Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




This document discusses modulation formats including minimum shift keying (MSK) and Gaussian MSK. It provides details on MSK such as it having a modulation index of 0.5, which makes the signals orthogonal and easier to separate at the receiver. MSK provides benefits like constant envelope, good spectral efficiency, and better bit error rate performance compared to frequency shift keying. The document also contains equations for MSK, diagrams of MSK transmission and reception, and information on the power spectral density of MSK and how it compares to Gaussian MSK.















Overview of modulation formats focusing on Minimum Shift Keying (MSK) and Gaussian MSK.
Information on available lecture videos to support learning, accessible at the given YouTube link.
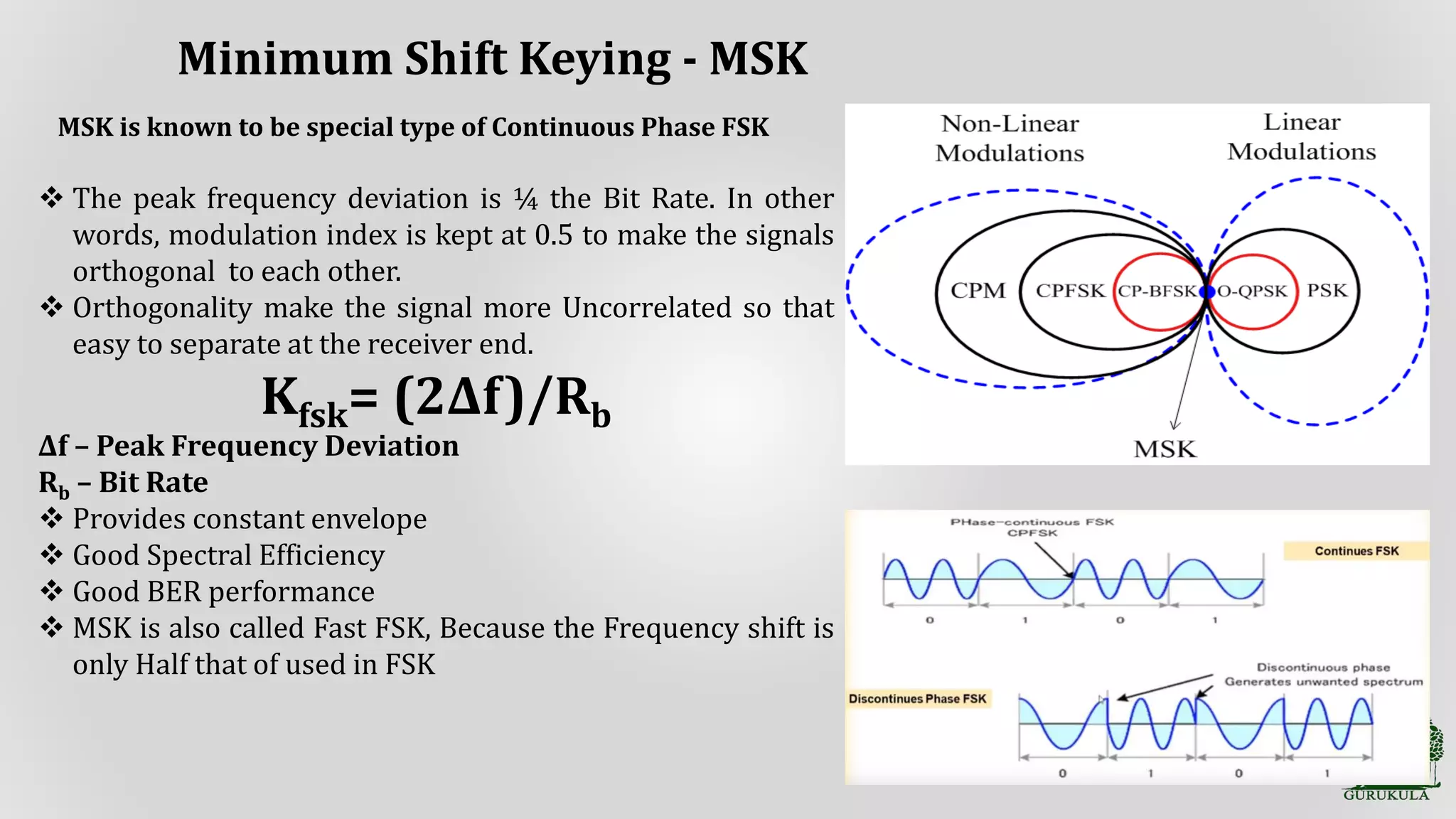
Explanation of MSK, its properties such as peak frequency deviation and orthogonality, and benefits like spectral efficiency.
