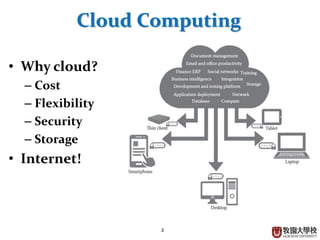
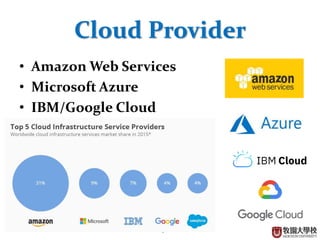
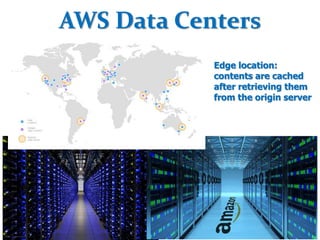
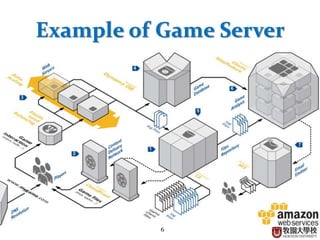
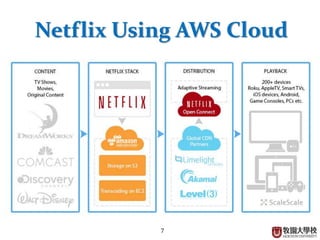
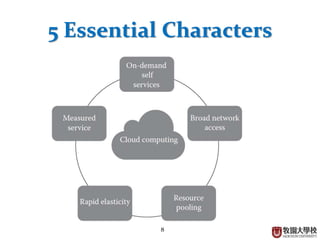
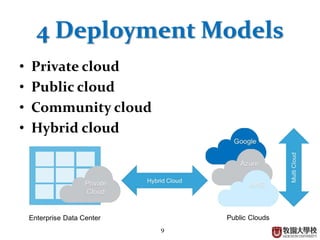
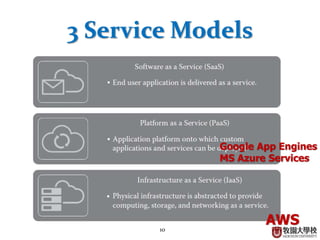
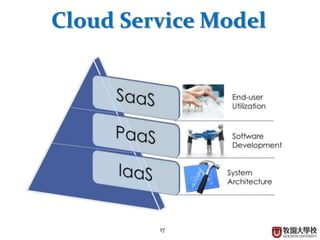
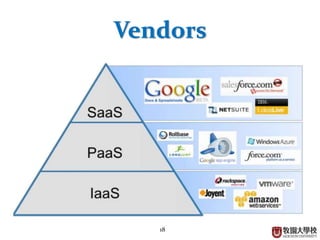
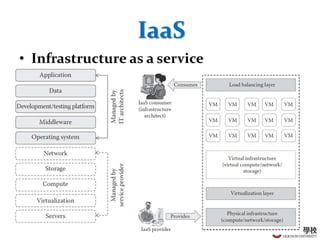
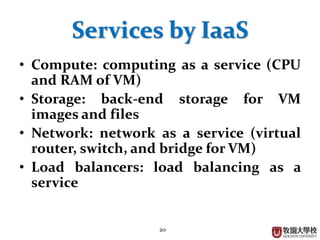
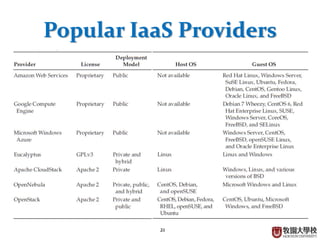
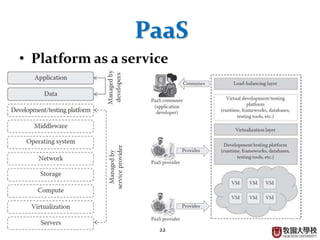
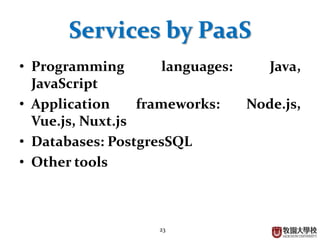
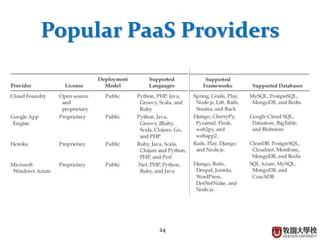
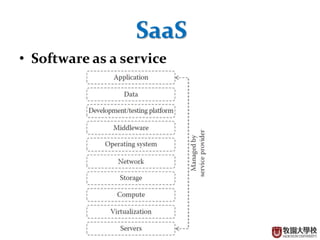
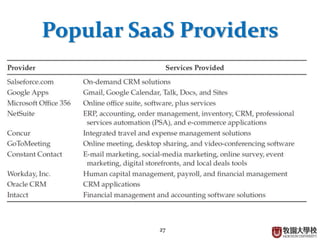
This document provides an overview of cloud computing fundamentals. It defines cloud computing as on-demand access to configurable computing resources over the internet. The document discusses key cloud concepts like deployment models (private, public, hybrid, community clouds), service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), and requirements for cloud services. Popular cloud providers like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud are presented for each service model. Benefits of cloud computing are also highlighted such as reduced costs, flexibility, and global access to resources.
![Cloud Computing
Fundamentals
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to and all credits should go to:
[1] K. Chandrasekaran, Essentials of Cloud Conputing, CRC Press, 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-200205024758/75/Cloud-Computing-1-2048.jpg)