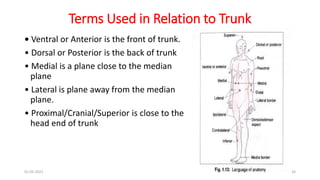
The document presents a detailed overview of medical terminology related to anatomy, including definitions, positions of the body, and terms related to movements of various body parts. It covers different anatomical approaches, anatomical planes, and axes, along with descriptions of body positions and common movements. Additionally, it includes clinical terminology, example questions, and references for further reading.