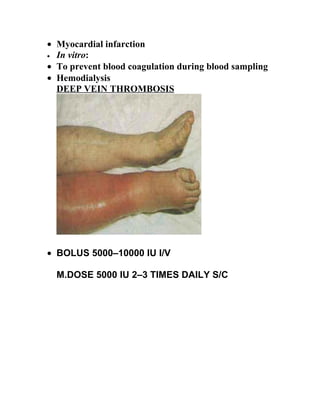
- The document discusses anticoagulation and blood clotting. It describes how blood clots form and are broken down, as well as drugs that can regulate clotting such as heparin, warfarin, and dicoumarol. It provides details on the coagulation factors, classes of anticoagulant drugs, the blood clotting process, and coagulation disorders.