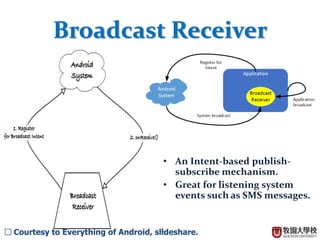
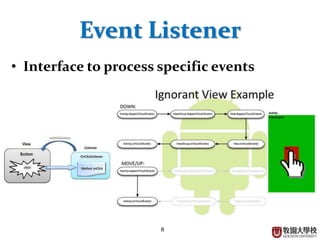
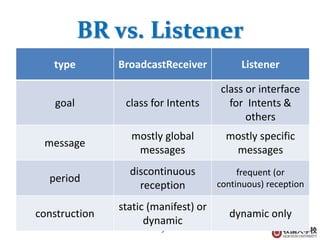
This document discusses BroadcastReceivers in Android. A BroadcastReceiver is an intent-based publish-subscribe system that allows apps to receive system events like SMS messages. BroadcastReceivers can receive and react to system broadcasts, broadcasts from other apps, and initiate broadcasts to other apps. They are registered either dynamically in code or statically in the AndroidManifest.xml file. Broadcasts are sent using the sendBroadcast or sendOrderedBroadcast methods and an Intent. Ordered broadcasts are executed in a defined order while normal broadcasts run asynchronously. The BroadcastReceiver object is only valid during the onReceive method call.
![Android –
BroadcastReceiver
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] Everything of Android, slideshare.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-200205024846/75/Android-Broadcast-Receiver-1-2048.jpg)