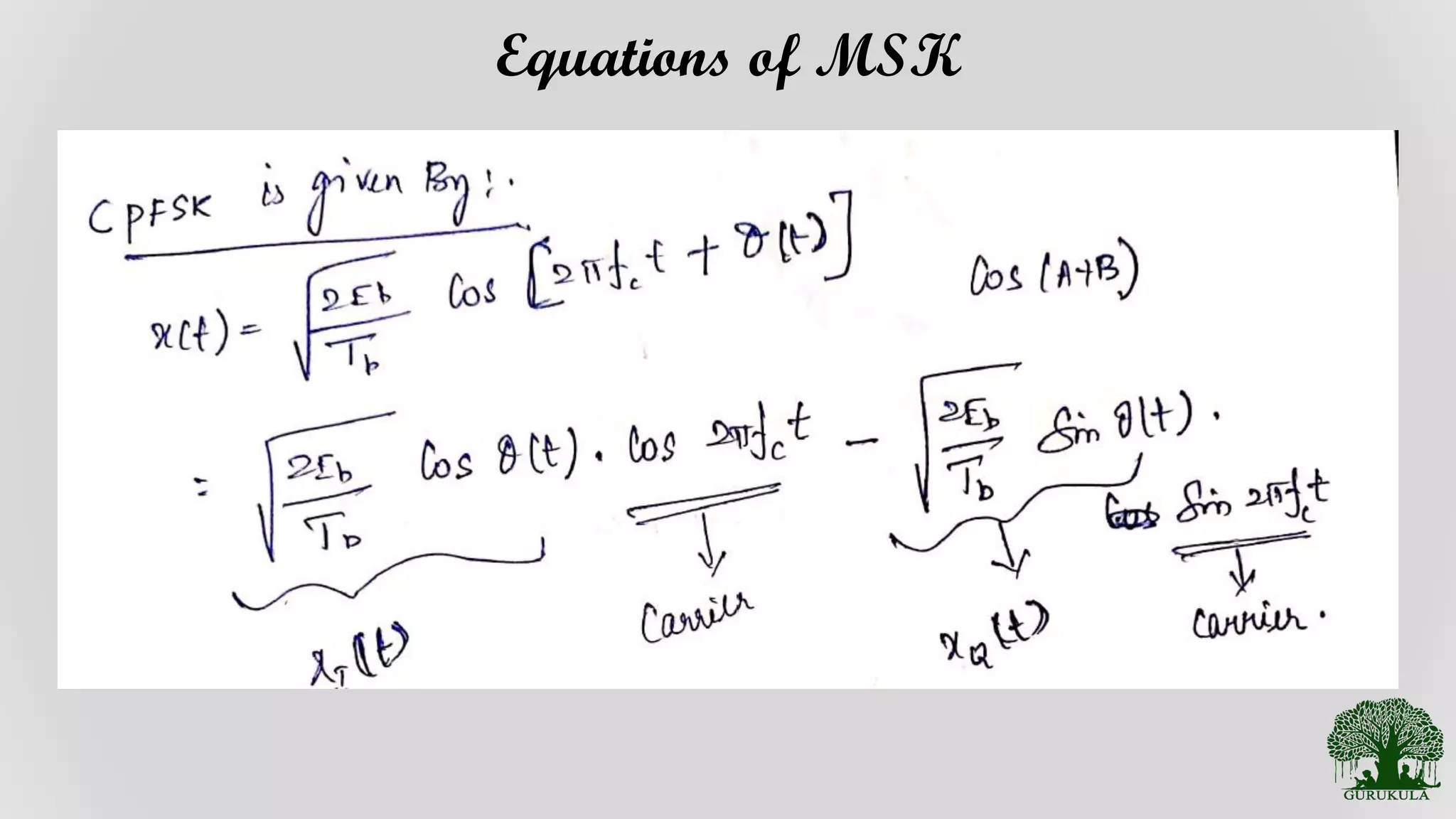
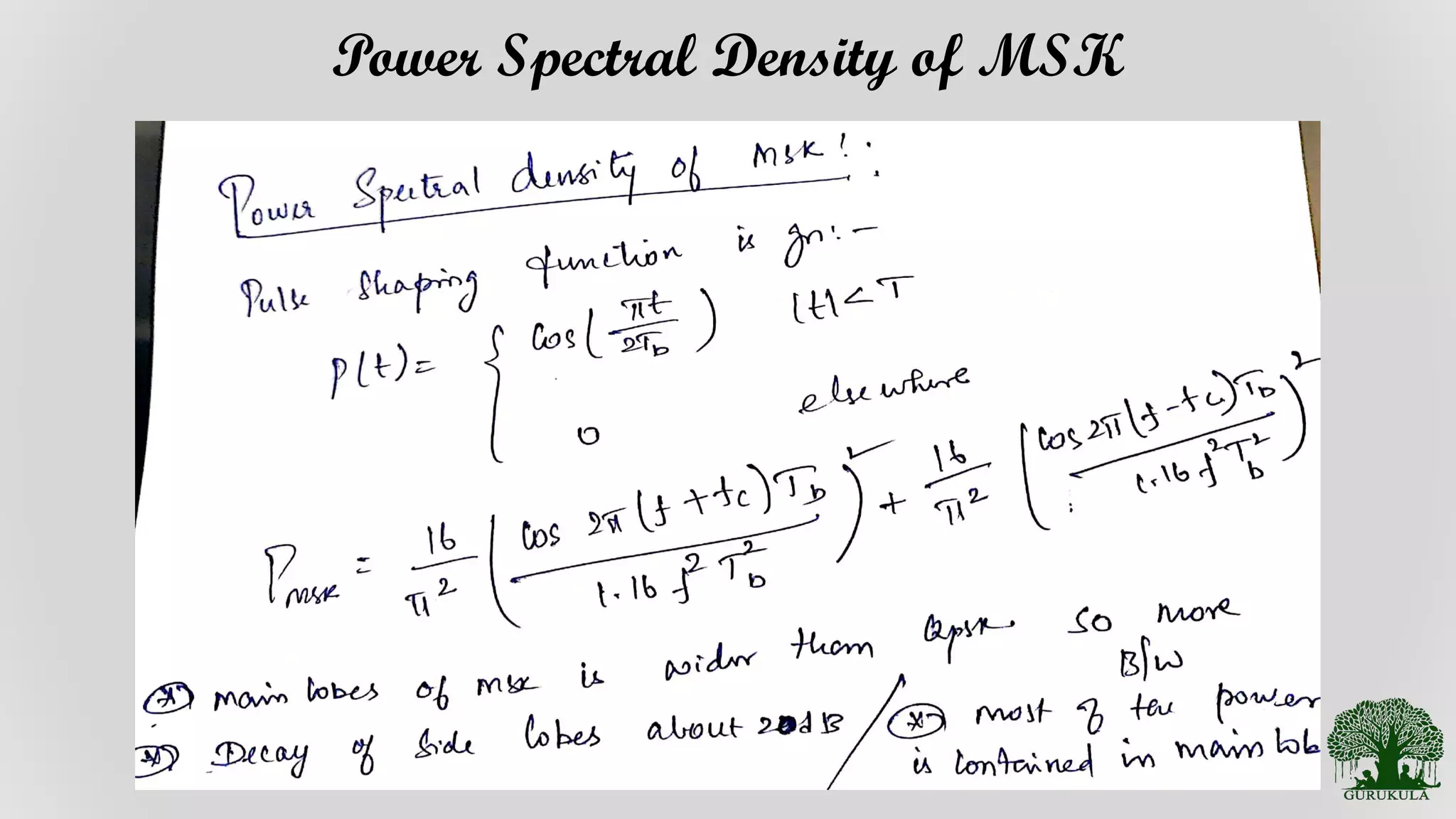
Details and formulation of equations related to Minimum Shift Keying.
