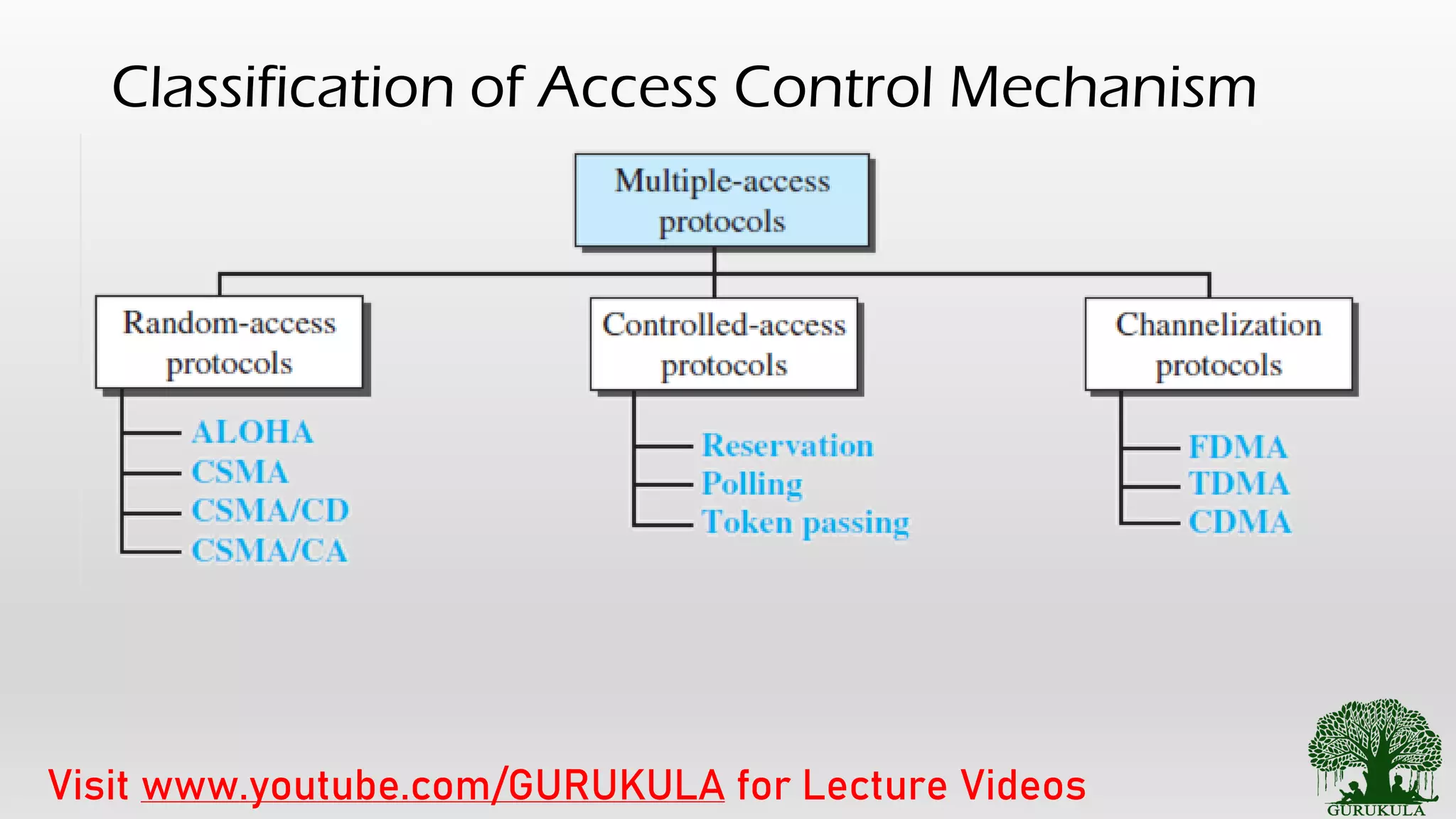
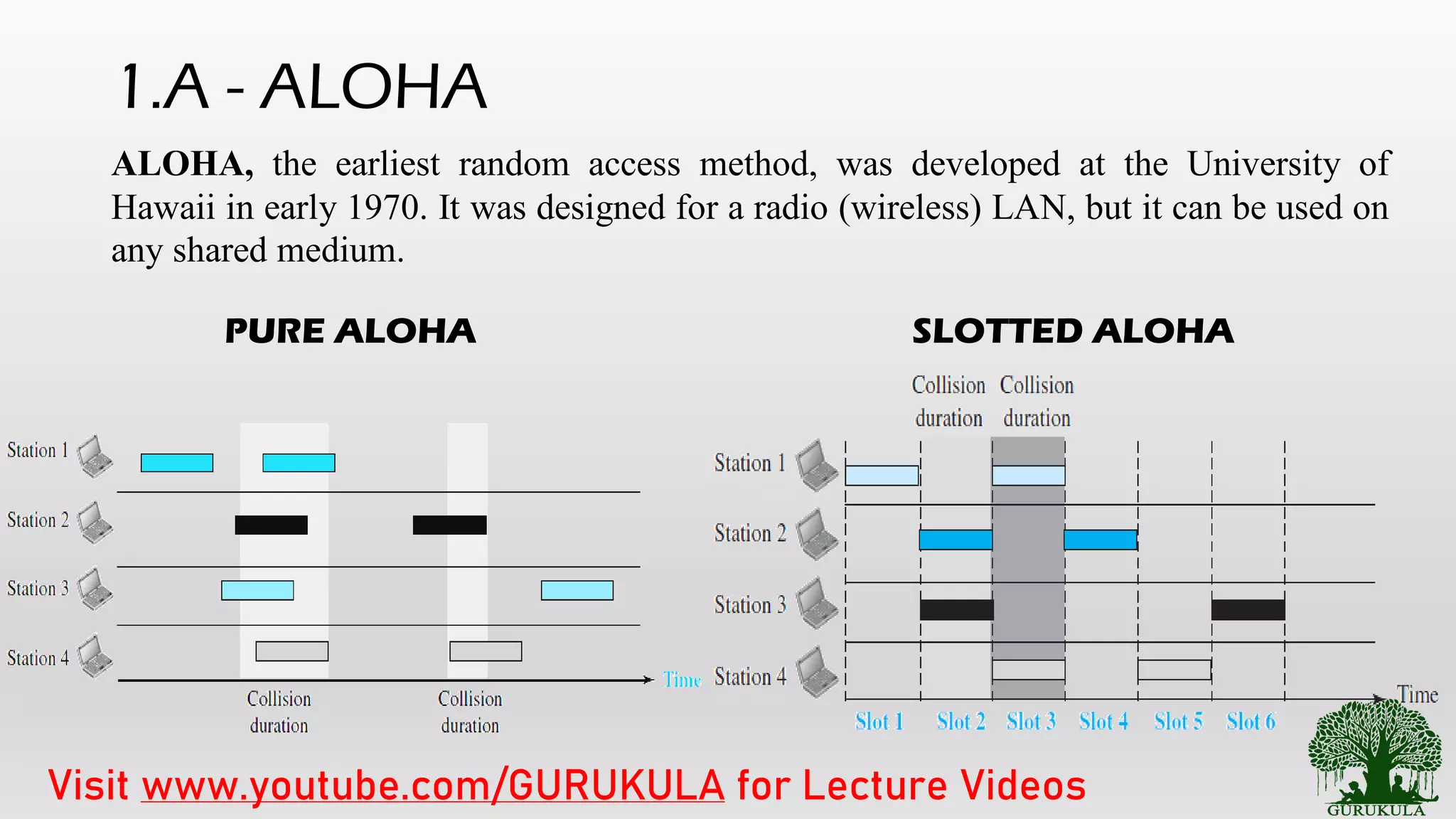
This document discusses access control methods in data link layers for communication networks. It explains the need for access control when multiple nodes use a shared medium like wireless networks. Access control mechanisms are classified into random access protocols and scheduled access protocols. Random access protocols like ALOHA and CSMA are described. CSMA variants including 1-persistent, p-persistent and CSMA/CD used in Ethernet are summarized. The document concludes with an overview of access control methods and references for further reading.
