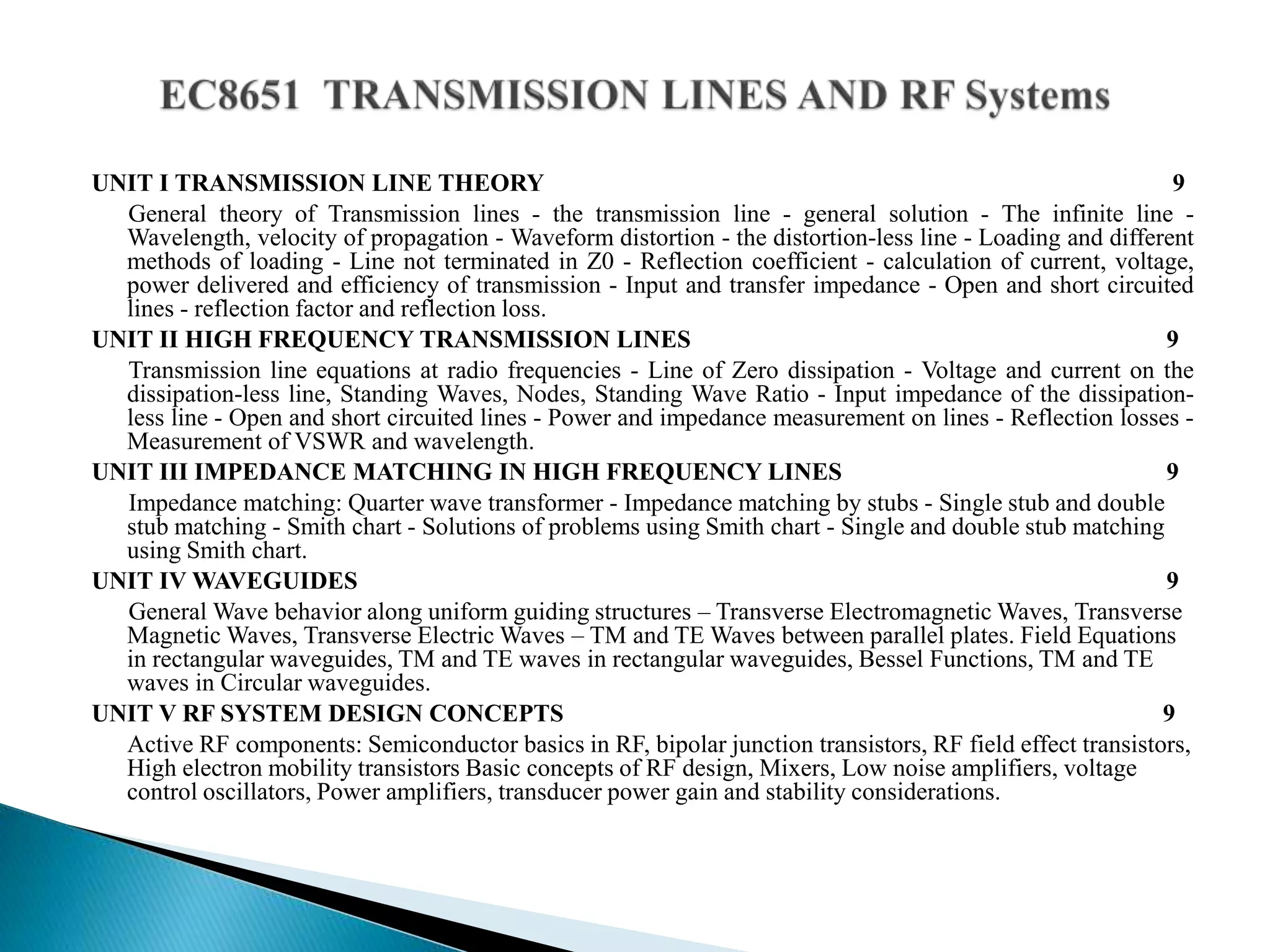
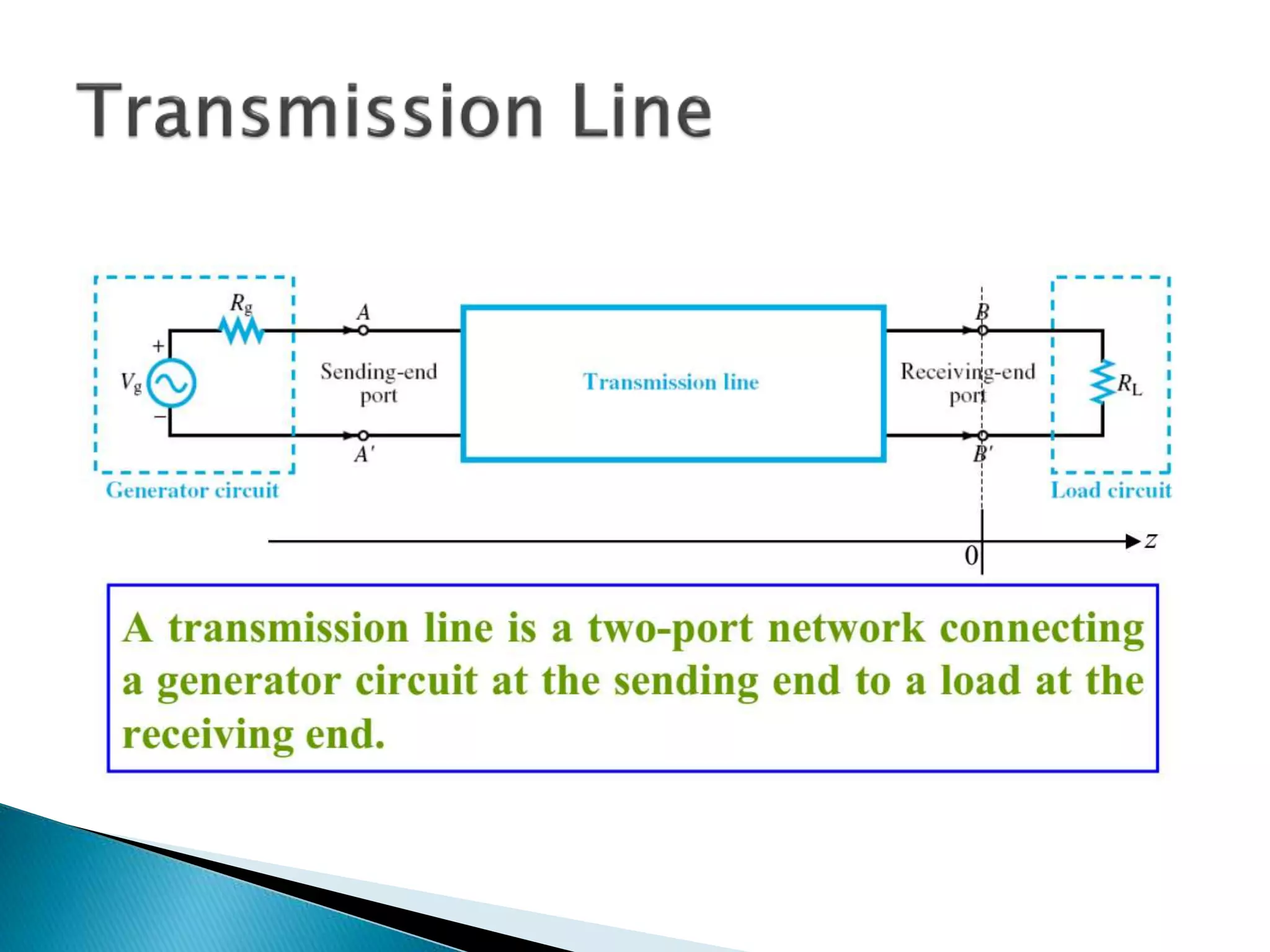
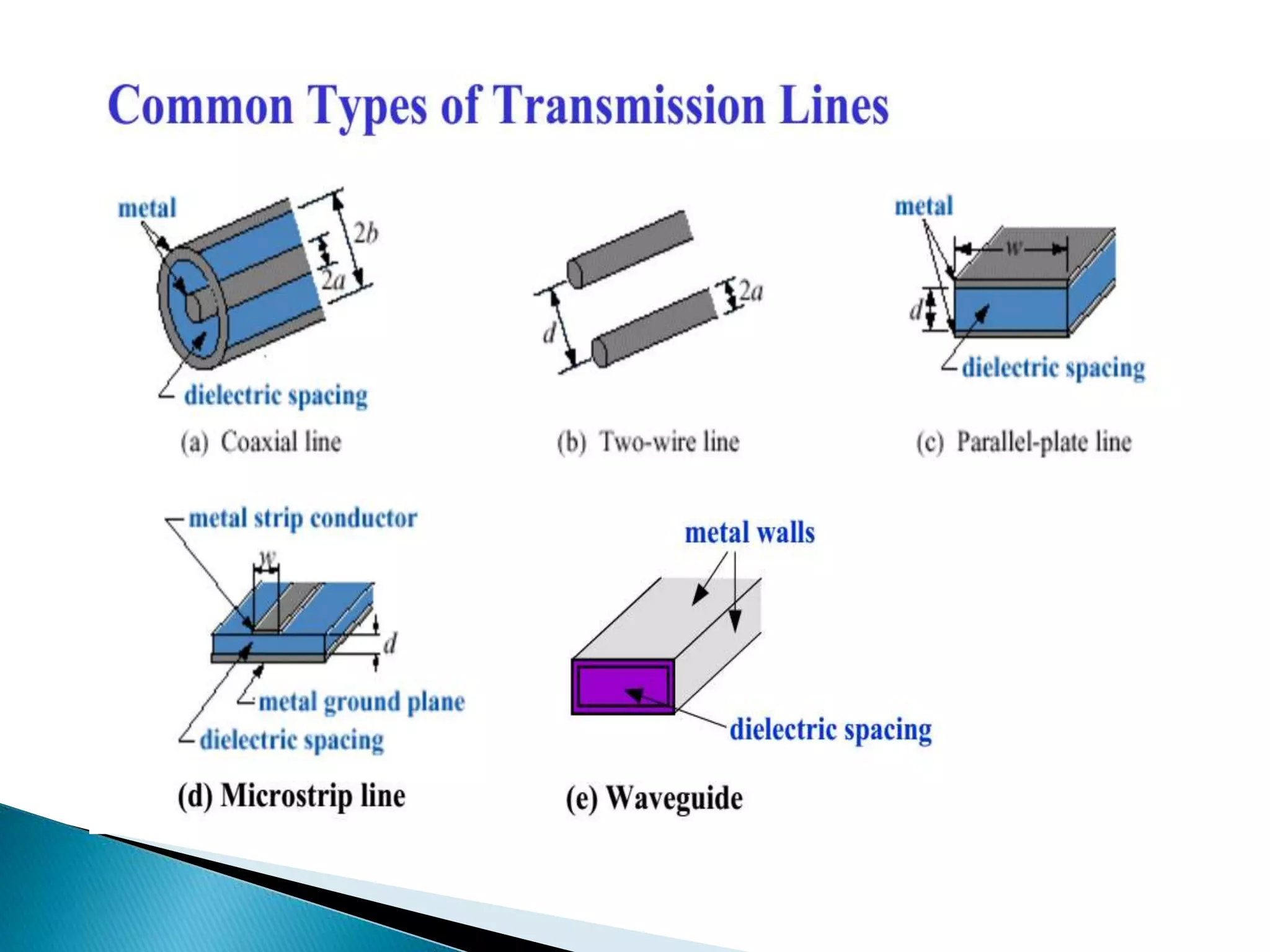
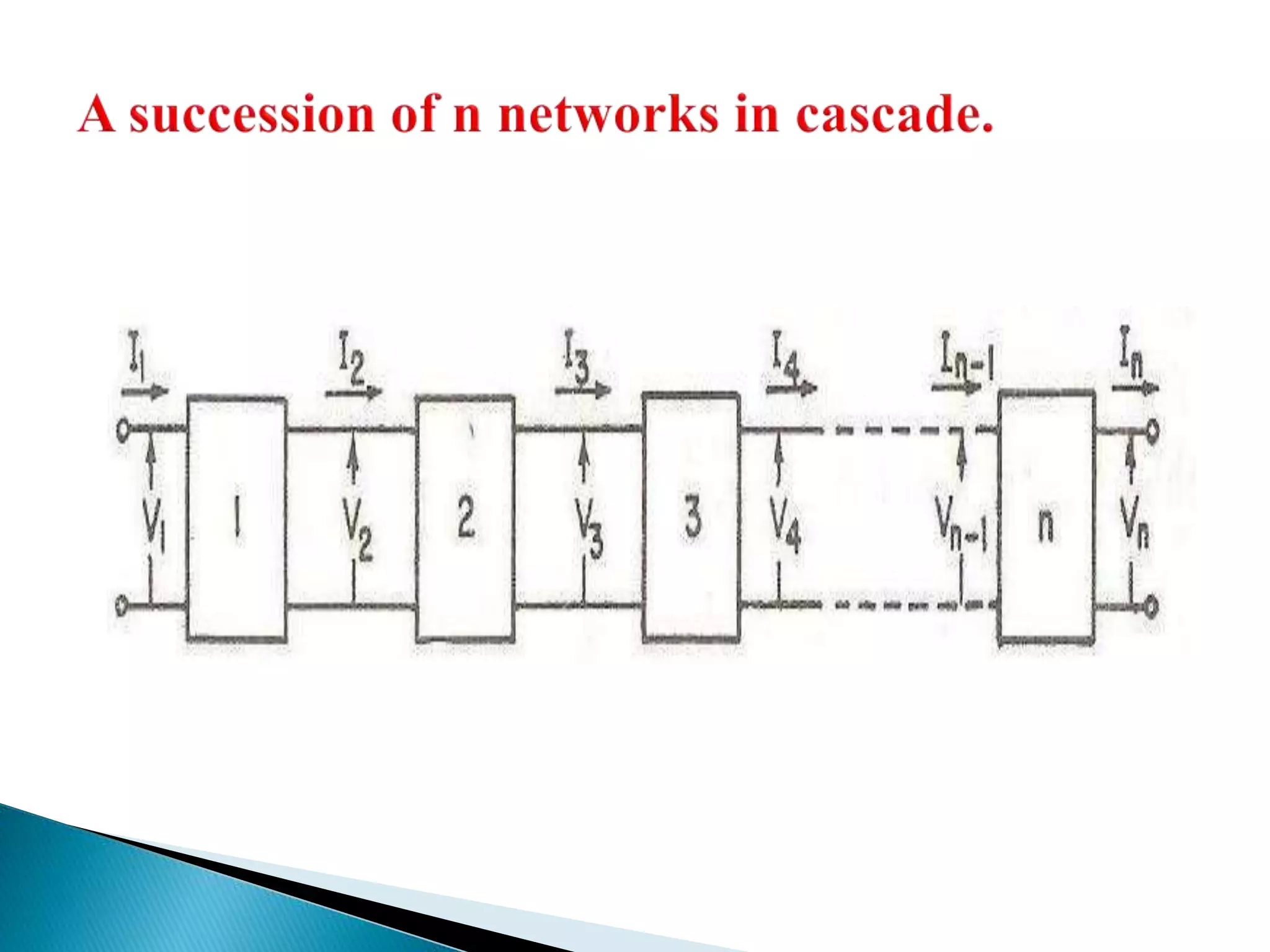
