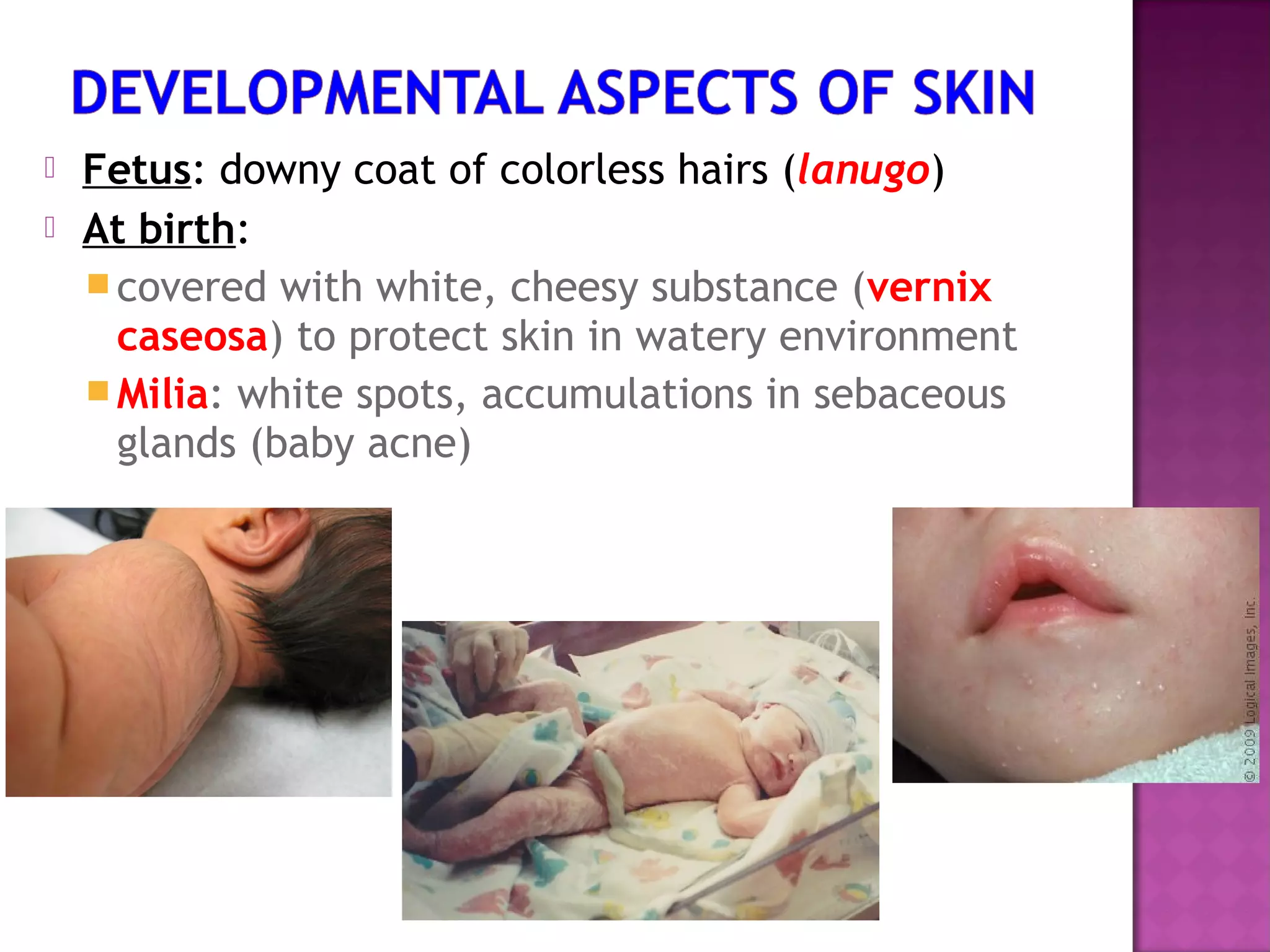
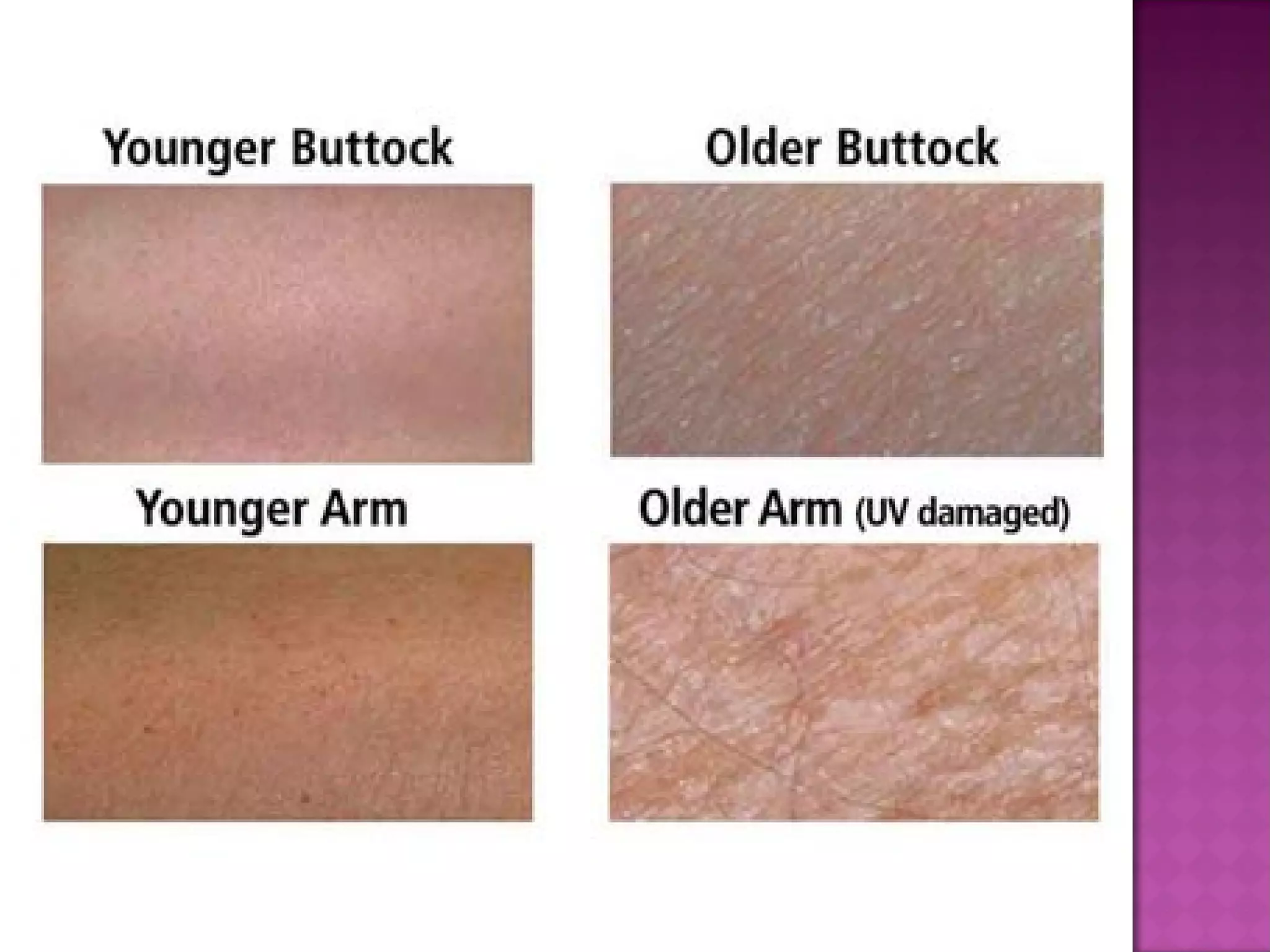
The document discusses different types of skin cancers affecting 1 in 5 Americans, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, detailing their characteristics and treatment methods. It also outlines the dangers of burns, including types and their effects on the body, and provides insight into skin development from infancy to old age. Key factors for recognizing melanoma include asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter, and elevation.