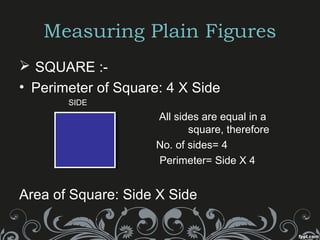
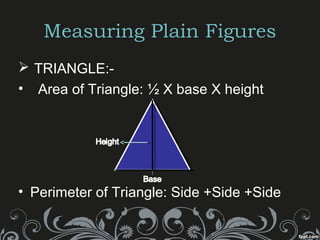
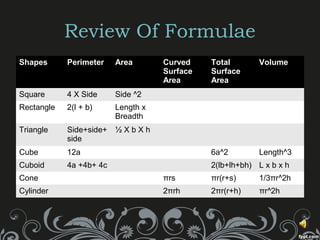
This document provides information about mensuration, which is the measurement of geometric figures. It begins with acknowledging the teacher for providing the opportunity to present on this topic. It then defines important terms like perimeter, area, volume, and introduces plain and solid figures. Formulas for calculating the perimeter, area, surface area and volume of squares, rectangles, triangles, cubes, cuboids, cylinders and cones are presented along with examples. The document concludes by listing the group members who prepared the presentation.