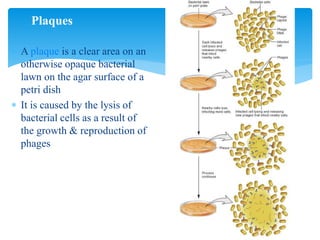
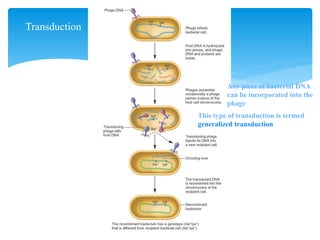
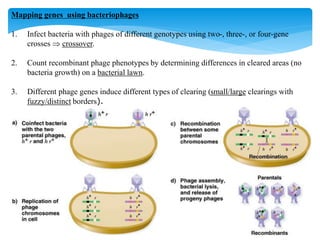
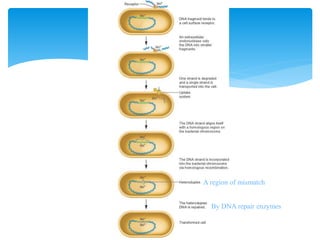
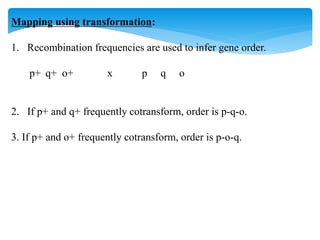
This document discusses several methods of genetic transfer and mapping in bacteria:
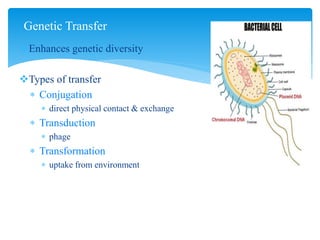
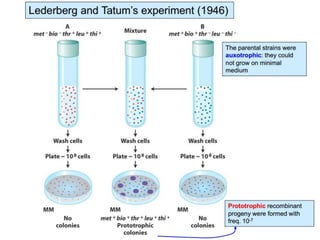
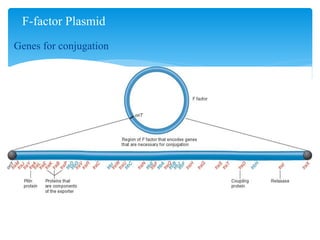
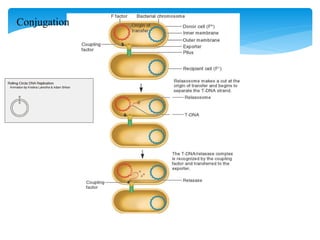
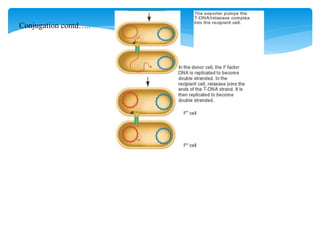
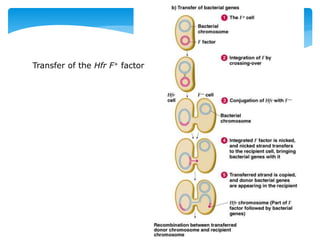
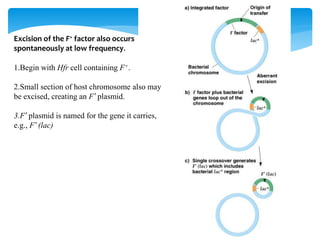
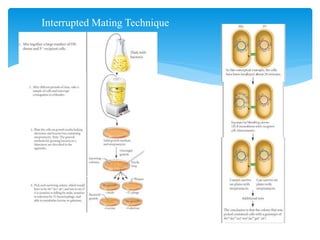
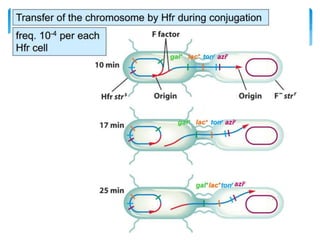
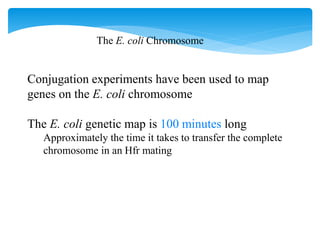
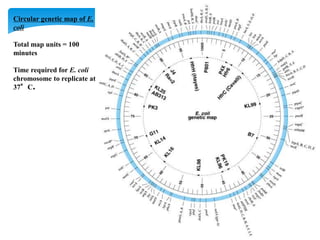
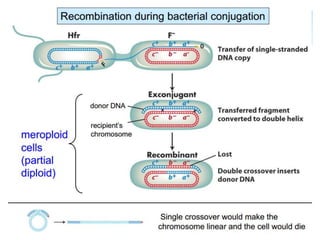
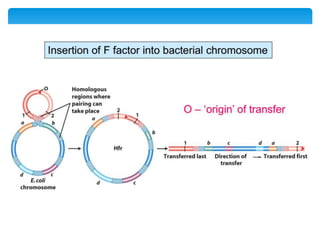
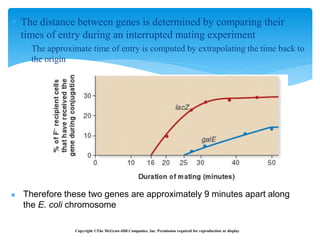
1. Conjugation, where genetic material is transferred between bacteria through direct contact. This can be used to map genes by interrupting mating at time points and analyzing recombinants.
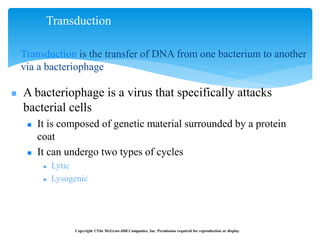
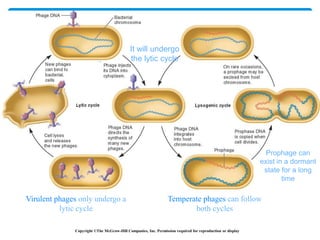
2. Transduction, where genes are transferred between bacteria via bacteriophages. Phage crosses can also be used to map genes.
3. Transformation, where bacteria take up extracellular DNA from their environment. The frequency of different genes co-transforming can indicate their order on the chromosome.
These natural processes of genetic transfer allow bacteria to evolve and have been exploited to study bacterial genetics and develop genetic maps. Interrupted mating, ph