1. The document discusses transmission line theory and parameters. Key topics covered include:
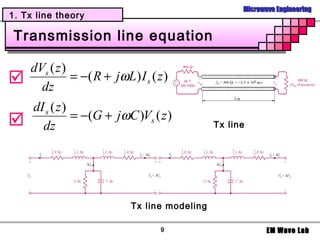
- Telegrapher's equation and circuit model for transmission lines
- Wave propagation and characteristic impedance calculations
- Reflection coefficient and standing wave ratio definitions
- Comparisons of transmission line, circuit, and field theories
2. Specific transmission line types are analyzed, including planar lines, coaxial cables. Equations are given for calculating the capacitance, conductance, inductance, resistance, and characteristic impedance of these common line configurations.
3. Simulation and modeling techniques for transmission lines are briefly mentioned, such as the transmission line matrix method for modeling microstrip lines in antennas and circuits.




![Microwave Engineering
1. Tx line theory
Circuit model
ˆ
Propagation in the a z direction
Length ∆z : R∆z[ Ω], L∆z[ H ], G∆z[1 / Ω], C∆z[ F ]
lim: infinitesimal approach
∆z →0
7 EM Wave Lab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-transmissionline-120810003450-phpapp01/85/Transmission-Line-7-320.jpg)



















![Microwave Engineering
2. Tx line parameters
Coaxial line
ρL
∫S D • dS = Q 2πρLD = ρ L L D = 2πρ a ρ
ρL
E= aρ
2πε ' ρ
a ρL ρ ρ b
Vo = − ∫
a
dρ = − L ln ρ b = L ln
b 2πε ' ρ 2πε ' 2πε ' a
Cross section
2πε
C= [ F/m]
ln(b / a )
Coaxial line + connector
28 EM Wave Lab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-transmissionline-120810003450-phpapp01/85/Transmission-Line-28-320.jpg)
![Microwave Engineering
2. Tx line parameters
Coaxial line
ε C ε σ 2πσ
RC = , = , G = C ⇒ G = [1 / Ωm]
σ G σ ε ln(b / a)
µId b µ b
Φ= ln , Lext = ln [ H / m]
2π a 2π a
1 1 1 1 1
Rinner = , Router = ⇒R= + [ Ω / m]
2πaδσ c 2πbδσ c 2πδσ c a b
The characteristic impedance of a coax
Lext 1 µ b
Z0 = = ln
C 2π ε a
29 EM Wave Lab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-transmissionline-120810003450-phpapp01/85/Transmission-Line-29-320.jpg)