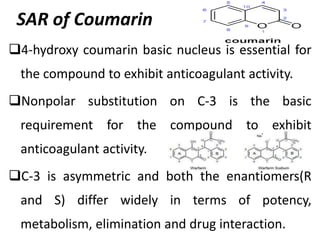
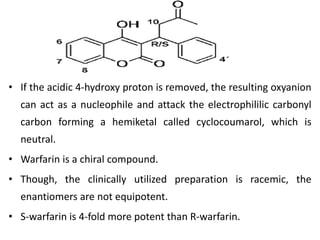
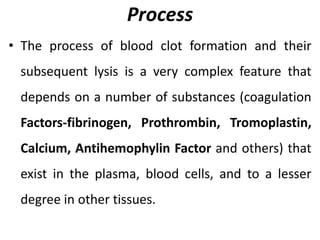
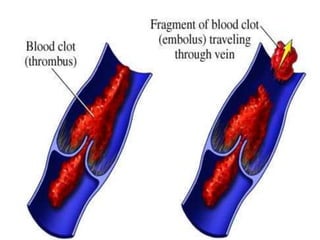
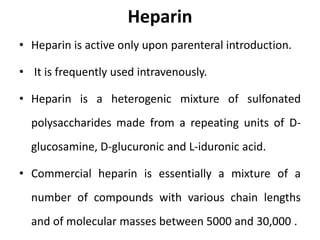
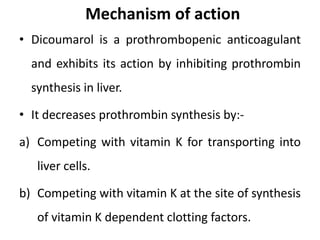
Direct-acting anticoagulants like heparin work directly in the blood to inhibit coagulation factors. Heparin is extracted from pig intestines and bovine lungs. Indirect anticoagulants called oral anticoagulants or vitamin K antagonists inhibit coagulation factor synthesis in the liver. Coumarin derivatives like warfarin and dicoumarol are commonly used oral anticoagulants that act by inhibiting vitamin K and decreasing prothrombin synthesis. Warfarin is effective for treating deep vein thrombosis while dicoumarol has fallen out of favor due to side effects and unpredictable response. Anticoagulants must be closely monitored to prevent bleeding complications.















































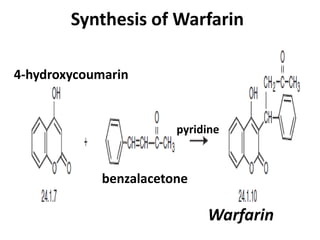
![Synthesis of Warfarin
• Warfarin
• 3-(α-acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin
(24.1.10), is synthesized via Michael reaction
by attaching 4-hydroxycoumarin (24.1.7) to
benzalacetone in the presence of pyridine
[14–19].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anticoagulentsfinalppt-230614103650-ccd0c91c/85/Anticoagulents-Final-ppt-pptx-57-320.jpg)