This document discusses connective tissues (CT), including their definition, characteristics, components, cells, fibers, ground substance, classification, and examples. It aims to describe CT characteristics and components, classify different CT types, and correlate CT type with function. Key points include:
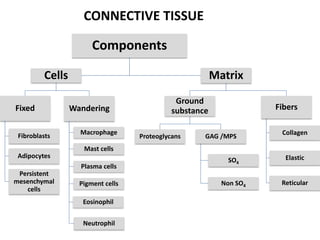
- CT connect and bind other tissues, with a predominantly extracellular matrix containing widely spaced cells, few blood vessels, and classification based on matrix, cells, and fibers.
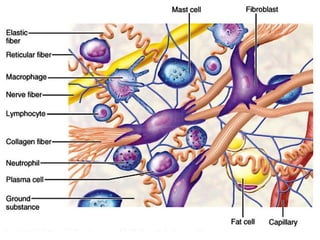
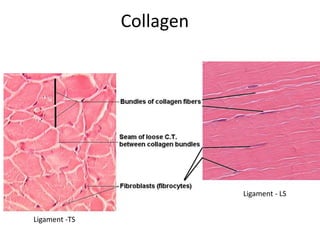
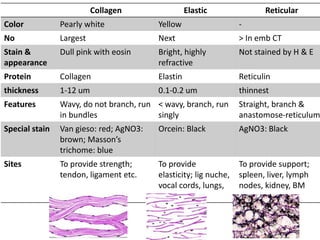
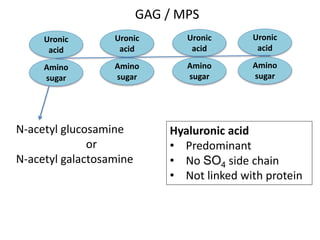
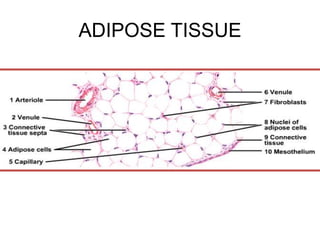
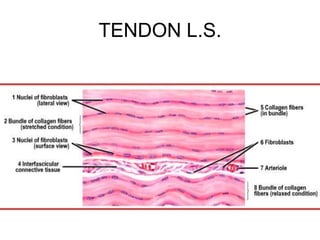
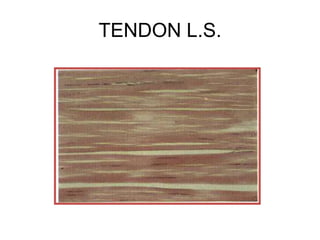
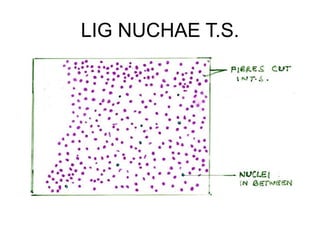
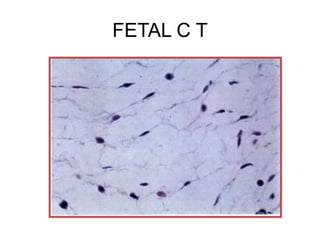
- Components include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells, plasma cells, pigment cells, collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers suspended in a ground substance of proteoglycans.
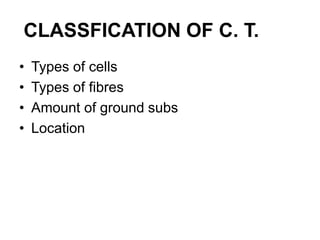
- CT are classified based on cell and fiber types as well as ground