Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times

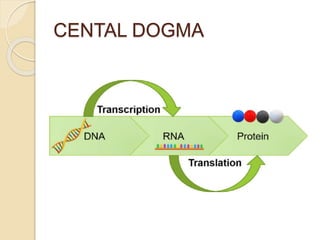
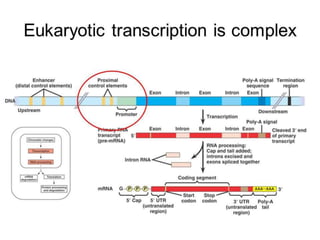


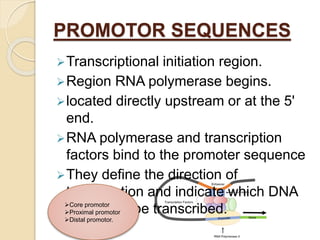
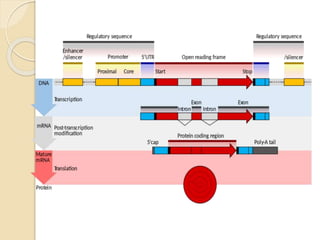
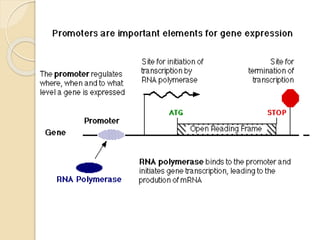
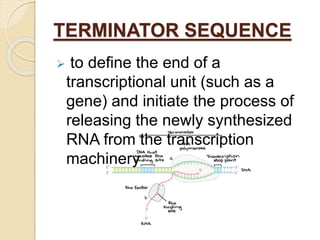
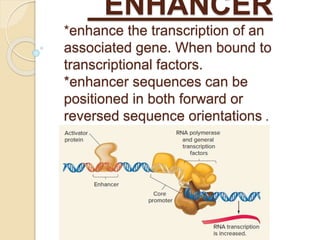
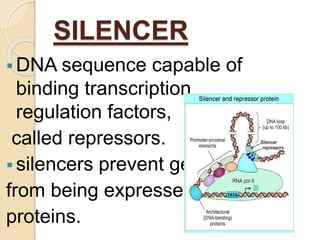
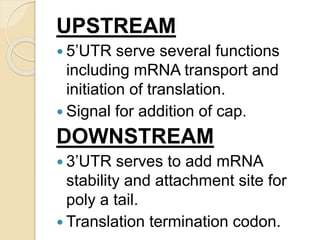
The document outlines the structure of eukaryotic genes, including components such as exons (coding sequences), introns (non-coding sequences), promoter sequences (regions for transcription initiation), and terminator sequences (defining the end of transcription). It details the roles of enhancers in transcription enhancement and silencers in gene expression regulation. Additionally, it discusses the functions of 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) in mRNA stability and translation initiation.