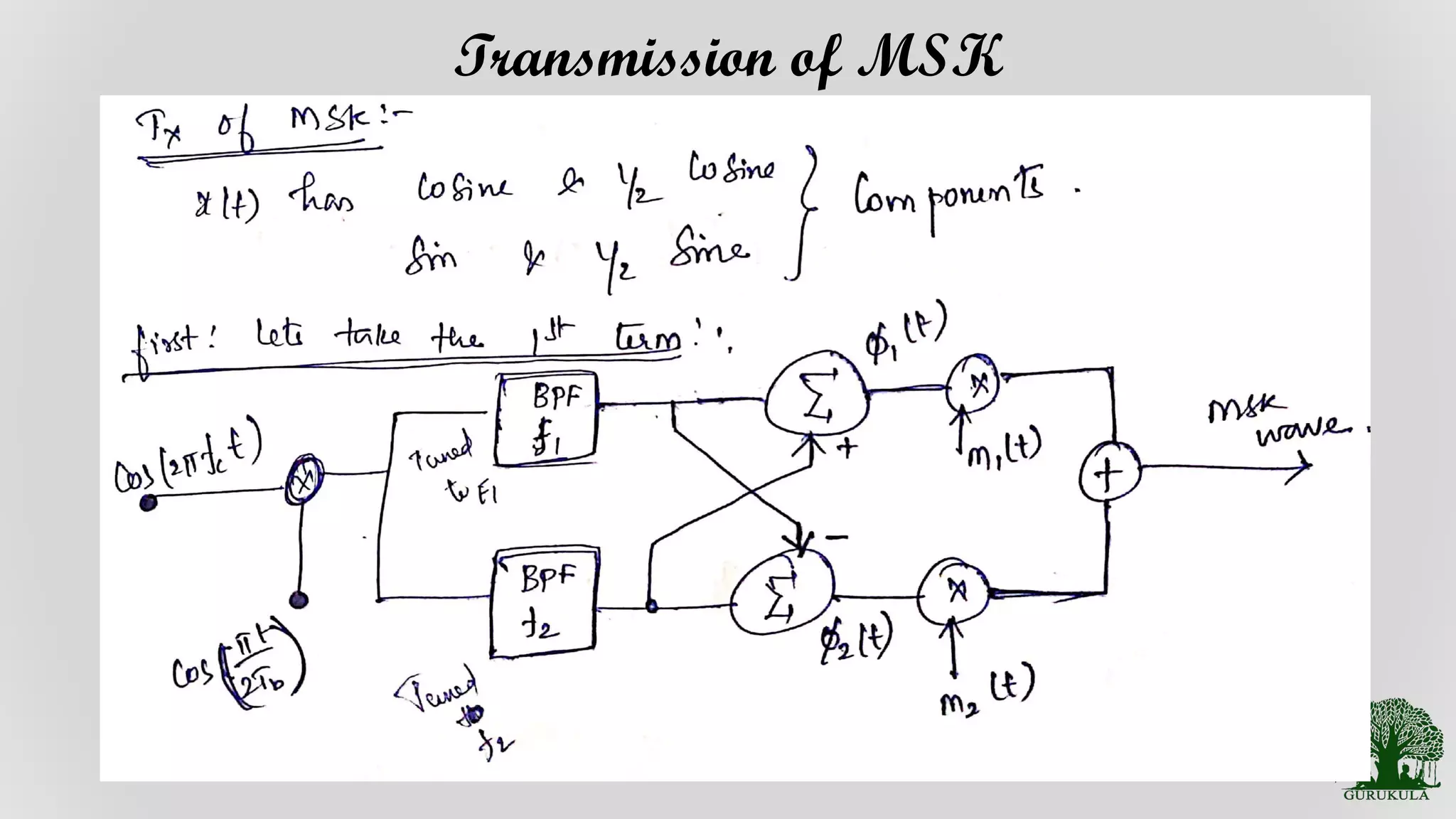
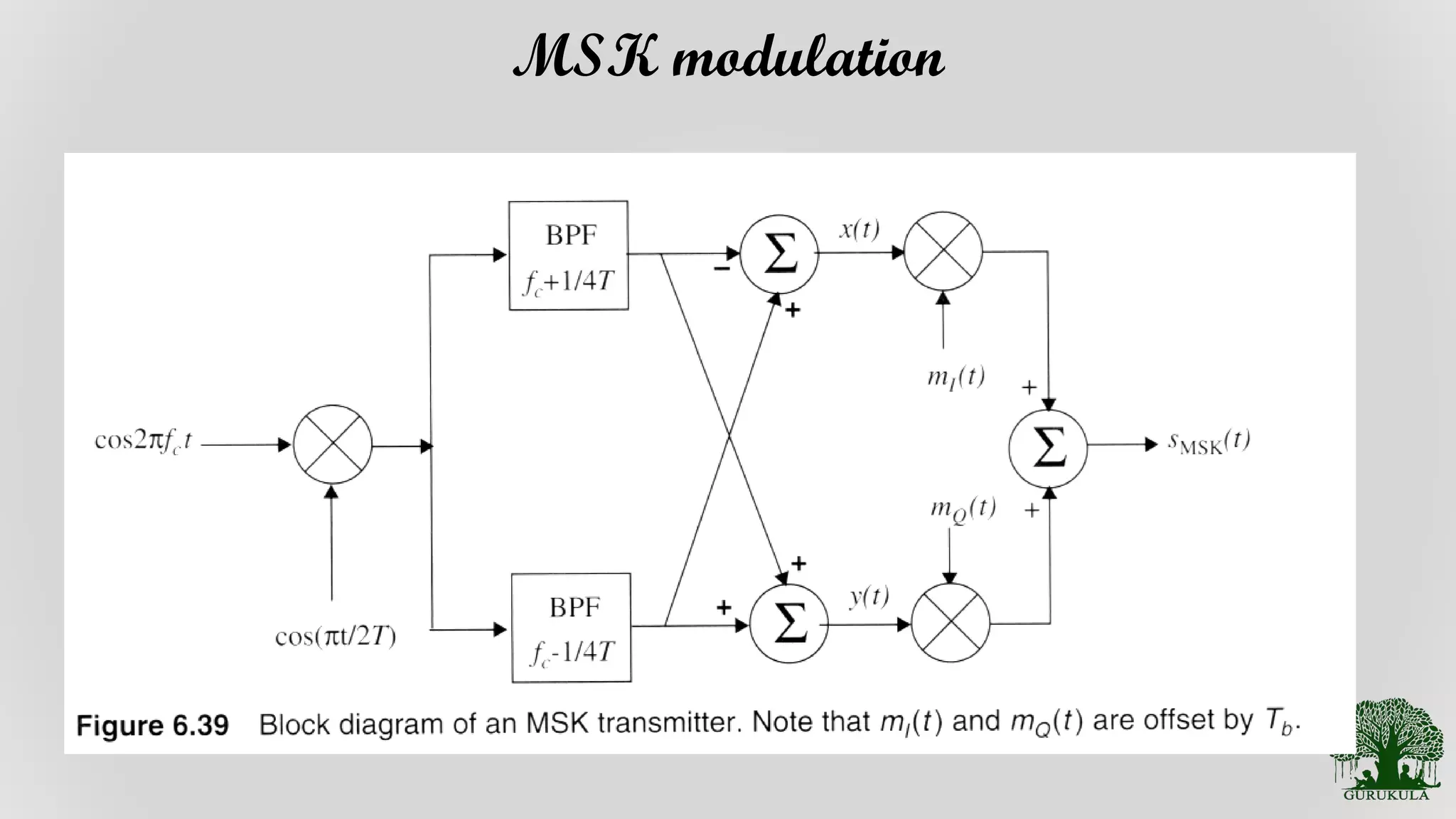
Discussion on the process and considerations involved in the