The document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology, detailing its architecture including piconets and scatternets, as well as the various layers such as radio, baseband, and L2CAP. It describes the frame formats and types used in Bluetooth communication, highlighting the role of each layer and the mechanisms for data transmission. Additionally, it cites references for further reading on data communication and networking.





![Session Summary
• Introduction of Bluetooth
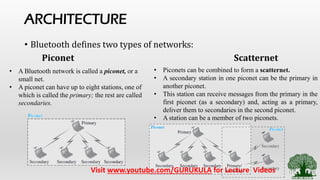
• Architecture of Bluetooth – Piconet and Scatternet
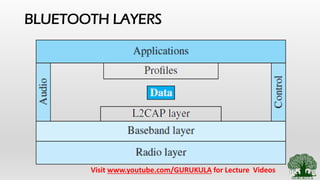
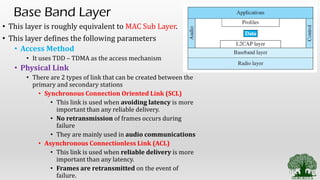
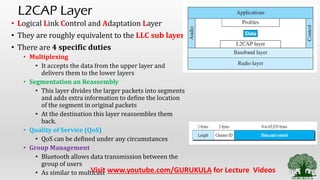
• Bluetooth Layers [ Radio, Base Band, L2cap Layers – Functions]
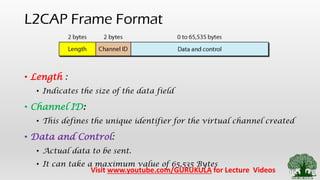
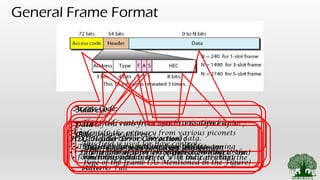
• Frame Format of Blutooth and its Types [1 slot, 3 slot, 5 slot]
Visit www.youtube.com/GURUKULA for Lecture Videos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200809145207/85/2-8-bluetooth-ieee-802-15-12-320.jpg)
