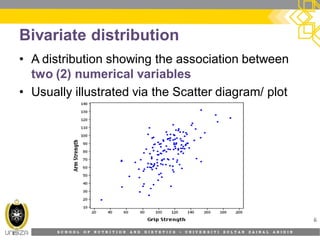
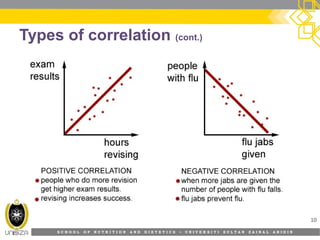
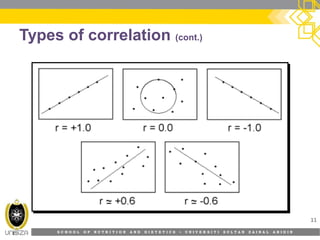
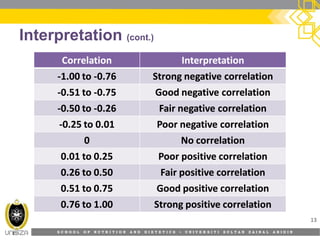
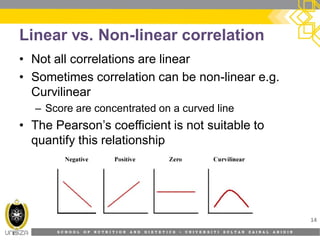
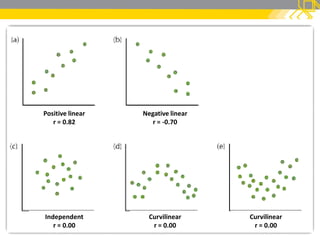
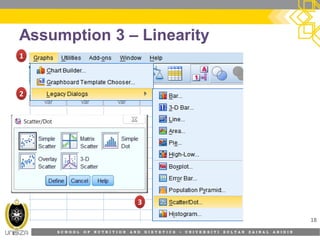
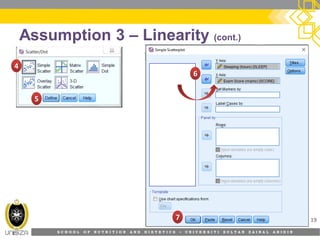
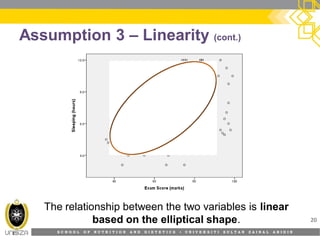
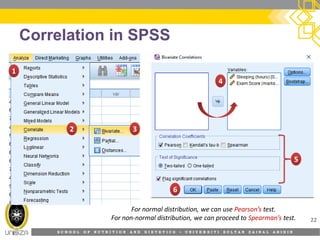
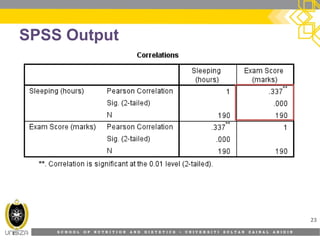
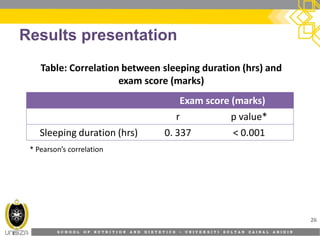
This document discusses correlation analysis and its use in SPSS. It defines correlation as a measurement of the relationship between two variables. Pearson's r and Spearman's rho correlations are described, along with their assumptions and interpretations. The document provides examples of positive, negative, and no correlation. It also demonstrates how to conduct and interpret correlation analysis in SPSS, including checking assumptions and presenting results. The goal is for students to understand different types of correlation and how to perform correlations in SPSS.