transmission of MSK signals.
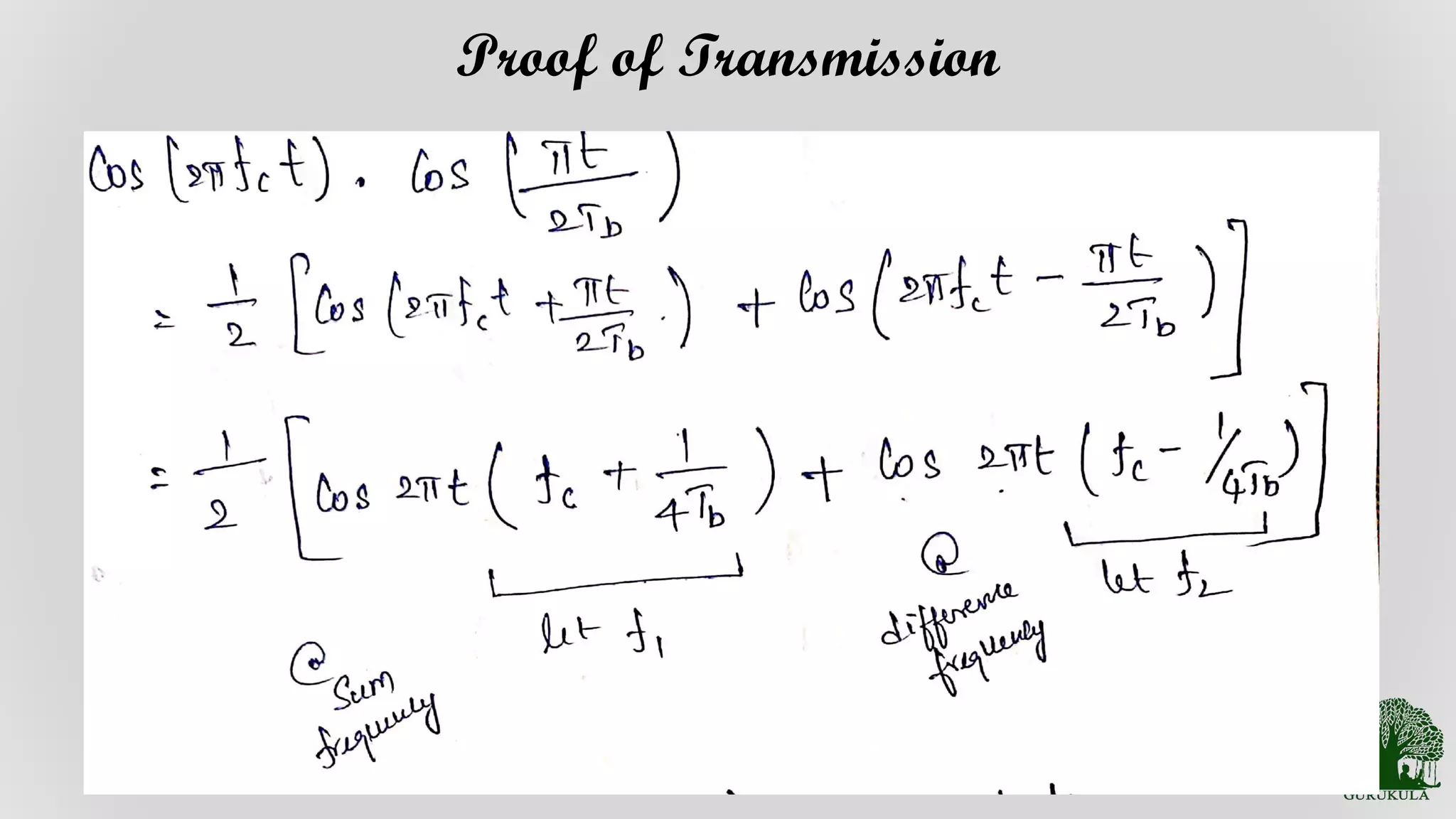
Theoretical proof underpinning the transmission process of MSK modulation.
