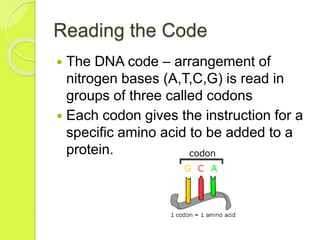
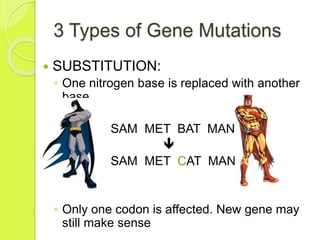
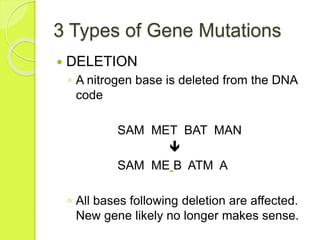
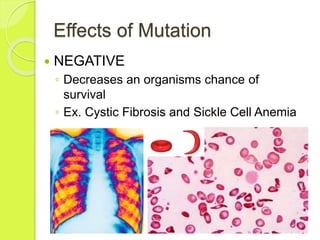
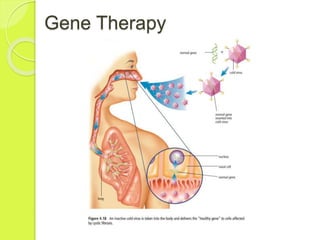
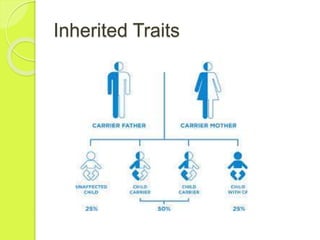
Gene mutations occur when the sequence of nitrogen bases that make up a gene changes. There are three types of mutations: substitutions replace one base with another, additions insert an extra base, and deletions remove a base. Mutations can have positive, negative, or neutral effects on an organism's chances of survival. Mutagens like viruses, smoke, radiation, and chemicals cause DNA mutations and sometimes lead to cancer. Gene therapy aims to correct mutations by replacing the mutated gene with a healthy copy delivered via inactive viruses, though it remains experimental.