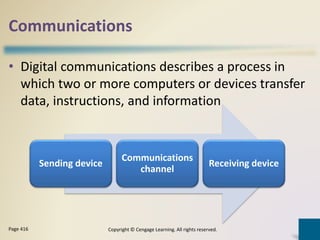
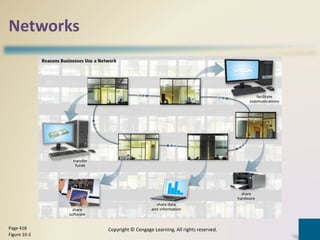
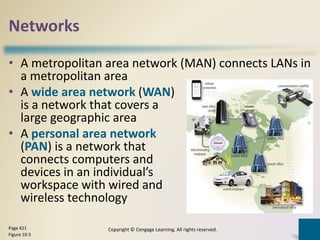
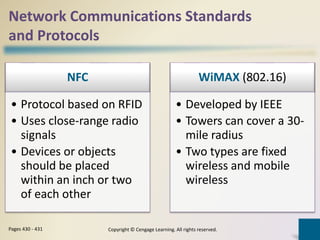
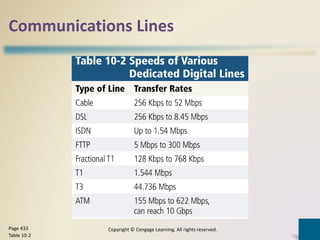
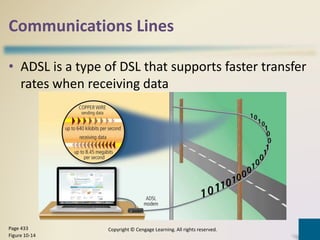
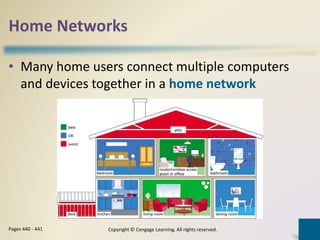
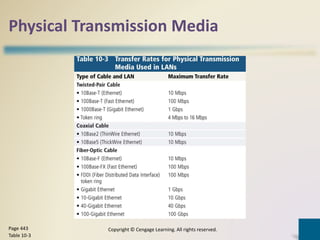
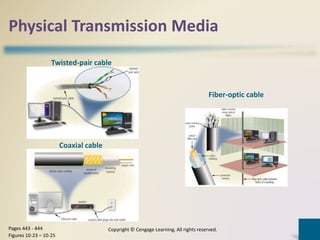
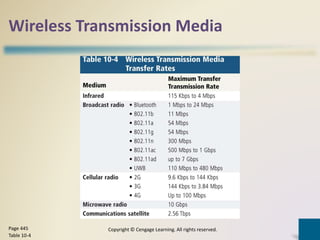
Digital communications involves the transfer of data between sending and receiving devices via communications channels. Networks connect computers and devices together, providing advantages like facilitating communications, sharing resources, and transferring information. The chapter describes various network types including LANs, WANs, MANs, and PANs, as well as different network architectures, topologies, standards, protocols, communications software, lines, devices, transmission media, and how to set up a home network.