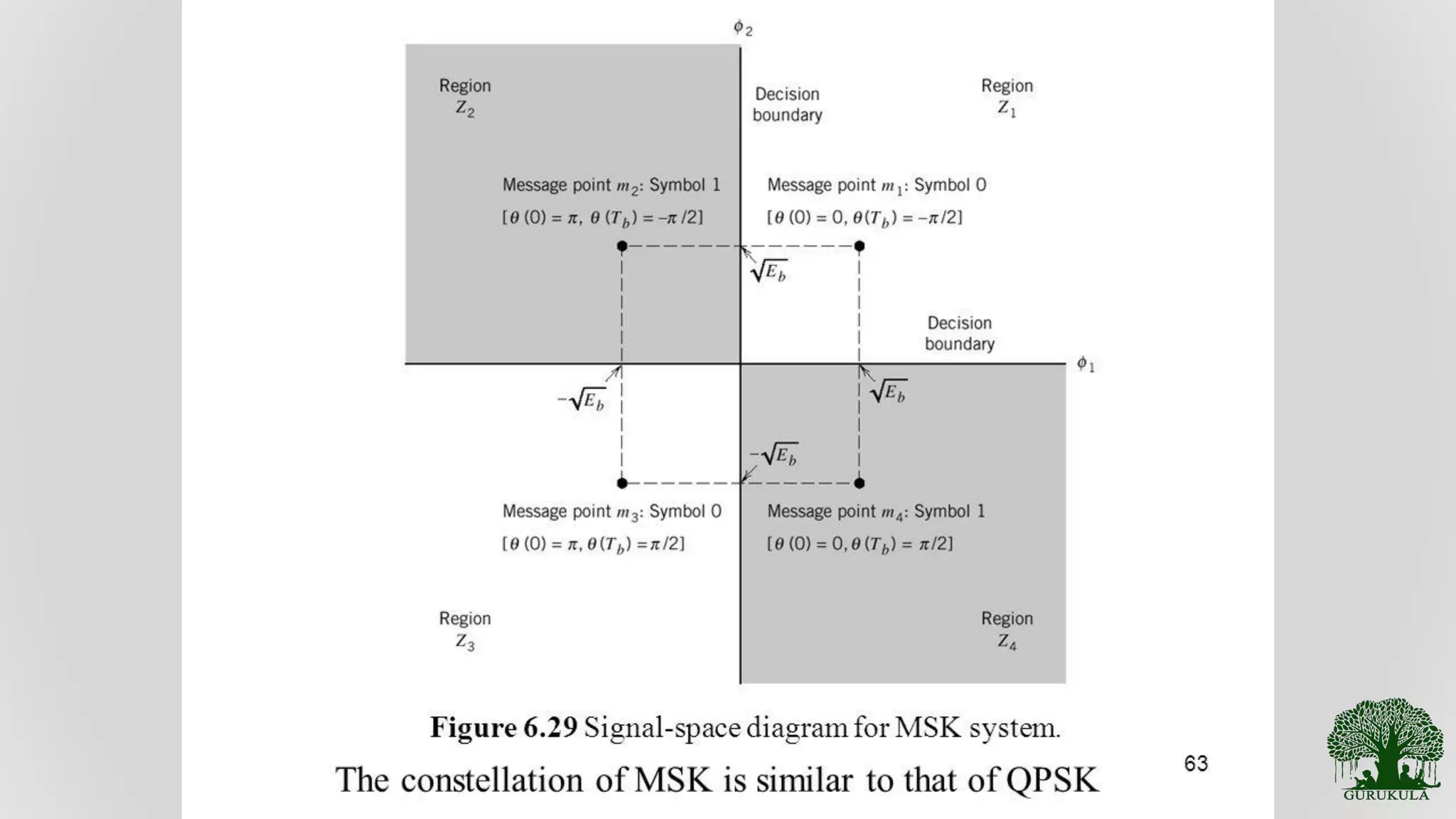
General review and characteristics of MSK modulation techniques.
