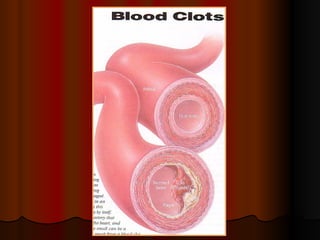
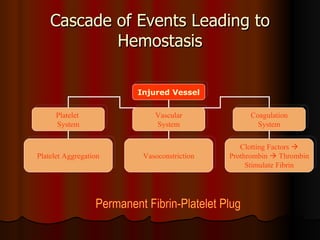
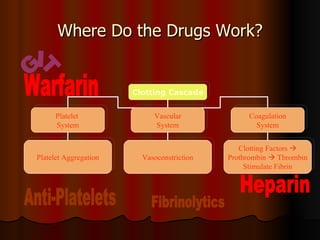
The document discusses various agents used to treat coagulation disorders and bleeding risks. It outlines the blood coagulation mechanism and lists common risk factors for blood clots. It then describes different classes of drugs that work at different points in the coagulation cascade, including anticoagulants like heparin and warfarin that prevent clotting, fibrinolytics that break up existing clots, and antiplatelets that reduce platelet aggregation. It also discusses drugs used for bleeding disorders and important drug interactions.