Embed presentation
Downloaded 85 times



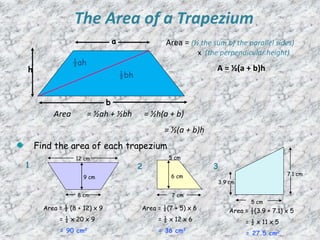
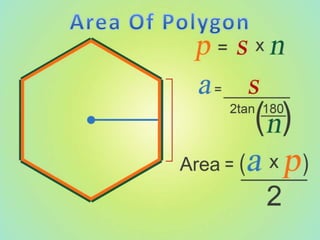
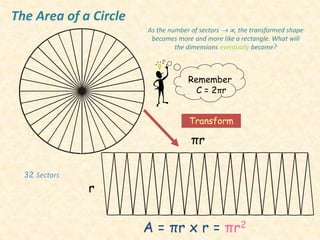
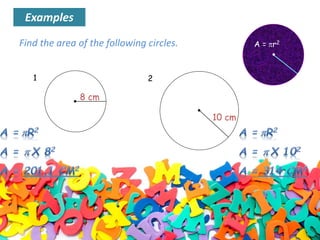
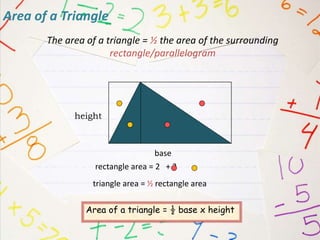
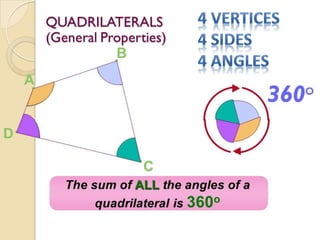


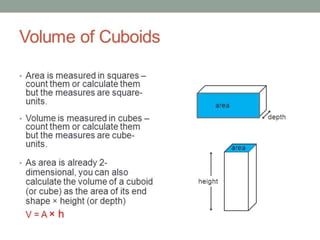
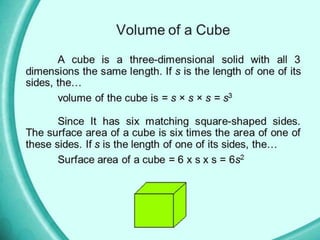
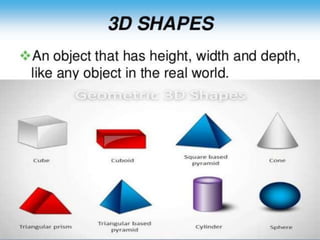
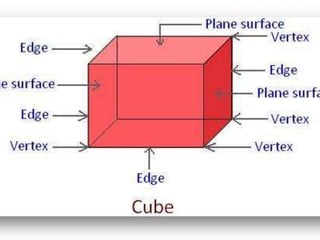
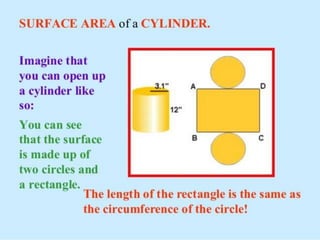
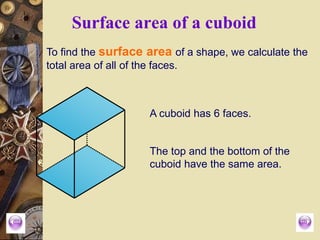
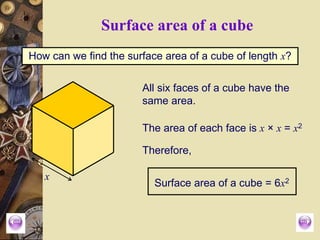
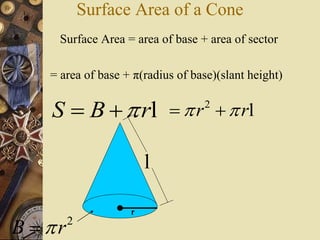


The document outlines formulas for calculating the areas of various geometrical shapes, including trapeziums, circles, triangles, cubes, cuboids, and cones. It provides specific examples and calculations for each shape's area and discusses surface area concepts. Additionally, it briefly addresses the volume of solids and surface area calculations.




















