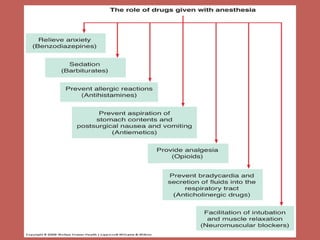
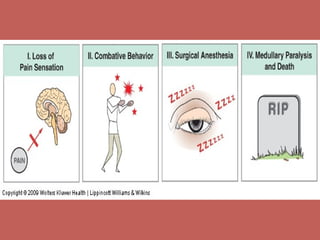
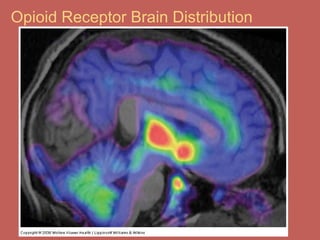
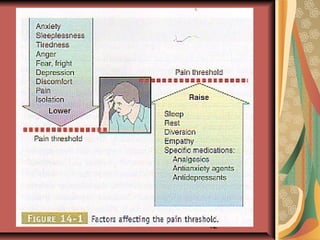
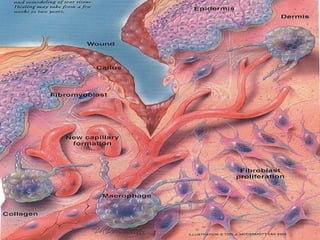
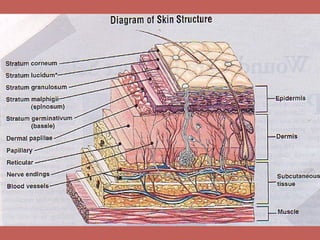
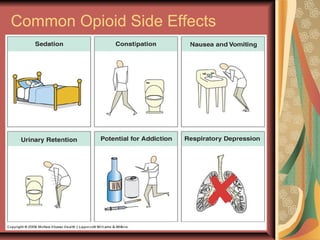
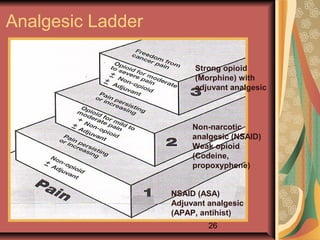
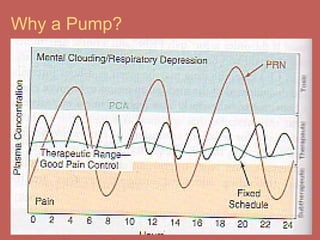
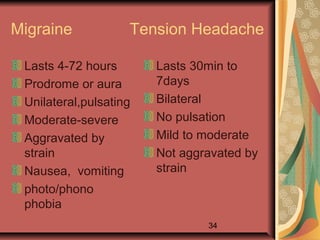
This document discusses pain management and anesthetics. It covers topics like general anesthesia, local anesthetics, opioids, non-opioid pain relievers, and the treatment of migraines. It also examines non-drug pain management techniques and provides an overview of headache classification and therapeutic agents for treatment.