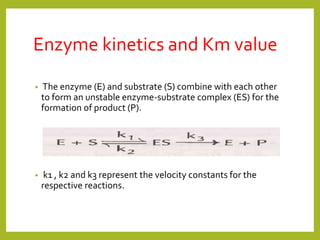
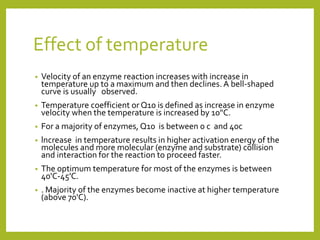
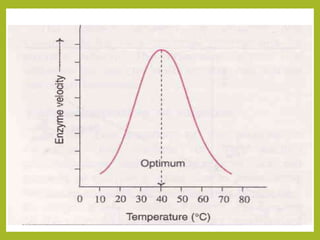
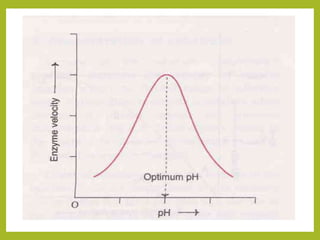
1. The document discusses enzyme kinetics and the factors that affect it, including concentration of enzyme and substrate, temperature, pH, product concentration, and activators.
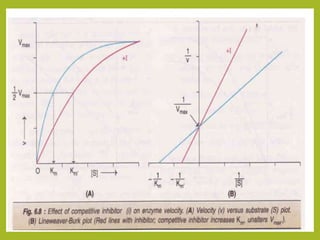
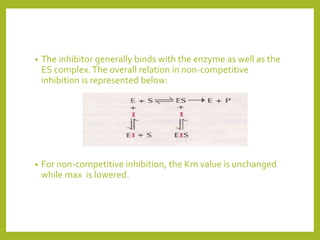
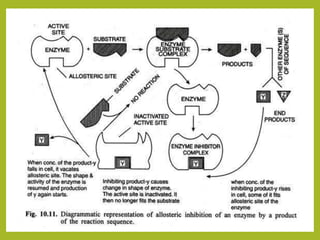
2. It also covers enzyme inhibition, describing reversible inhibition as competitive or non-competitive, and irreversible inhibition.
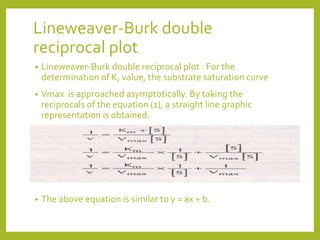
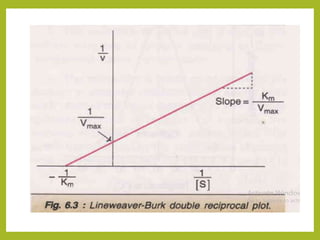
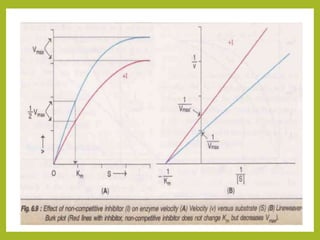
3. Key concepts explained are Michaelis-Menten kinetics, the Michaelis constant Km, Lineweaver-Burk plots, and the effects of various factors on the reaction rate.

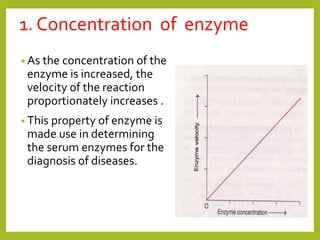
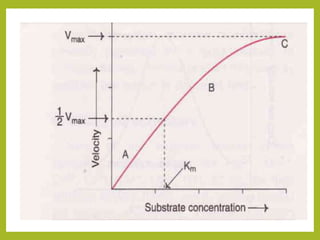
![2. Concentration of substrate
• A key factor affecting the rate of a reaction
catalyzed by an enzyme is the concentration of
substrate, [S].
• Increase in the substrate concentration
gradually increases the velocity of enzyme
reaction.
• Three distinct phases of the reaction are
observed in the graph (A-linear; B-curve; C-
almost unchanged).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymeskineticsmsc2ndsemsujata-201124173057/85/Enzymes-kinetics-7-320.jpg)
![Order of reaction
• When the velocity of the reaction is almost proportional
to the substrate concentration (i.e. [S] is less than Km),
the rate of the reaction is said to be first order with
respect to substrate.
• When the [S] is much greater than Km, the rate of
reaction is independent of substrate concentration, and
the reaction is said to be zero order.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymeskineticsmsc2ndsemsujata-201124173057/85/Enzymes-kinetics-8-320.jpg)