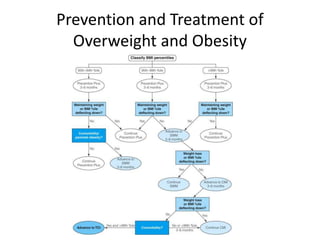
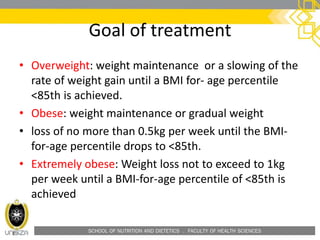
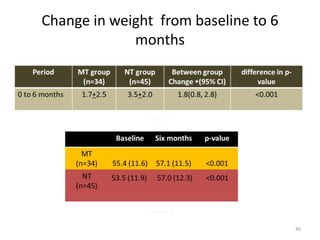
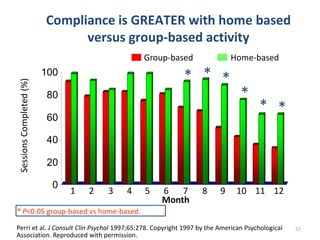
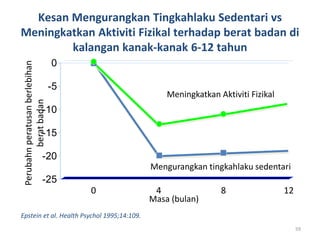
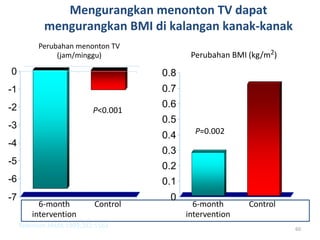
This document outlines a lecture on child and preadolescent nutrition. It discusses normal growth and development in children, including adiposity rebound. It also covers energy and nutrient needs, common nutrition problems like iron deficiency and dental caries, and childhood obesity including predictors, assessment, and treatment approaches. The goal of obesity treatment is weight maintenance or gradual weight loss until a healthy BMI is achieved.