Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


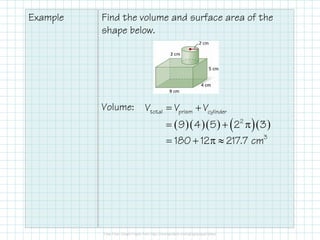
![Example Find the volume and surface area of the
shape below.
Surface Area:
total prism cylS S L= +
( ) ( ) ( )[ ] ( )( )prismS 5 2 9 2 4 2 9 4
202
= + +
=
( )( )cylL 2 2 3
12
= π
= π
2
totalS 202 12 239.7 cm= + π ≈
We only need lateral area
because the one visible base
of the cylinder offsets the
missing circle on the prism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-170512135627/85/5-13-6-Composite-Shapes-4-320.jpg)
To find the surface area and volume of composite shapes, break them down into simpler component shapes and combine their individual areas and volumes. When calculating surface area, account for any portions of shapes that may be overlapped or covered by other shapes. Volumes simply add together while surface areas require considering both visible surfaces and any surfaces that may be obscured by other components.



![Example Find the volume and surface area of the
shape below.
Surface Area:
total prism cylS S L= +
( ) ( ) ( )[ ] ( )( )prismS 5 2 9 2 4 2 9 4
202
= + +
=
( )( )cylL 2 2 3
12
= π
= π
2
totalS 202 12 239.7 cm= + π ≈
We only need lateral area
because the one visible base
of the cylinder offsets the
missing circle on the prism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-170512135627/85/5-13-6-Composite-Shapes-4-320.jpg)