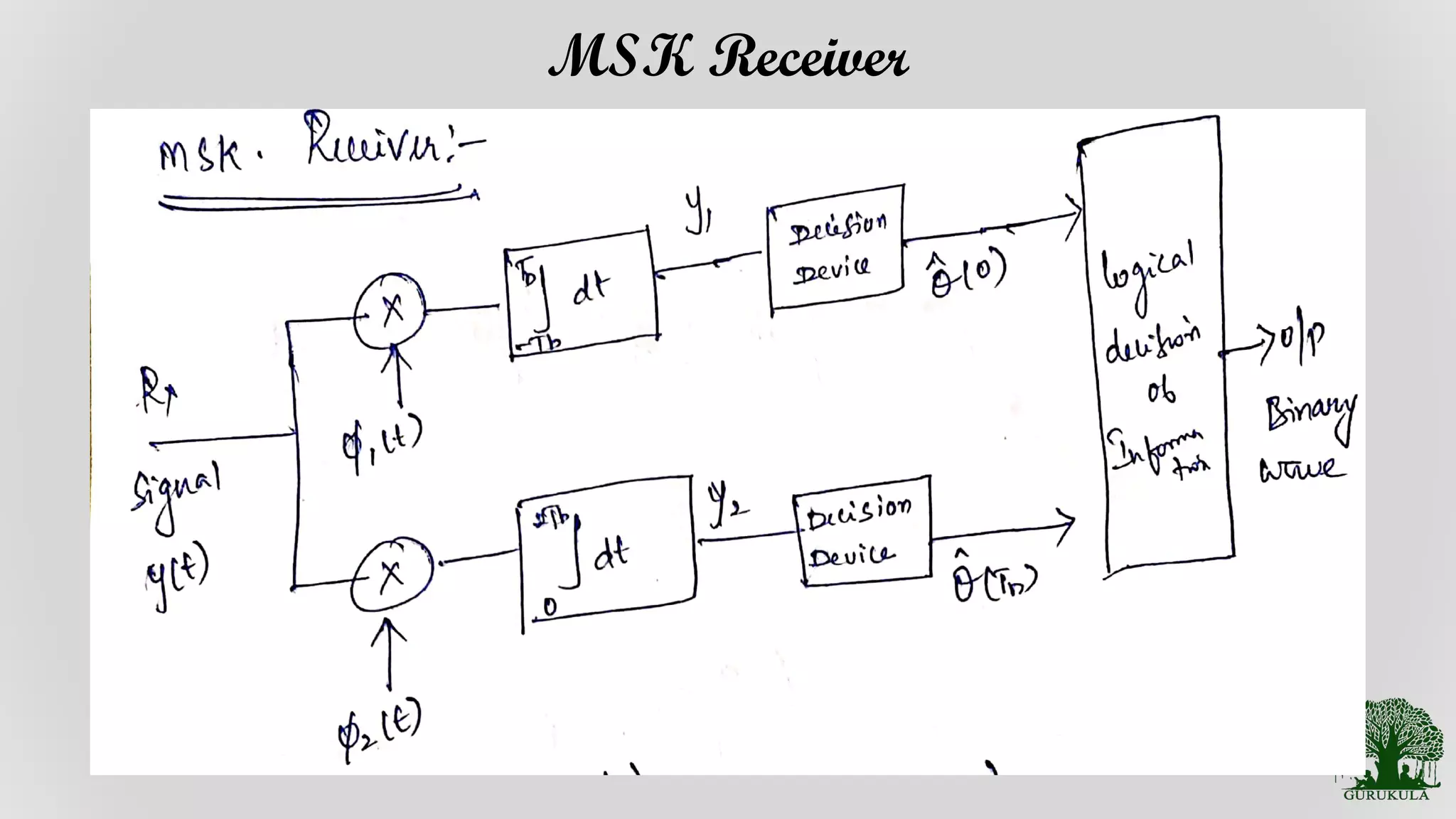
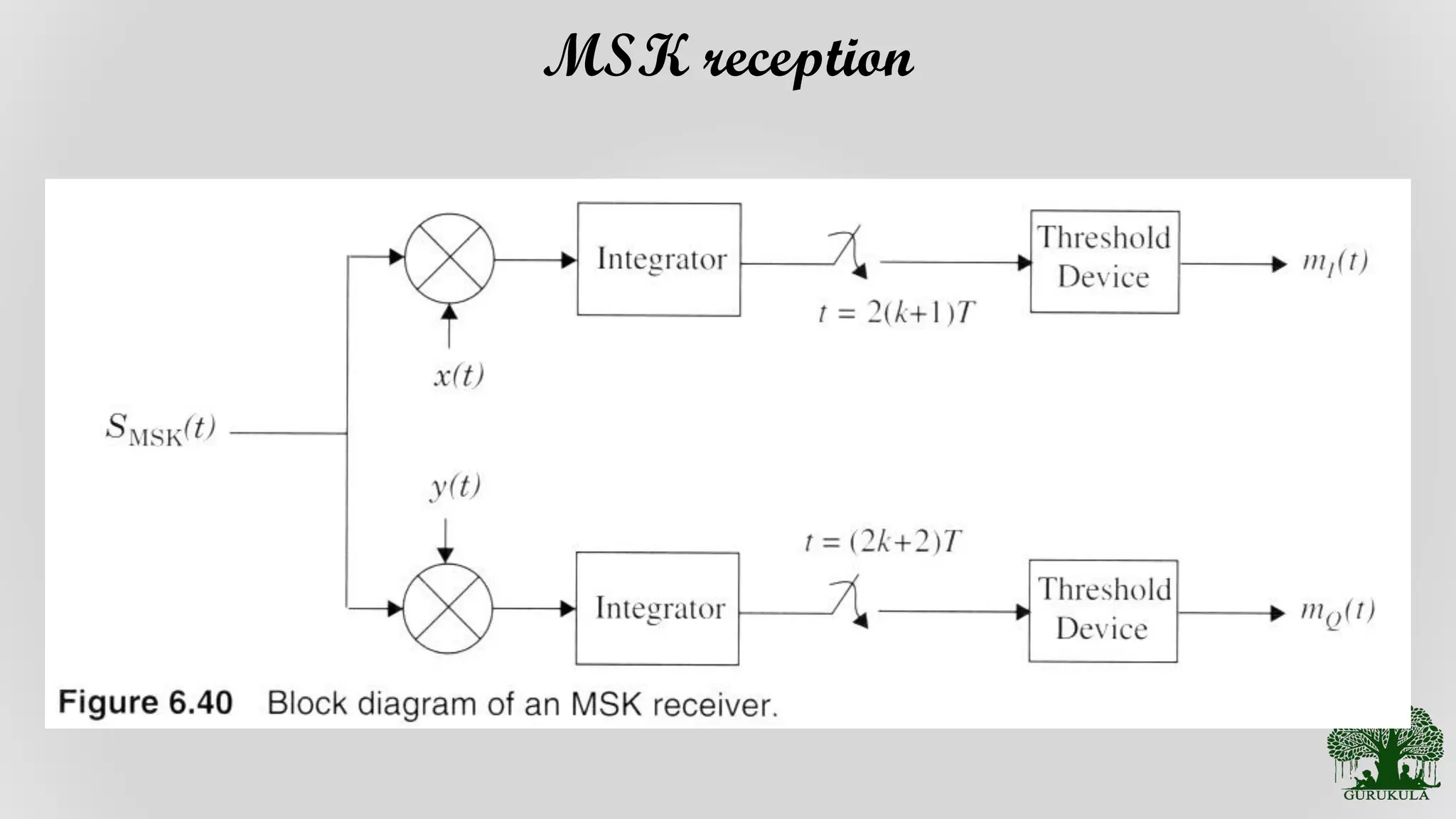
Description of receivers designed for processing MSK signals effectively.
