Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

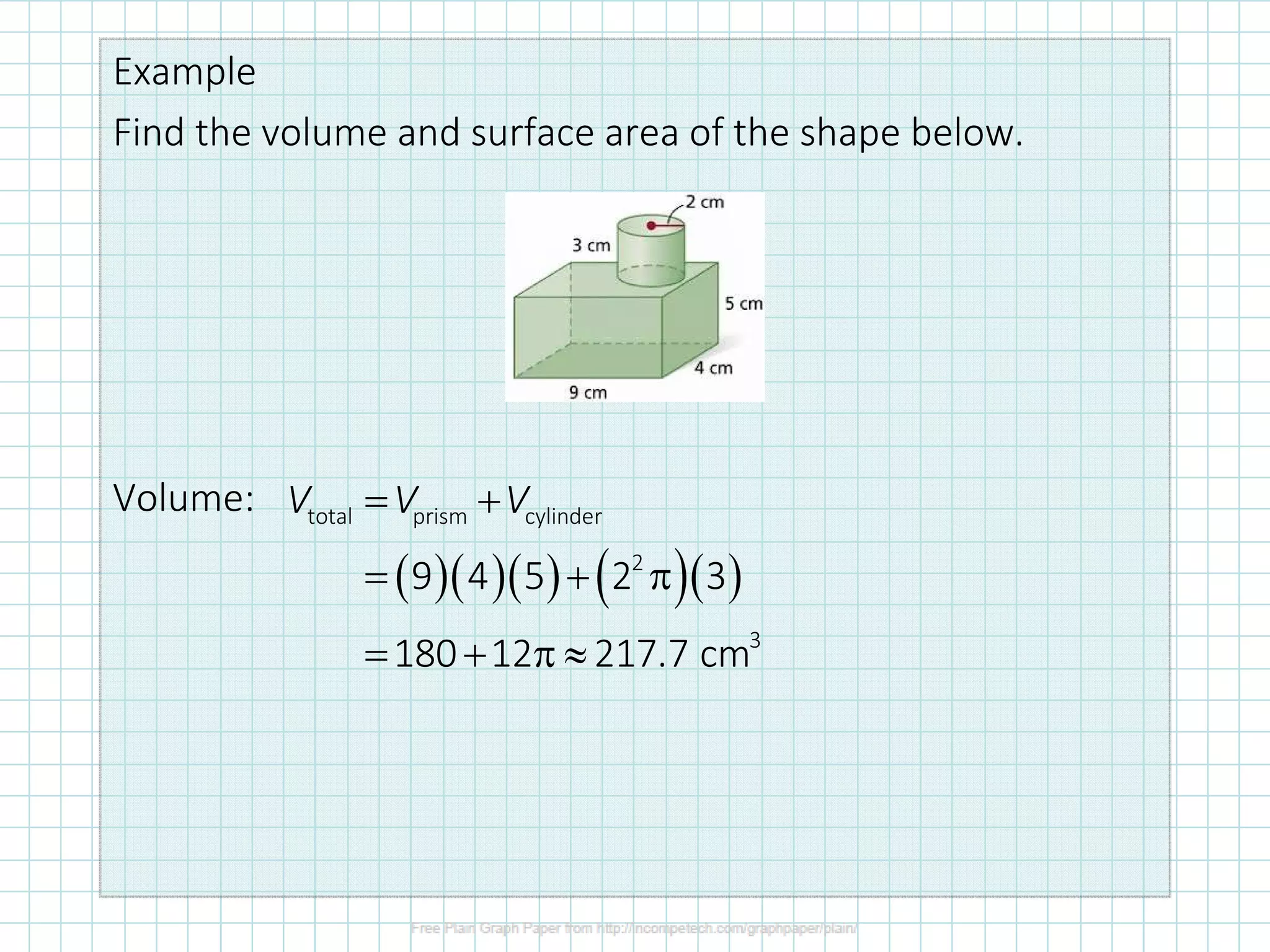
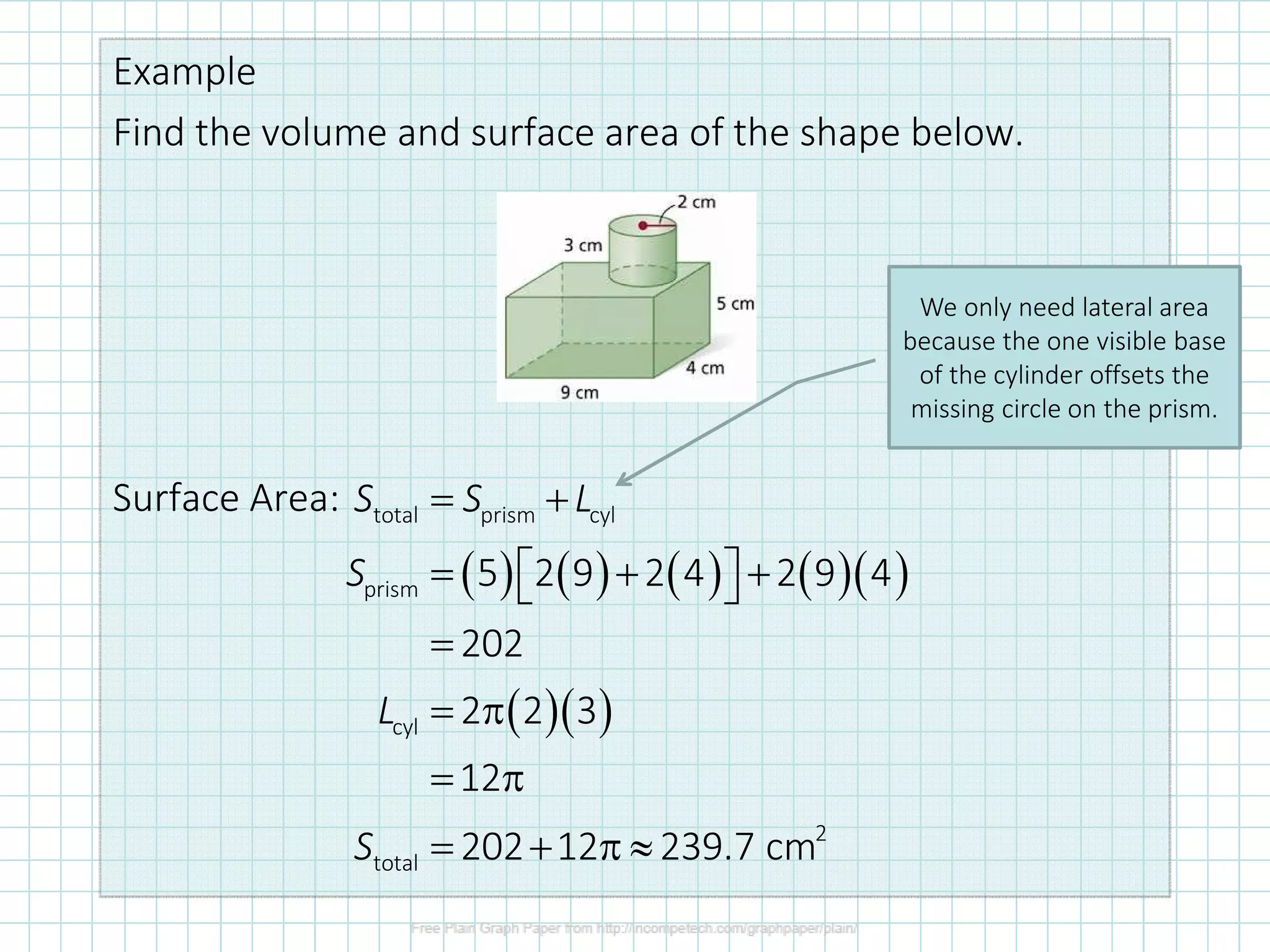
The student is able to find the surface area and volume of composite figures made up of simpler shapes. To solve such problems, one breaks the composite figure down into constituent shapes like prisms and cylinders and then calculates the surface area and volume of each shape individually before summing them. For surface area, one must account for any overlapping portions between shapes.



