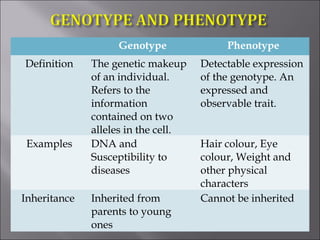
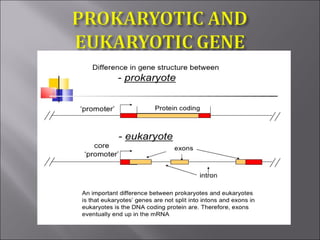
This document explains key genetic concepts, including definitions of genes, alleles, genotypes, and phenotypes, alongside their roles in heredity and expression. It describes the structure of DNA, including the significance of promoters, exons, introns, and codons in gene transcription and translation. Various genetic terms such as 'genetics,' 'genome,' and the types of alleles are also discussed.