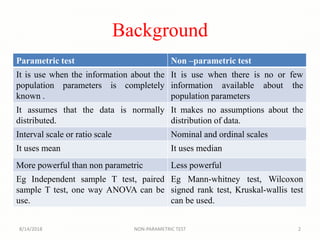
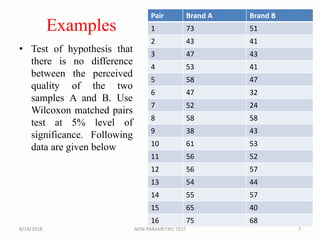
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric statistical hypothesis test used to compare two related samples or repeated measurements to determine if their population mean ranks differ, serving as an alternative to the paired t-test when normal distribution cannot be assumed. It requires paired data from the same population and assesses the significance of differences in ranks. The document also includes guidelines for conducting the test and examples illustrating its application.





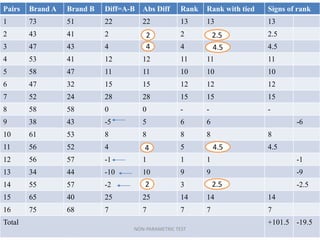
![ Since in pair number 8 there is no significant difference
between A and B brand so total sample number is
reduced to 15.
Total W-= [-19.5]= 19.5
Total W+= [+101.5]= 101.5
Since calculated value 19.5 is less than tabled value
(25) of W at 5% level of significance. Hence, we reject
the null hypothesis and concluded that there is
difference between the perceived quality of the two
samples.
8/14/2018 10NON-PARAMETRIC TEST](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wilcoxonsignedranktest-180814084835/85/Wilcoxon-signed-rank-test-10-320.jpg)