![Communication
Networks
Access Control
in datalink layer
[Random Access Methods]
Part - 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200802171714/75/2-3-access-control-random-access-methods-part-1-1-2048.jpg)




![Session Summary
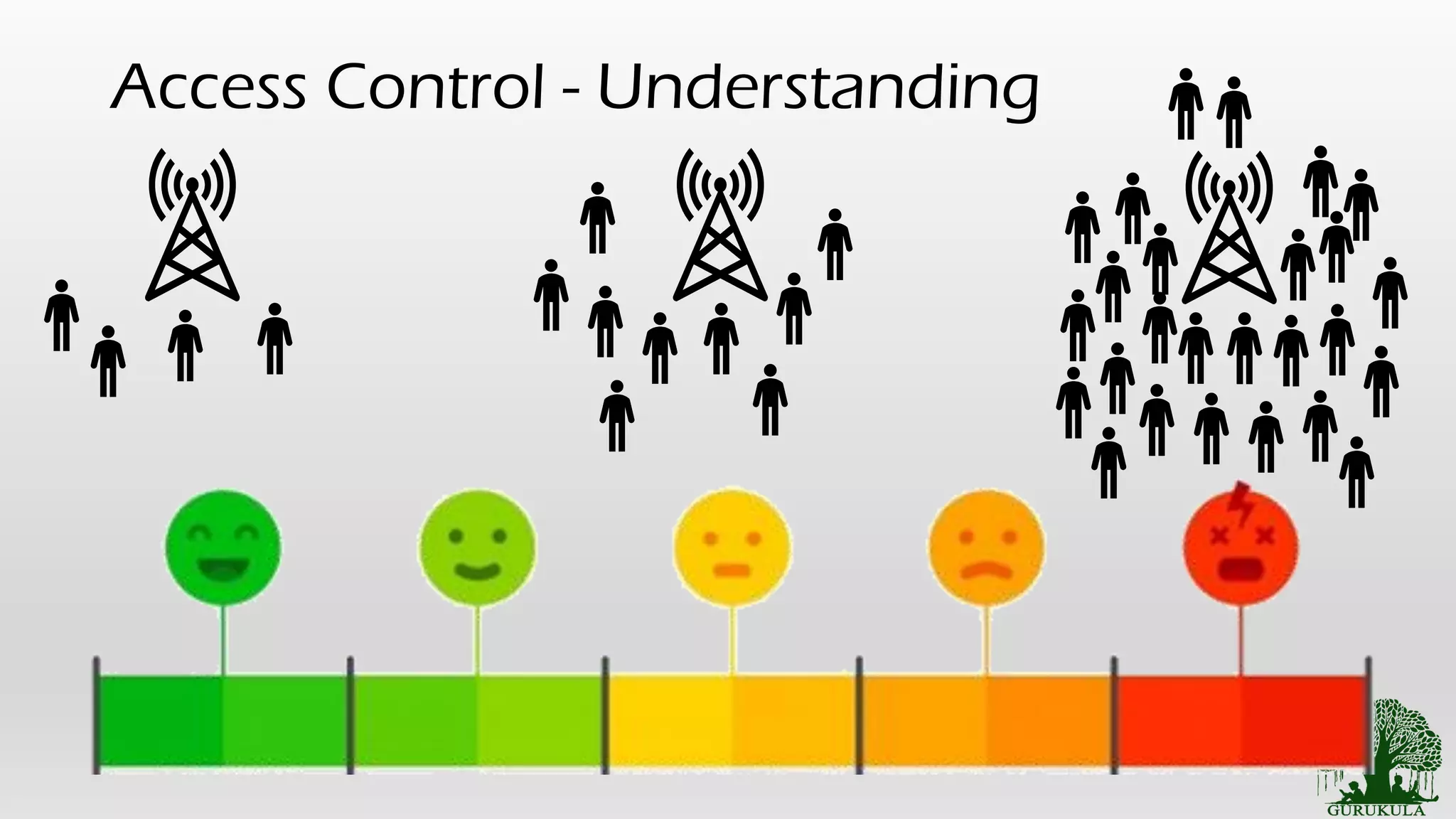
• Access Control [Similar to people accessing the cell tower]
• Random Access Methods [Checks the channel randomly, Idle –
Transmit, Busy – Check again]
• ALOHA [Pure ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA]
• CSMA [ 1 Persistent, n Persistent, p Persistent]
• CSMA – CD [widely used in Ethernet]
• CSMA – CA [widely used in WLAN]
Visit www.youtube.com/GURUKULA for Lecture Videos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200802171714/75/2-3-access-control-random-access-methods-part-1-10-2048.jpg)
