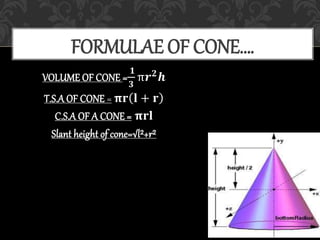
This document provides information about mensuration and different shapes used in mensuration. It defines mensuration as the assignment of numbers to measurements of objects or events. It then discusses different measurement systems like the metric system and imperial system. It provides details on common 3D shapes like cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and hemispheres. For each shape, it lists key properties and provides formulas to calculate volume, total surface area, curved surface area, and other measurements.