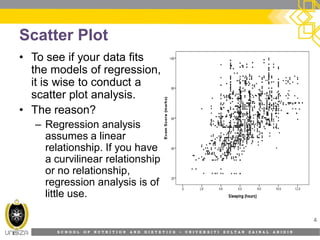
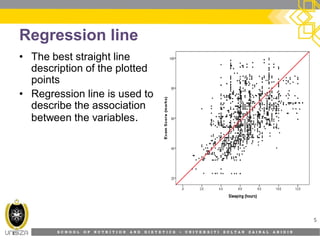
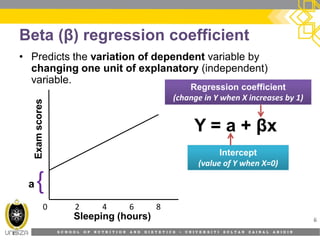
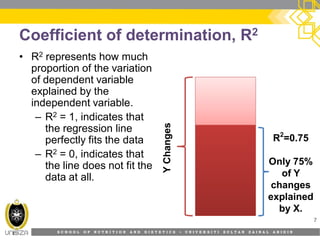
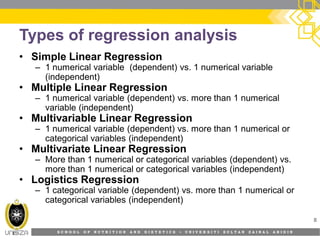
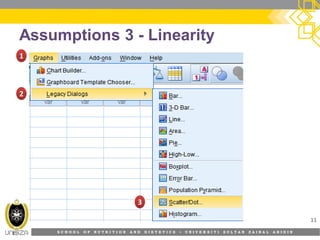
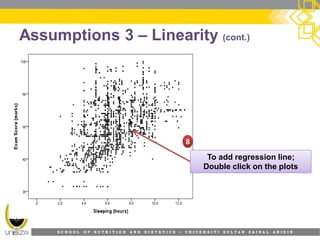
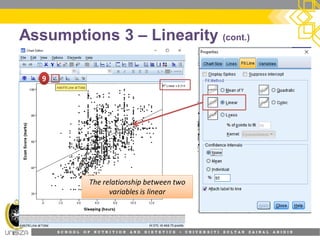
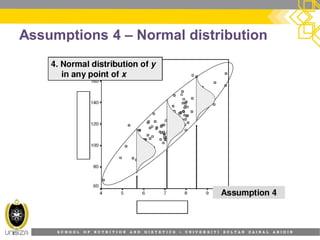
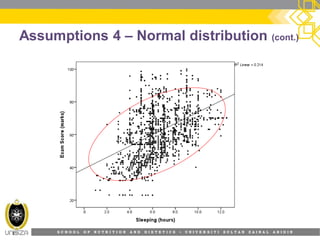
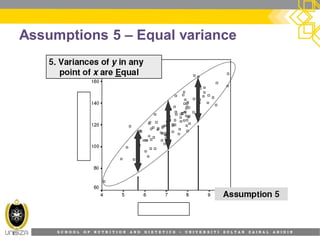
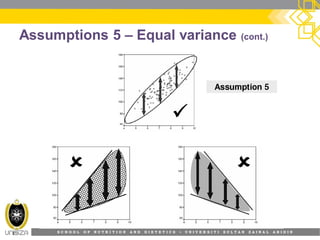
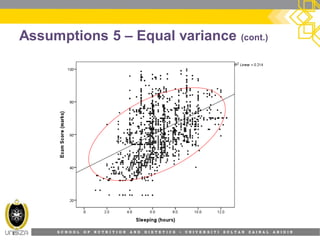
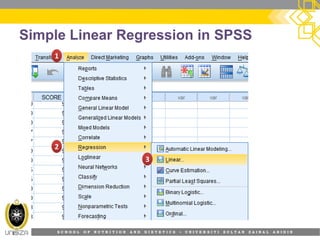
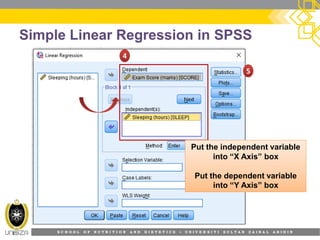
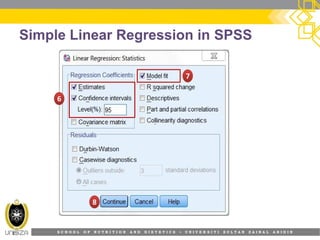
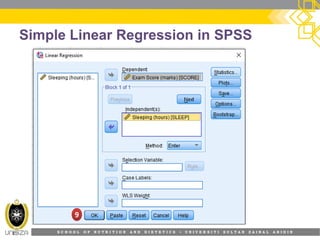
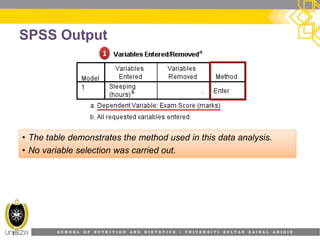
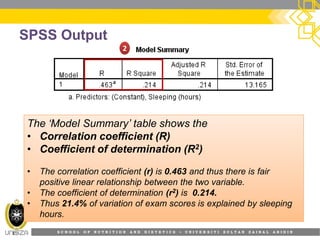
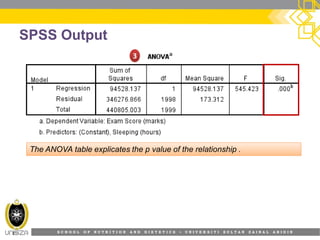
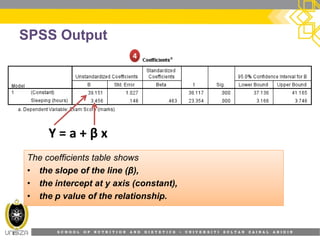
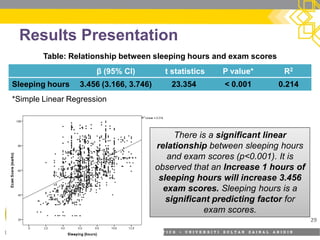
This document provides an overview of simple linear regression analysis. It discusses key topics like the regression line, coefficient of determination, assumptions of linear regression, and how to perform and interpret a simple linear regression in SPSS. The learning outcomes are to identify regression types, explain assumptions, perform regression in SPSS, and interpret the outputs. An example analyzing the relationship between sleeping hours and exam scores is used to demonstrate these concepts.