Insights into how MSK signals are received, focusing on reception strategies.
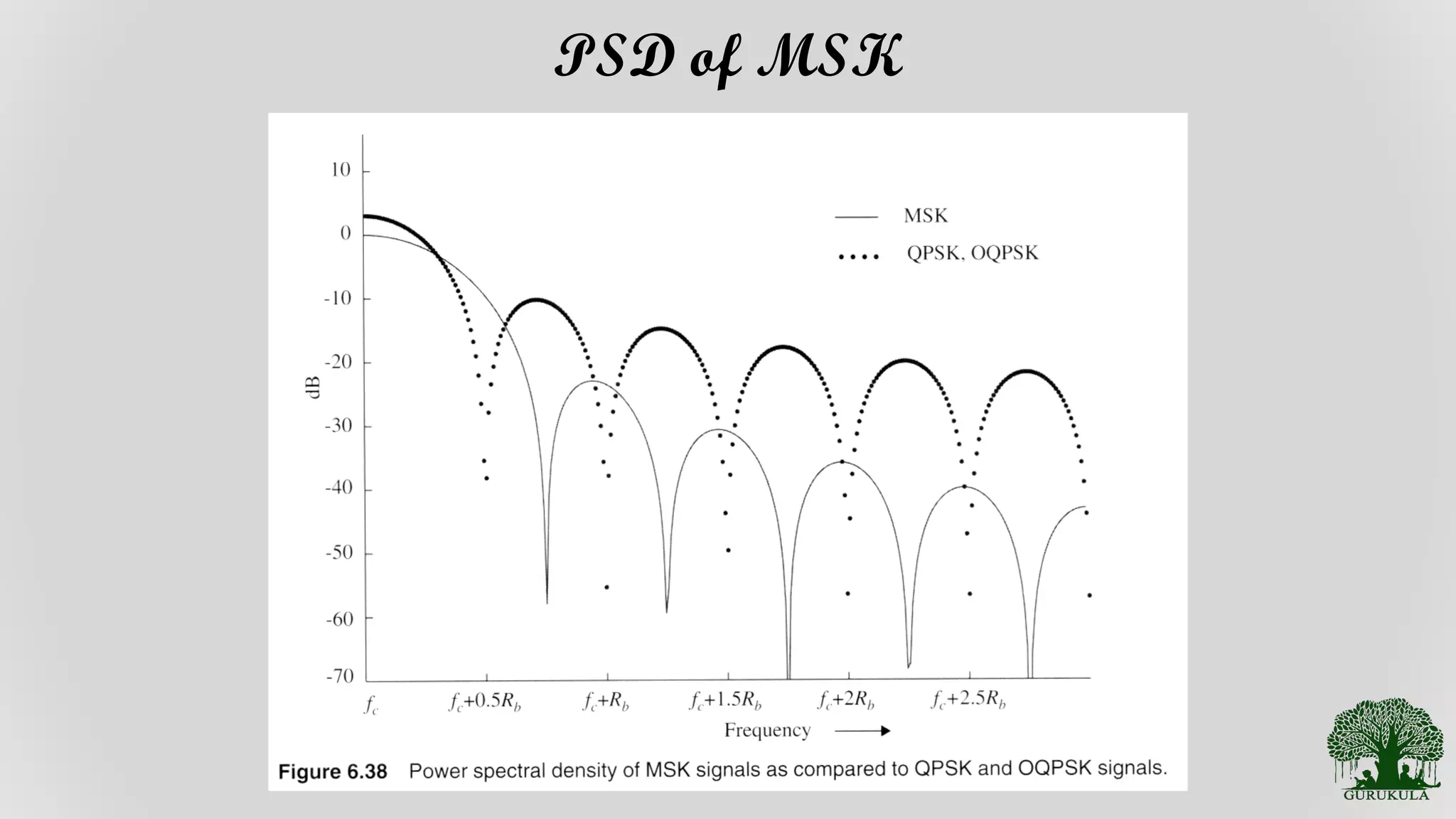
Exploration of the power spectral density characteristics specific to MSK.
Further analysis and interpretation of the power spectral density of MSK signals.
