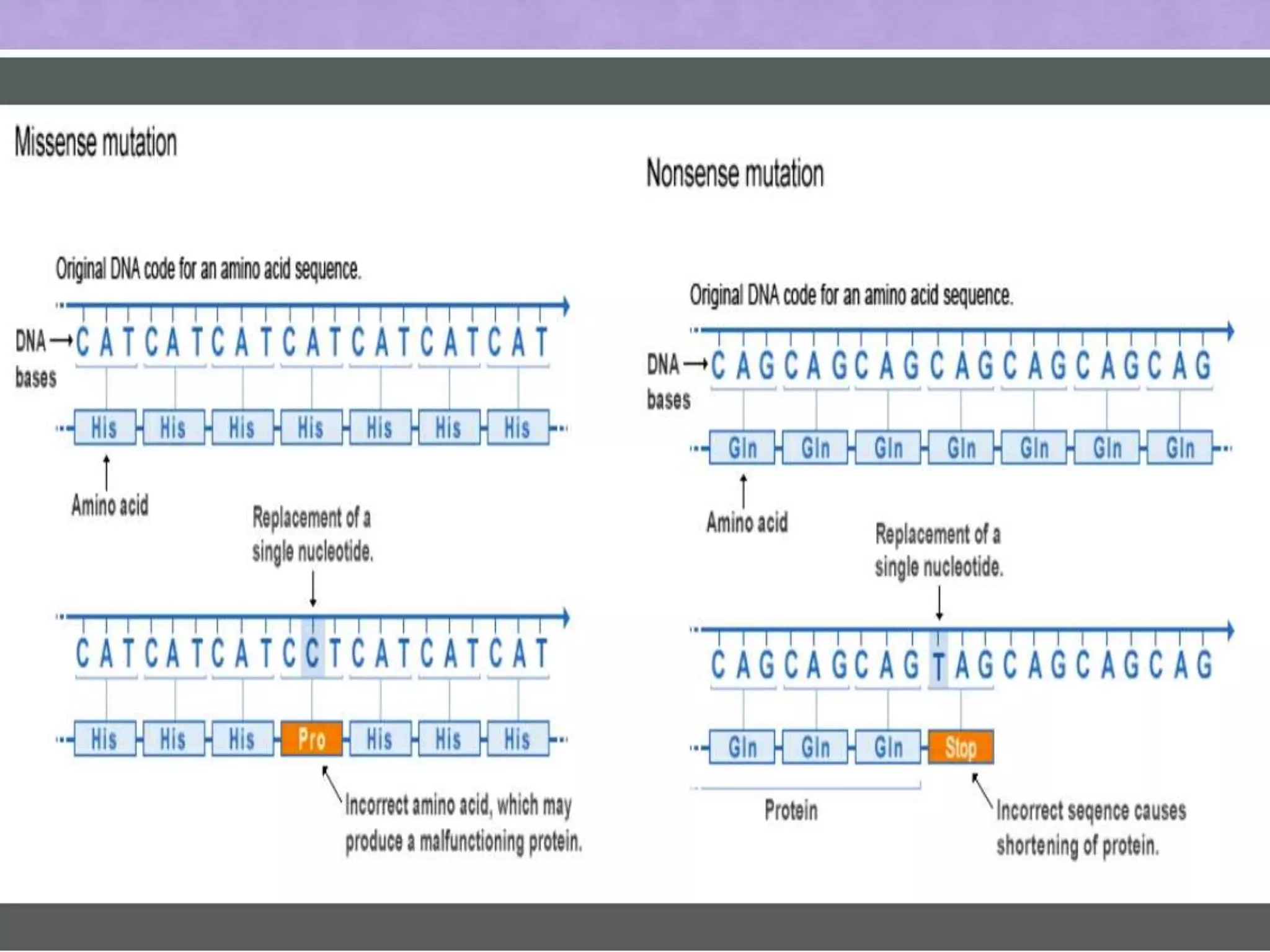
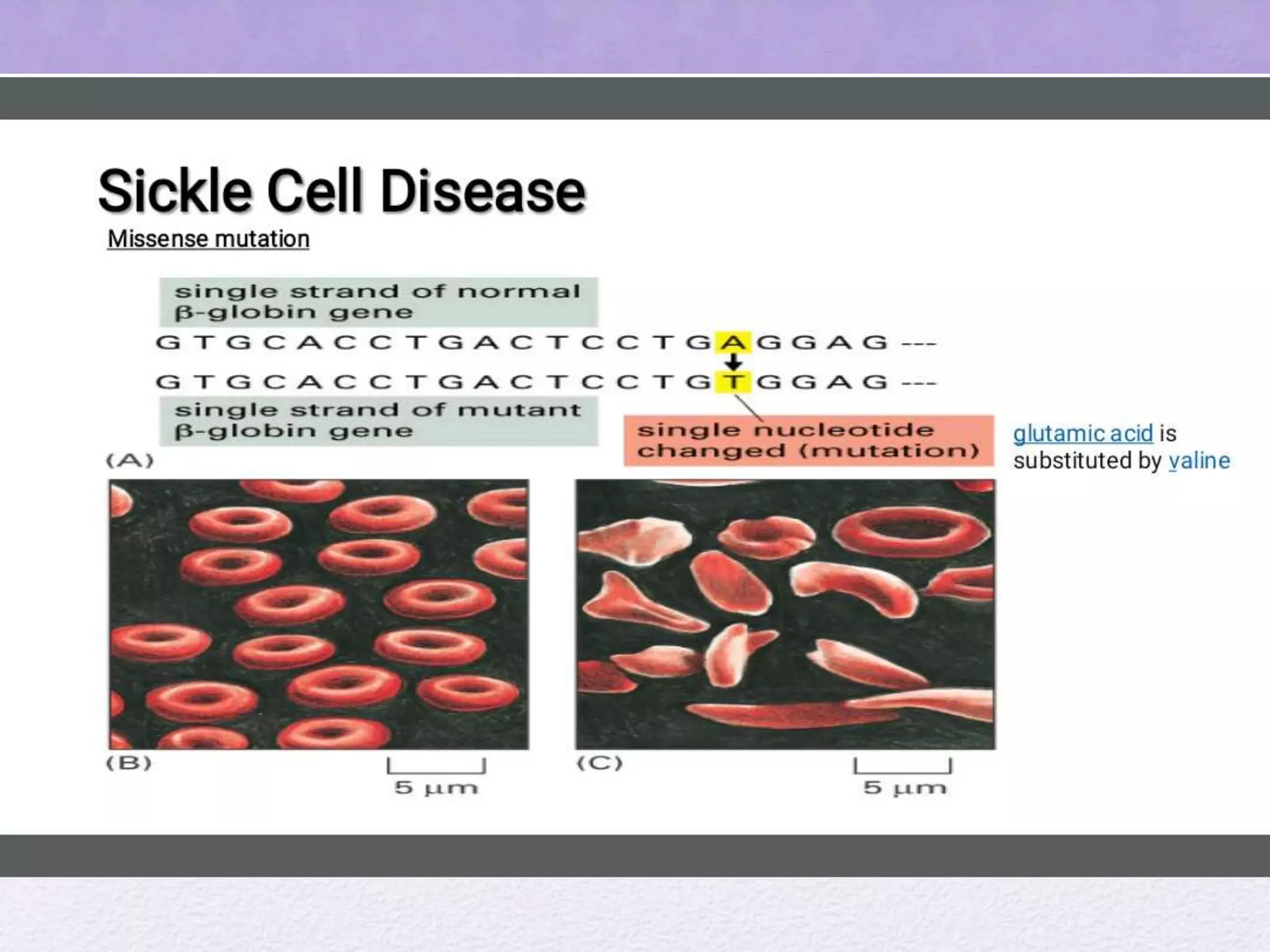
Gene mutations are alterations in DNA nucleotide sequences that can result in non-functioning proteins. There are two main types of mutations: hereditary mutations inherited from parents that are present throughout life, and acquired mutations that occur during life and are present in only certain cells. Mutations can be caused by mutagens like radiation, viruses, bacteria, or errors during DNA replication. Different types of mutations include missense mutations where one nucleotide is substituted, nonsense mutations where one nucleotide causes premature protein stopping, and insertion/deletion/duplication mutations that alter the number of nucleotides. Gene mutations can cause genetic disorders and diseases like cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia. While mutations may be harmful, some can be beneficial or have no effect



![MUTATGENS
• Substances or factors that causes mutations in
DNA are known as mutagens.
• Mutagens may be:
Ionizing radiation: X rays,
Gama rays, and alpha particles and UV radiation.
metabolite of
benzo[a]pyrene from tobacco smoke.
Virus; Rous sarcomas virus
Bacteria; Helicobacter pylori](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genemutationpresentation1-190807132438/75/Gene-mutation-IN-Detail-And-structure-Symptoms-Cause-5-2048.jpg)