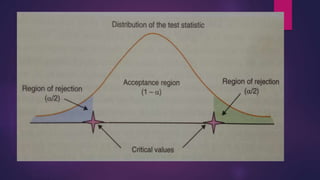
This document discusses the Z-test, a statistical test used to compare means and proportions. The Z-test can be used to test if a sample mean differs from a population mean, if two sample means are equal, or if two population proportions are equal. It assumes the population is normally distributed. The steps involve formulating hypotheses, choosing a significance level, calculating the Z-statistic, and comparing it to a critical value to determine if the null hypothesis should be rejected or accepted. The Z-test is useful when sample sizes are large but requires knowing the population standard deviation.