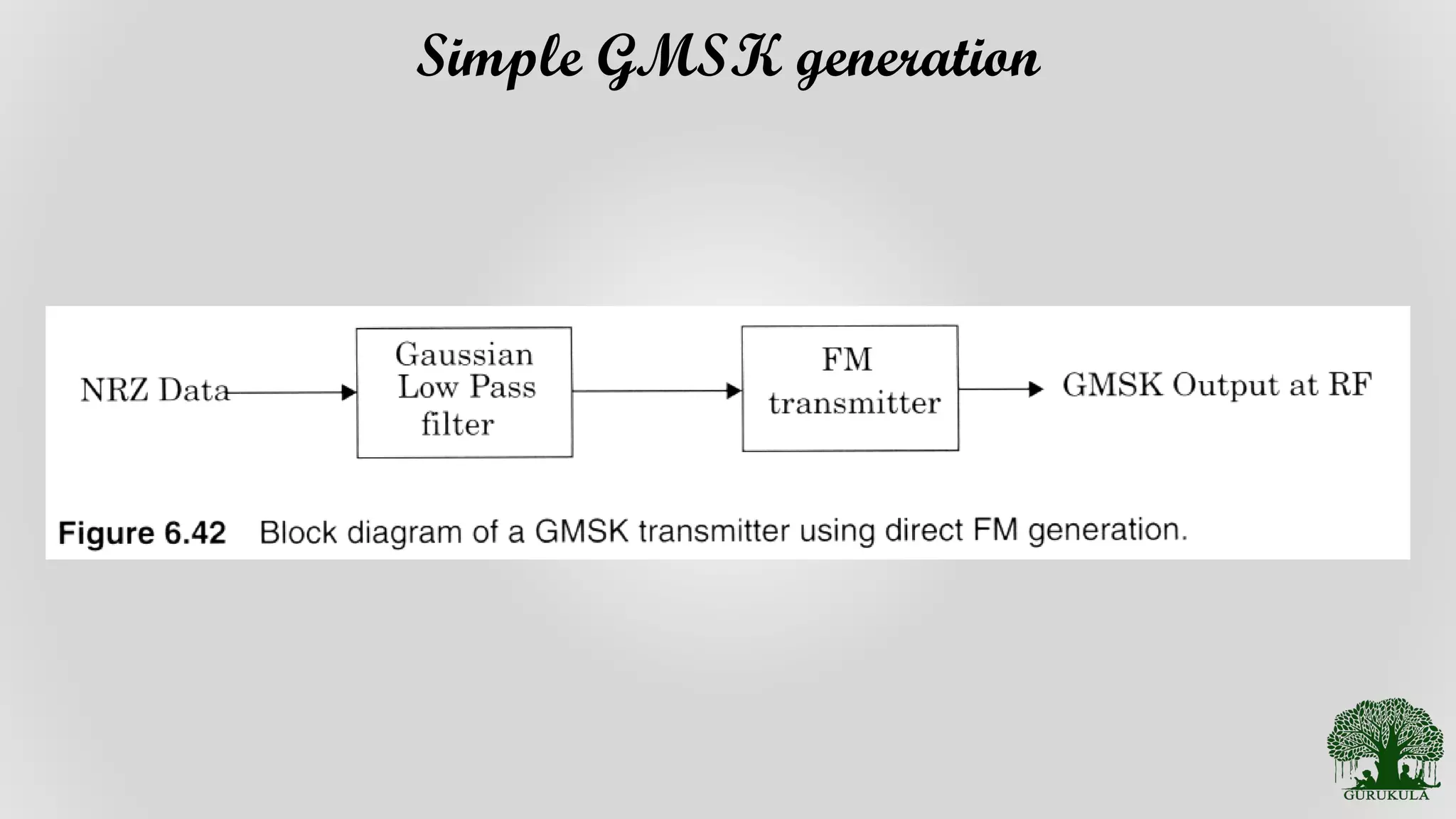
Steps and methods for the simple generation of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying signals.
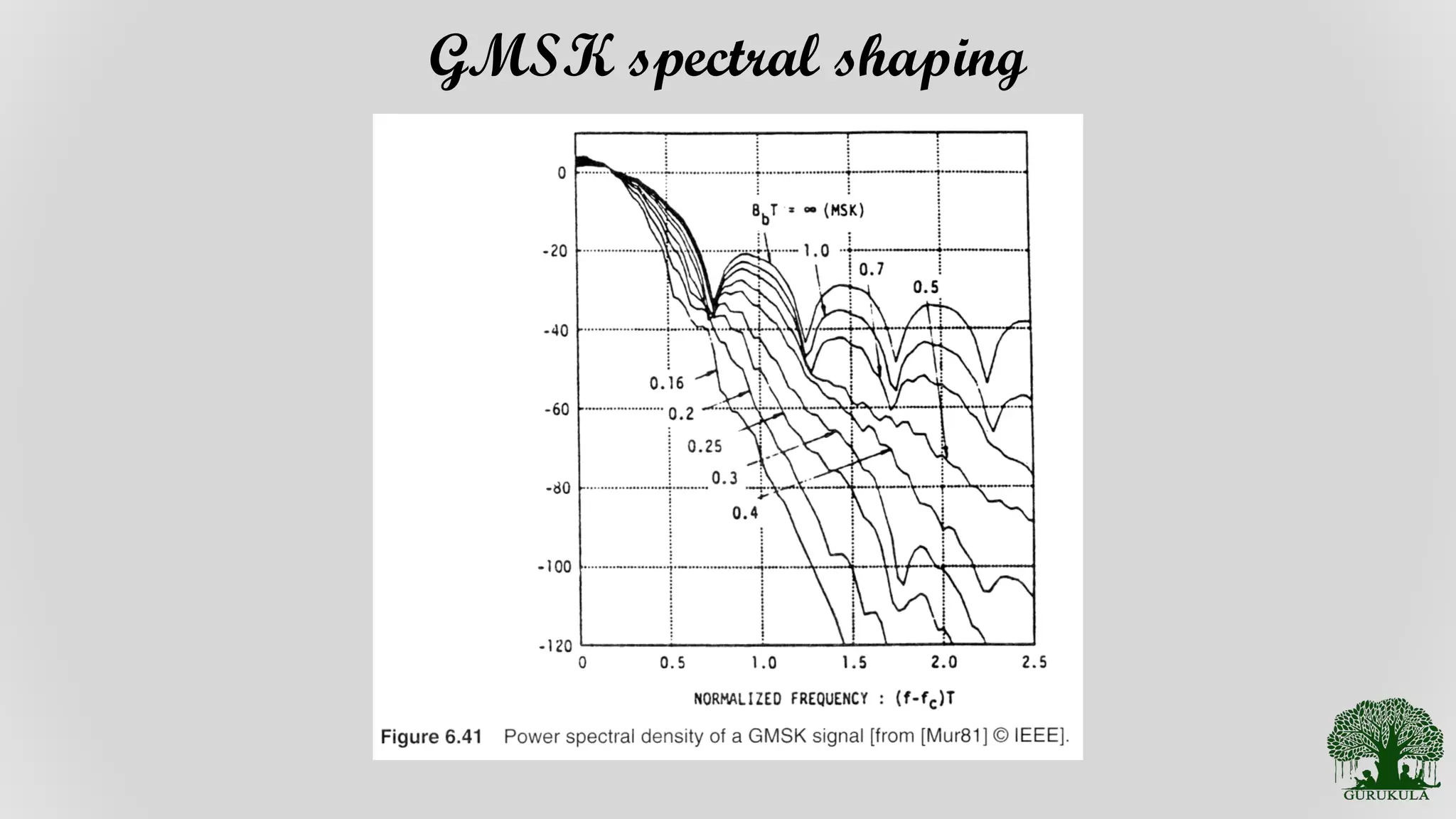
Discussion on the spectral shaping techniques applied to Gaussian MSK for improved performance.