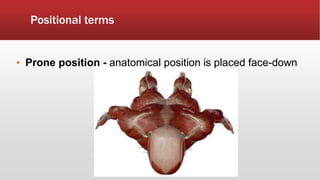
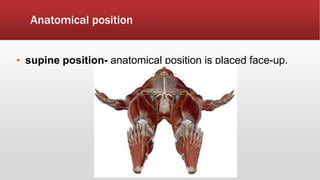
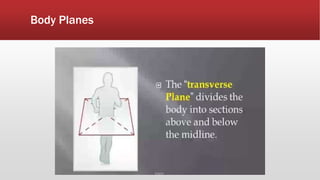
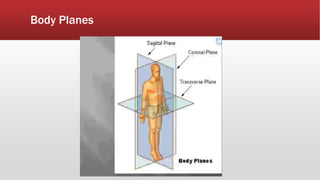
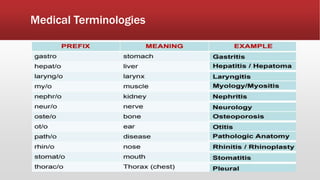
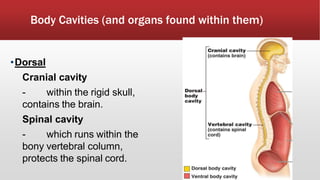
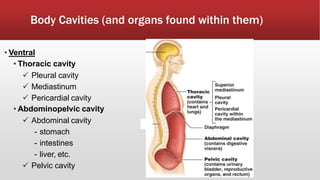
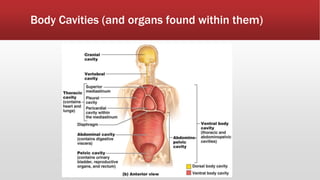
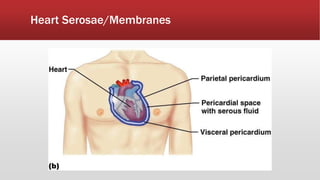
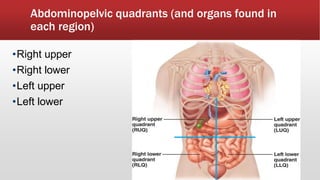
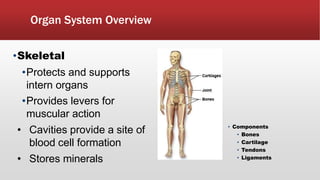
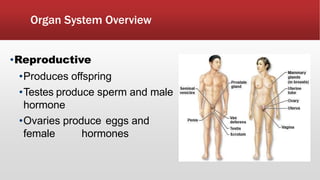
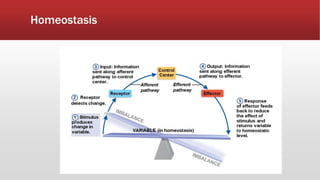
The document provides an overview of human anatomy and physiology. It discusses the main body systems including integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive. It covers anatomical terminology including positional, regional, and directional terms. It also describes the levels of structural organization from cells to organ systems. Additionally, it discusses homeostasis and how the body maintains stable internal conditions through feedback mechanisms.