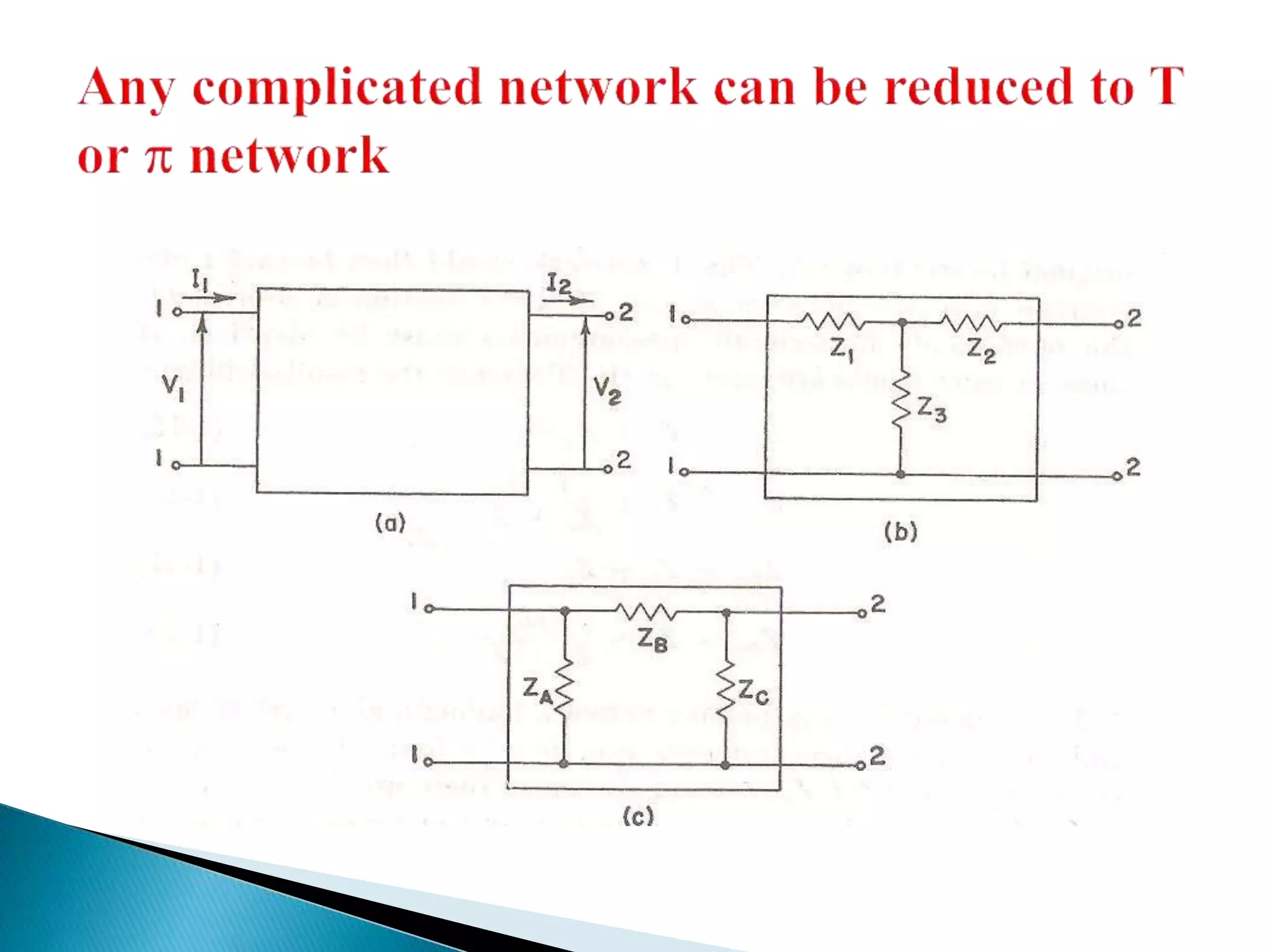
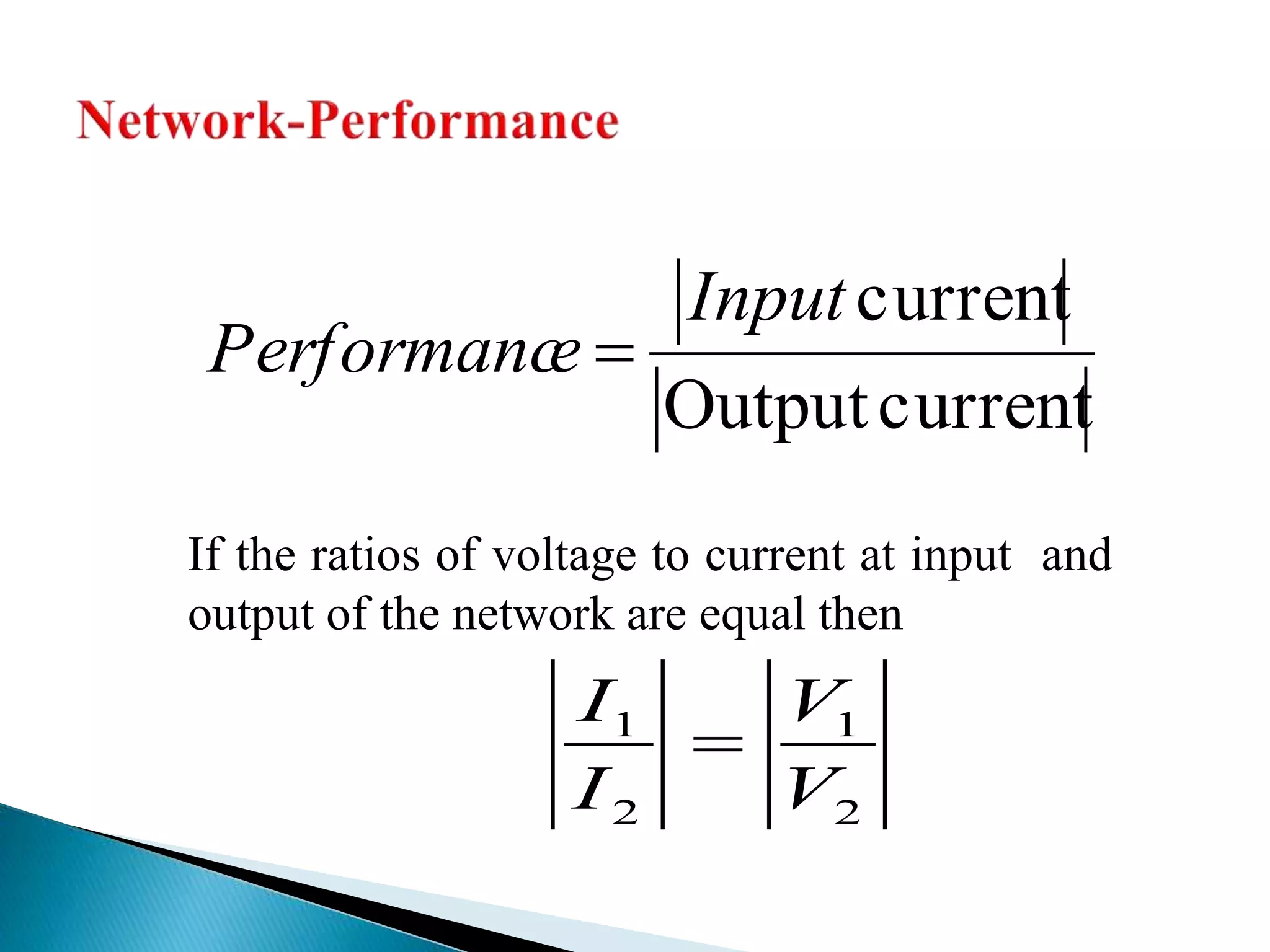
This document outlines the course units for a transmission line theory course. Unit I covers the general theory of transmission lines, including characteristic impedance and the propagation constant which determines attenuation. The transmission line carries signals like telephone, computer data, TV and more. Unit II deals with transmission at radio frequencies including standing waves. Unit III covers impedance matching using techniques like stubs and the Smith chart. Unit IV discusses waveguides and wave behavior in guided structures. Unit V is about RF system design components and concepts. The goals are for students to analyze various transmission line types and impedance matching, and apply concepts to guided transmission systems and RF design.