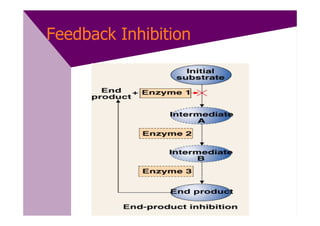
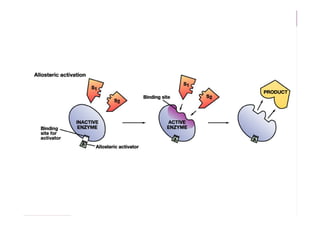
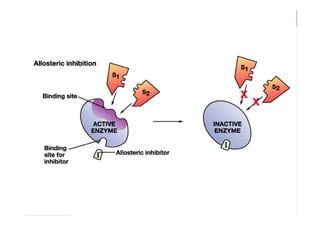
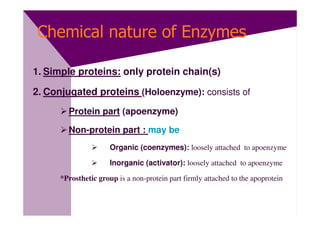
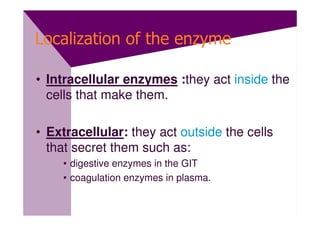
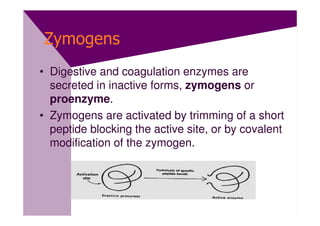
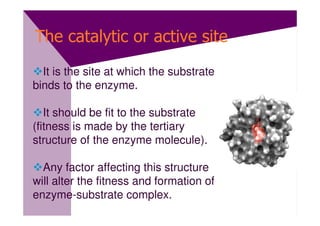
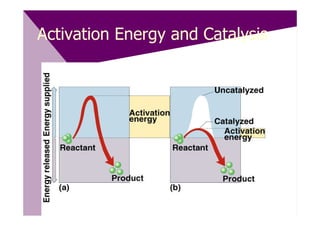
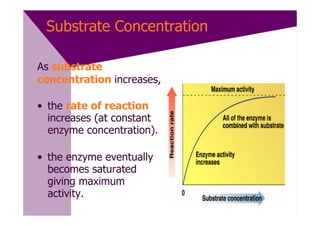
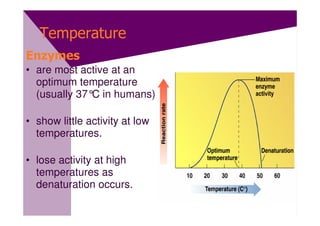
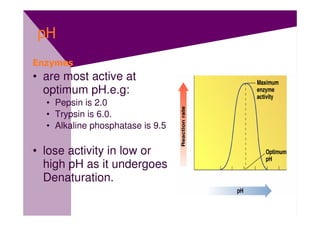
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts and speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They are highly specific and function most effectively within a certain pH range and temperature. The active site of the enzyme binds to the substrate and the transition state requires lower activation energy than without the enzyme. The turnover number refers to the number of substrate molecules an enzyme can convert to products per unit time. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like substrate and inhibitor concentration, pH, temperature, and cofactors. Different types of inhibitors like competitive, non-competitive, and allosteric inhibitors can bind to enzymes and decrease their activity.










![Michaelis constant (Km)
• Km is equal to the substrate
concentration [S] at which the
reaction is half of its maximum
(½Vmax).
• It expresses the affinity of the
enzyme to its substrate.
• Low Km means high affinity of the
enzyme to the substrate
• High Km means low affinity of the
enzyme to the substrate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51196538-enzymeschapter3-120406051958-phpapp02/85/51196538-enzymes-chapter-3-18-320.jpg)
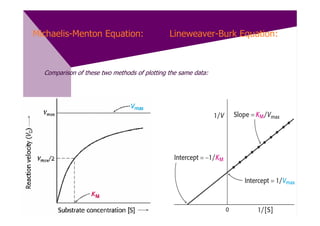
![Enzymes – Lineweaver-Burk Equation
V = Vmax [S]
[S] + Km
Inverting the Equation yields: 1 = Km 1 + 1 .
(Lineweaver-Burke Equation) V Vmax [S] Vmax
By plotting 1/ V as a function of 1/[S],
a linear plot is obtained:
Slope = Km/Vmax
y-intercept = 1/Vmax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51196538-enzymeschapter3-120406051958-phpapp02/85/51196538-enzymes-chapter-3-19-320.jpg)

![Cofactors
• Most enzymes are associated with non-protein part which may be:
metal-ion as zinc, copper, iron
prosthetic group as flavine nucleotide, biotin, 4’-
phophopantetheine (of pantothenic acid), or cobamide.
coenzyme as nicotinamide nucleotide, NAD or NADP
• All these cannot be isolated from the protein part of the enzyme (apo-
enzyme) by dialysis.
• The protein part of the enzyme (apo-enzyme) + [metal, prosthetic
group, or the coenzyme] = holoenzyme](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51196538-enzymeschapter3-120406051958-phpapp02/85/51196538-enzymes-chapter-3-24-320.jpg)
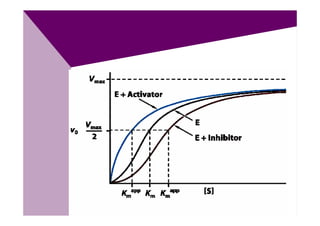
![Inhibitors (I)
Inhibition may be reversible or irreversible.
• Reversible: If the inhibitor binds non-covalently to
the enzyme
• Irreversible: If the inhibitor binds covalently to the
enzyme
If [S] is > [I], only part of enzyme molecules are
occupied by the [I] and the inhibition will be
proportionate to [I].
[I] increases Km, so, more substrate is needed to
reach Vmax.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51196538-enzymeschapter3-120406051958-phpapp02/85/51196538-enzymes-chapter-3-25-320.jpg)

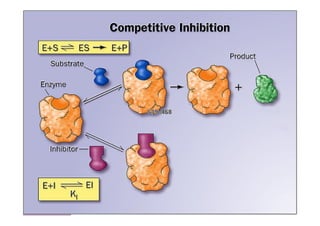
![Competitive inhibitors
• If [I] is > [S], E-I complex is formed, and it fails to dissociate.
So, inhibition of the E-S complex reaction takes place.
• Examples of competitive inhibitors:
• Allopurinol competes with hypoxanthine for xanthine oxidase
inhibiting the formation of uric acid, so it is used in treatment of
hyperuricemia (gout).
• Dicumarol or Warfarine compete with vitamin K, for epoxide
reductase, so they are used to reduce prothrombin synthesis.
• Statins (e.g. atorvastatin) competes with HMGCoA for its reductase,
so, it inhibits cholesterol synthesis.
• Methotrexate competes with dihydrofolic acid for dihydrofolate
reductase, so, it inhibits DNA synthesis and used in treatment of
cancers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51196538-enzymeschapter3-120406051958-phpapp02/85/51196538-enzymes-chapter-3-28-320.jpg)
![Non-competitive inhibitors
• The inhibitor binds to the enzyme in site away
from the catalytic site.
• Inhibition cannot be reverted by increasing [S].
• Km is not changed because the inhibitor does
not interfere with E-S formation, but Vmax is,
apparently reduced.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51196538-enzymeschapter3-120406051958-phpapp02/85/51196538-enzymes-chapter-3-30-320.jpg)